Chapter 2. Software
The Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) IaaS cloud is implemented as a collection of interacting services that control compute, storage, and networking resources. To manage the cloud, administrators can use a web-based dashboard or command-line clients to control, provision, and automate OpenStack resources. RHOSP also has an extensive API that is available to all cloud users.
The following diagram provides a high-level overview of the RHOSP core services and their relationship with each other.
Figure 2.1. RHOSP core services and their relationships
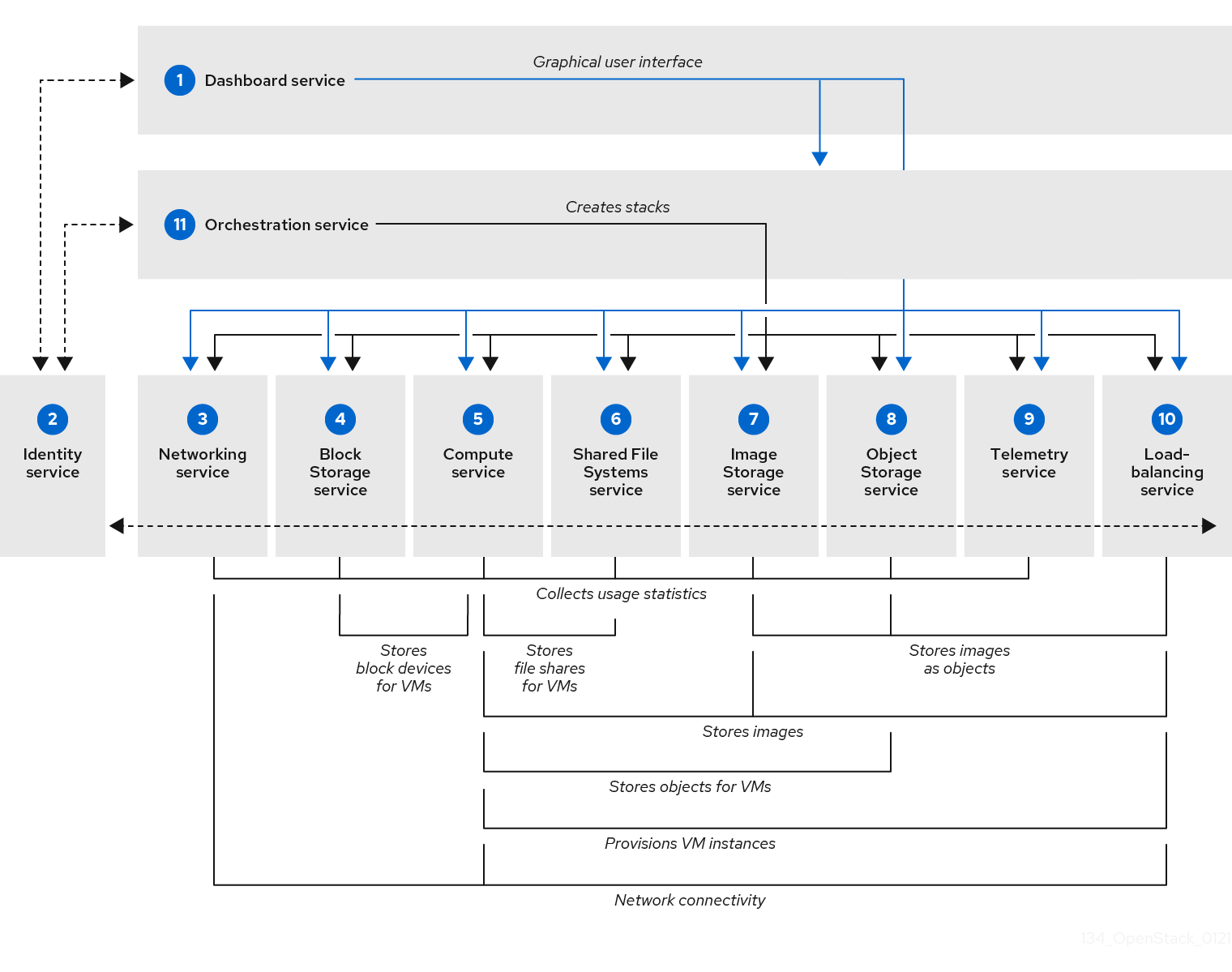
The following table describes each component in the diagram and provides links for the component documentation section.
