Chapter 1. Install and Configure OpenStack Bare Metal Provisioning (ironic)
OpenStack Bare Metal Provisioning (ironic) provides the components required to provision and manage physical (bare metal) machines for end users. Bare Metal Provisioning in the overcloud interacts with the following OpenStack services:
- OpenStack Compute (nova) provides scheduling, tenant quotas, IP assignment, and a user-facing API for virtual machine instance management, while Bare Metal Provisioning provides the administrative API for hardware management. Choose a single, dedicated openstack-nova-compute host to use the Bare Metal Provisioning drivers and handle Bare Metal Provisioning requests.
- OpenStack Identity (keystone) provides request authentication and assists Bare Metal Provisioning in locating other OpenStack services.
- OpenStack Image service (glance) manages images and image metadata used to boot bare metal machines.
- OpenStack Networking (neutron) provides DHCP and network configuration for the required Bare Metal Provisioning networks.
Bare Metal Provisioning uses PXE to provision physical machines. The following diagram outlines how the OpenStack services interact during the provisioning process when a user launches a new bare metal machine.
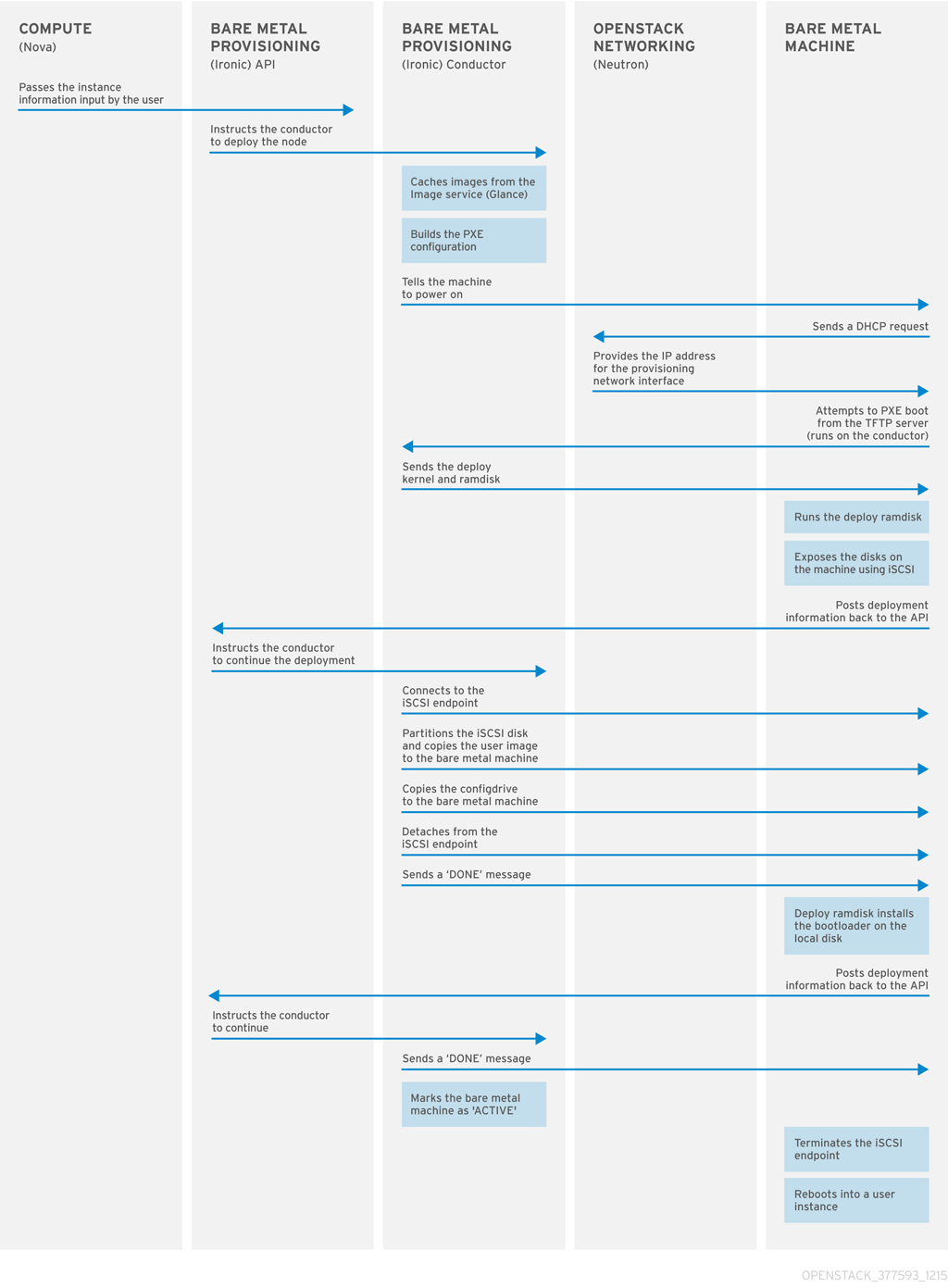
1.1. Requirements
This chapter outlines the requirements for setting up Bare Metal Provisioning, including installation assumptions, hardware requirements, and networking requirements.