| Service | Code | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | horizon | Web browser-based dashboard that you use to manage OpenStack services. | |
| 2 | keystone | Centralized service for authentication and authorization of OpenStack services and for managing users, projects, and roles. | |
| 3 | neutron | Provides connectivity between the interfaces of OpenStack services. | |
| 4 | cinder | Manages persistent block storage volumes for virtual machines. | |
| 5 | nova | Manages and provisions virtual machines running on hypervisor nodes. | |
| 6 | manila | Provisions shared file systems that multiple compute instances, bare metal nodes, or containers can consume. | |
| 7 | glance | Registry service that you use to store resources such as virtual machine images and volume snapshots. | |
| 8 | swift | Allows users to store and retrieve files and arbitrary data. | |
| 9 | ceilometer | Provides measurements of cloud resources. | |
| 10 | octavia | Provides load balancing services for the cloud. | |
| 11 | heat | Template-based orchestration engine that supports automatic creation of resource stacks. | |
| 12 | barbican | REST API designed for the secure storage, provisioning and management of secrets. |
Each OpenStack service contains a functional group of Linux services and other components.
2.1. Components
This section describes each of the OpenStack components:
OpenStack Dashboard service (horizon)
OpenStack Dashboard service provides a graphical user interface for users and administrators to create and launch instances, manage networking, and set access control.
The Dashboard service provides the Project, Admin, and Settings default dashboards. The modular design enables the dashboard to interface with other products such as billing, monitoring, and additional management tools.
OpenStack Identity service (keystone)
OpenStack Identity service provides user authentication and authorization to all OpenStack components. Identity service supports multiple authentication mechanisms, including user name and password credentials, token-based systems, and AWS-style log-ins.
OpenStack Networking service (neutron)
OpenStack Networking service handles creation and management of a virtual networking infrastructure in the OpenStack cloud. Infrastructure elements include networks, subnets, and routers.
OpenStack Block Storage service (cinder)
OpenStack Block Storage service provides persistent block storage management for virtual hard drives. With Block Storage, users can create and delete block devices, and manage attachment of block devices to servers.
OpenStack Compute service (nova)
OpenStack Compute service serves as the core of the RHOSP cloud by providing and managing virtual machine instances on demand. The Compute service abstracts the underlying hardware and interacts with other RHOSP services to create and provision instances in a RHOSP cloud.
OpenStack Shared File Systems service (manila)
OpenStack Shared File Systems service provides shared file systems that Compute instances can use. The basic resources offered by the Shared File Systems are shares, snapshots, and share networks.
OpenStack Image service (glance)
OpenStack Image service is a registry for virtual disk images. Users can add new images or take a snapshot of an existing server for immediate storage. You can use the snapshots for backup or as templates for new servers.
OpenStack Object Storage service (swift)
Object Storage service provides an HTTP-accessible storage system for large amounts of data, including static entities such as videos, images, email messages, files, or VM images. Objects are stored as binaries on the underlying file system with metadata stored in the extended attributes of each file.
OpenStack Telemetry service (ceilometer)
OpenStack Telemetry service provides user-level usage data for RHOSP-based clouds. You can use the data for customer billing, system monitoring, or alerts. Telemetry can collect data from notifications sent by existing OpenStack components such as Compute usage events, or by polling RHOSP infrastructure resources such as libvirt.
OpenStack Load-balancing service (octavia)
OpenStack Load-balancing service provides a Load Balancing-as-a-Service (LBaaS) implementation that supports multiple provider drivers. The reference provider driver (Amphora provider driver) is an open-source, scalable, and highly available load balancing provider. It accomplishes its delivery of load balancing services by managing a fleet of virtual machines, collectively known as amphorae, which it creates on demand.