1.1.1. Bare Metal Provisioning Installation Assumptions
Bare Metal Provisioning is a collection of components that can be configured to run on the same node or on separate nodes. The configuration examples in this guide install and configure all Bare Metal Provisioning components on a single node. This guide assumes that the services for OpenStack Identity, OpenStack Image, OpenStack Compute, and OpenStack Networking have already been installed and configured. Bare Metal Provisioning also requires the following external services, which must also be installed and configured as a prerequisite:
- A database server in which to store hardware information and state. This guide assumes that the MariaDB database service is configured for the Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment.
- A messaging service. This guide assumes that RabbitMQ is configured for the environment.
If you used the director to deploy your OpenStack environment, the database and messaging services are installed on a controller node in the overcloud.
Red Hat OpenStack Platform requires iptables instead of firewalld on Compute nodes and OpenStack Networking nodes running Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Firewall rules in this document are set using iptables.
Hardware introspection (ironic-inspector) uses iptables to blacklist the MAC addresses of ironic nodes. In the event that another process has locked iptables while ironic-inspector is attempting to make a modification, ironic-inspector uses the iptables -w flag, where supported (version 1.4.21, or higher).
1.1.2. Bare Metal Provisioning Hardware Requirements
A node running all Bare Metal Provisioning components requires the following hardware:
- 64-bit x86 processor with support for the Intel 64 or AMD64 CPU extensions.
- A minimum of 6 GB of RAM.
- A minimum of 40 GB of available disk space.
- A minimum of two 1 Gbps Network Interface Cards. However, a 10 Gbps interface is recommended for Bare Metal Provisioning Network traffic, especially if you are provisioning a large number of bare metal machines.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 (or later) installed as the host operating system.
Alternatively, install and configure Bare Metal Provisioning components on a dedicated openstack-nova-compute node; see Compute Node Requirements in the Director Installation and Usage guide for hardware requirements.
1.1.3. Bare Metal Provisioning Networking Requirements
Bare Metal Provisioning requires at least two networks:
- Provisioning network: This is a private network that Bare Metal Provisioning uses to provision and manage bare metal machines. The Bare Metal Provisioning Network provides DHCP and PXE boot functions to help discover bare metal systems. This network should ideally use a native VLAN on a trunked interface so that Bare Metal Provisioning serves PXE boot and DHCP requests. This is also the network used to control power management through out-of-band drivers on the bare metal machines to be provisioned.
- External network: A separate network for remote connectivity. The interface connecting to this network requires a routable IP address, either defined statically or dynamically through an external DHCP service.
1.1.4. Bare Metal Machine Requirements
Bare metal machines that will be provisioned require the following:
- Two NICs: one for the Bare Metal Provisioning Network, and one for external connectivity.
- A power management interface (e.g. IPMI) connected to the Bare Metal Provisioning Network. If you are using SSH for testing purposes, this is not required.
- PXE boot on the Bare Metal Provisioning Network at the top of the system’s boot order, ahead of hard disks and CD/DVD drives. Disable PXE boot on all other NICs on the system.
Other requirements for bare metal machines that will be provisioned vary depending on the operating system you are installing. For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, see the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Installation Guide. For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6, see the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Installation Guide.
1.2. Configure OpenStack for the Bare Metal Provisioning Service
Every OpenStack service has a user name and password that is used to authenticate it with the Identity service. Each service also needs to be defined with the OpenStack Identity service and have an endpoint URL associated with it for Internal, Admin and Public connectivity.
To configure the Bare Metal Provisioning Service from the director node:
Source the
overcloudrcfile:source ~stack/overcloudrc
# source ~stack/overcloudrcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the OpenStack Bare Metal Provisioning user:
openstack user create --password IRONIC_PASSWORD --enable IRONIC_USER openstack role add --project service --user IRONIC_USER admin
# openstack user create --password IRONIC_PASSWORD --enable IRONIC_USER # openstack role add --project service --user IRONIC_USER adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Here,
IRONIC_USERis the user for the Bare Metal Provisioning service andIRONIC_PASSWORDis the password.Create the OpenStack Bare Metal Provisioning service:
openstack service create --name ironic --description "Ironic bare metal provisioning service" baremetal
# openstack service create --name ironic --description "Ironic bare metal provisioning service" baremetalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the virtual IP (VIP) address that the other OpenStack services are using:
openstack endpoint list -c "Service Name" -c "PublicURL" --long
# openstack endpoint list -c "Service Name" -c "PublicURL" --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output of this command lists the services and their
Public URL, which are usually all on the same server and use the same IP address.Get the Internal API network address of the Compute node that you are installing the Bare Metal Provisioning service on:
route -n
# route -nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output of this command lists the IP routing table with the IP addresses and the
interfacefor each of the IP addresses.The Internal API network address is then used to create a service endpoint.
You can check the IP address associated with the NIC to use for the Internal and Admin URLs as follows:
ifconfig INTERFACE
# ifconfig INTERFACECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the service endpoint:
openstack endpoint create --publicurl http://VIP:6385 --internalurl http://COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IP:6385 --adminurl http://COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IP:6385 --region regionOne SERVICE_ID
# openstack endpoint create --publicurl http://VIP:6385 --internalurl http://COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IP:6385 --adminurl http://COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IP:6385 --region regionOne SERVICE_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Here,
VIPis the virtual IP address configured in HAProxy,COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IPis the IP address for the Compute node running the Bare Metal Provisioning service that is connected to the Internal API network andSERVICE_IDis the ID of the Bare Metal Provisioning service created using theservice createcommand.
Next, you must configure the HAProxy to make sure you receive requests for the Public URL for the endpoints you created in the previous procedure. To configure the HAProxy value, ensure that you are logged in as the root user on your controller nodes.
Edit the
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgfile and add the following line at the end of the file:listen ironic bind VIP:6385 transparent server SERVER_NAME COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IP:6385 check fall 5 inter 2000 rise 2
listen ironic bind VIP:6385 transparent server SERVER_NAME COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IP:6385 check fall 5 inter 2000 rise 2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example:
-
VIPis the virtual IP address. -
SERVER_NAMEis the HAProxy identifying name for the Compute server where the Bare Metal Provisioning service will be installed and running. -
COMPUTE_INTERNAL_API_IPis the Internal API IP address of the Compute server where the Bare Metal Provisioning service will be installed and running. -
transparentallows the HAProxy to bind the IP address even if it does not exist on the Controller node so that in a clustered environment, the virtual IP address can move between controllers. check fall 5 inter 2000 rise 2refers to the following health checks on the back end server:-
fall 5- the server is considered unavailable after 5 consecutive failed health checks. -
inter 2000- the interval between health checks is 2000 ms or 2 seconds. -
rise 2- the server is considered available after 2 consecutive successful health checks.
-
-
Restart the HAProxy to make sure the changes take effect:
systemctl restart haproxy.service
# systemctl restart haproxy.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can get the following message stating the back end server is not available: haproxy[4249]: proxy ironic has no server available!. This message can be ignored for now, since you have not yet installed or configured the service.
1.3. Configure the Controller Nodes for Bare Metal Provisioning Service
The following steps need to be performed on all the controller nodes in your Red Hat OpenStack Platform deployment as a root user, with the exception of the Create the Bare Metal Provisioning Database section. You must perform that procedure on one controller since they all share the database.
On the Controller nodes, you need to make sure your Bare Metal Provisioning Network is connected to Open vSwitch so your OpenStack deployment can reach it.
Add a bridge into Open vSwitch:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-ironic ovs-vsctl add-port br-ironic IRONIC_PROVISIONING_NIC ovs-vsctl show
# ovs-vsctl add-br br-ironic # ovs-vsctl add-port br-ironic IRONIC_PROVISIONING_NIC # ovs-vsctl showCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Here
br-ironicis the name of the bridge andIRONIC_PROVISIONING_NICis the NIC connected to the Bare Metal Provisioning Network.With the
ovs-vsctl showcommand, you can see that a new bridge is created with the associated port, however you will notice that thebr-intintegration bridge lacks a patch to the new bridge.To get the new bridge added to the integration bridge, you need to update the following plugin files:
Update the ML2 configuration file,
/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.inias follows:-
For the
type_driversparameter, make sureflatis listed among the drivers, for example,type_drivers = vxlan,vlan,flat,gre. This is a comma delimited list. -
For the
mechanism_driversparameter, make sureopenvswitchoption is listed among the drivers, for example,mechanism_drivers =openvswitch. This is a comma delimited list. -
For the
flat_networksparameters, create a name to refer to the Bare Metal Provisioning Network, for example,ironicnet. Make sure this name is listed among theflat_networkslisted, for example,flat_networks =datacentre,ironicnet. This is a comma delimited list. -
If you are using a VLAN for the Bare Metal Provisioning Network, add the
network_vlan_rangesparameter with the following format:ironicnet:VLAN_START:VLAN_END, for example,network_vlan_ranges =datacentre:1:1000. This is a comma delimited list. -
The
enable_security_groupparameter should already be enabled. But if it is not set, change the value toTrue, for example,enable_security_group = True.