OpenStack Orchestration service (heat)
OpenStack Orchestration service provides templates to create and manage cloud resources such as storage, networking, instances, or applications. Use templates to create stacks, which are collections of resources.
OpenStack Bare Metal Provisioning service (ironic)
OpenStack Bare Metal Provisioning service supports physical machines for a variety of hardware vendors with hardware-specific drivers. Bare Metal Provisioning integrates with the Compute service to provision physical machines in the same way that virtual machines are provisioned, and provides a solution for the bare-metal-to-trusted-project use case.
OpenStack DNS-as-a-Service (designate)
NoteThis feature is available in this release as a Technology Preview, and therefore is not fully supported by Red Hat. It should only be used for testing, and should not be deployed in a production environment. For more information about Technology Preview features, see the Scope of Coverage Details.
DNSaaS includes a REST API for domain and record management. It is is multi-tenanted and integrates with OpenStack Identity Service (keystone) for authentication. DNSaaS includes a framework for integration with Compute (nova) and OpenStack Networking (neutron) notifications, allowing auto-generated DNS records. DNSaaS includes integration support for PowerDNS and Bind9.
OpenStack Key Manager service (barbican)
OpenStack Key Manager Service is a REST API designed for the secure storage, provisioning and management of secrets such as passwords, encryption keys, and X.509 Certificates. This includes keying material such as Symmetric Keys, Asymmetric Keys, Certificates, and raw binary data.
Red Hat OpenStack Platform director
Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) director is a toolset for installing and managing a complete RHOSP environment. It is based primarily on the OpenStack project TripleO, which is an abbreviation for OpenStack-On-OpenStack. This project uses OpenStack components to install a fully operational RHOSP environment. It includes new OpenStack components that provision and control bare metal systems to use as OpenStack nodes. It provides a simple method for installing a complete RHOSP environment. RHOSP director uses two main concepts: an undercloud and an overcloud. The undercloud installs and configures the overcloud.
OpenStack High Availability
To keep your Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) environment up and running efficiently, use RHOSP director to create configurations that offer high availability and load balancing across all major services in RHOSP.
OpenStack Operational Tools
Red Hat OpenStack Platform comes with an optional suite of tools, such as Centralized Logging, Availability Monitoring, and Performance Monitoring. These tools help you maintain your OpenStack environment.
2.2. Integration
You can integrate Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) with the following third-party software - Tested and Approved Software
2.3. Installation summary
Red Hat supports the following methods to install Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP):
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform director: RHOSP director is recommended for enterprise deployments. RHOSP director is a toolset for installing and managing a complete RHOSP environment. It is based primarily on the OpenStack project TripleO, which is an abbreviation for "OpenStack-On-OpenStack". This project takes advantage of OpenStack components to install a fully operational RHOSP environment. It includes new OpenStack components that provision and control bare metal systems to use as OpenStack nodes. It provides a simple method for installing a complete RHOSP environment. RHOSP director uses two main concepts: an undercloud and an overcloud. The undercloud installs and configures the overcloud. For more information, see Red Hat OpenStack Platform Director Installation and Usage.
packstack: Packstack is an OpenStack deployment that consists of a public network and a private network on one machine, hosting one CirrOS-image instance, with an attached storage volume. Installed OpenStack services include: Block Storage, Compute, Dashboard, Identity, Image, Networking, Object Storage, and Telemetry. Packstack is a command-line utility that rapidly deploys OpenStack.
NotePackstack deployments are intended only for POC-type testing environments and are not suitable for production. By default, the public network is only routable from the OpenStack host.
For more information, see Evaluating OpenStack: Single-Node Deployment.
See Installing and Managing Red Hat OpenStack Platform for a comparison of these installation options.
2.4. Subscriptions
To install Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP), you must register all systems in the OpenStack environment with Red Hat Subscription Manager, and subscribe to the required channels. For more information about the channels and repositories to deploy RHOSP, see the following guides:
- Requirements for installing using director in the Director Installation and Usage guide.
- Requirements for installing a single-node POC deployment