-
For the
In the
/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/openvswitch_agent.inifile, find thebridge_mappingsparameter and update as follows:bridge_mappings =datacentre:br-ex,ironicnet:br-ironic
bridge_mappings =datacentre:br-ex,ironicnet:br-ironicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The value of this comma delimited key-value pair maps the name of the Bare Metal Provisioning Network to the physical device which is connected to the network.
Restart the
neutron-openvswitch-agent.serviceto see thebr-ironicbridge as a part of the integration bridge:systemctl restart neutron-openvswitch-agent.service
# systemctl restart neutron-openvswitch-agent.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the
neutron-server.serviceso that it detects the new connection:systemctl restart neutron-server.service
# systemctl restart neutron-server.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you do not perform this step, trying to create the Bare Metal Provisioning Network within the OpenStack Networking service will fail with a message that the requested flat network does not exist.
1.3.1. Create the Bare Metal Provisioning Database
Create the database and database user used by Bare Metal Provisioning. All steps in this procedure must be performed on the database server, while logged in as the root user.
Creating the Bare Metal Provisioning Database
Connect to the database service:
mysql -u root
# mysql -u rootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the ironic database:
mysql> CREATE DATABASE ironic CHARACTER SET utf8;
mysql> CREATE DATABASE ironic CHARACTER SET utf8;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an ironic database user and grant the user access to the ironic database:
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ironic.* TO 'ironic'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD'; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ironic.* TO 'ironic'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD';
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ironic.* TO 'ironic'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD'; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ironic.* TO 'ironic'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD';Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace PASSWORD with a secure password that will be used to authenticate with the database server as this user.
Flush the database privileges to ensure that they take effect immediately:
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Exit the mysql client:
mysql> quit
mysql> quitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.3.2. Configure OpenStack Compute Services For Bare Metal Provisioning
Configure Compute services for the Bare Metal Provisioning driver. Using this driver enables Compute to provision physical machines using the same API that is used to provision virtual machines. Only one driver can be specified for each openstack-nova-compute node; a node with the Bare Metal Provisioning driver can provision only physical machines. It is recommended that you allocate a single openstack-nova-compute node to provision all bare metal nodes using the Bare Metal Provisioning driver. All steps in the following procedure must be performed on a chosen compute node, while logged in as the root user.
Configuring OpenStack Compute for the Bare Metal Provisioning
Set Compute to use the Bare Metal Provisioning scheduler host manager:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT scheduler_host_manager nova.scheduler.ironic_host_manager.IronicHostManager
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT scheduler_host_manager nova.scheduler.ironic_host_manager.IronicHostManagerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable the Compute scheduler from tracking changes in instances:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf DEFAULT scheduler_tracks_instance_changes false
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf DEFAULT scheduler_tracks_instance_changes falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the default filters as follows:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf DEFAULT baremetal_scheduler_default_filters AvailabilityZoneFilter,ComputeFilter,ComputeCapabilitiesFilter,ImagePropertiesFilter
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf DEFAULT baremetal_scheduler_default_filters AvailabilityZoneFilter,ComputeFilter,ComputeCapabilitiesFilter,ImagePropertiesFilterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set Compute to use default Bare Metal Provisioning scheduling filters:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT scheduler_use_baremetal_filters True
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT scheduler_use_baremetal_filters TrueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set Compute to use the correct authentication details for Bare Metal Provisioning:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace the following values:
- Replace PASSWORD with the password that Bare Metal Provisioning uses to authenticate with Identity.
- Replace IDENTITY_IP with the IP address or host name of the server hosting Identity.
- Replace IRONIC_API_IP with the IP address or host name of the server hosting the Bare Metal Provisioning API service.
Set the
novadatabase credentials on theironicCompute node:openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf database connection "mysql+pymysql://nova:NOVA_DB_PASSWORD@DB_IP/nova"
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf database connection "mysql+pymysql://nova:NOVA_DB_PASSWORD@DB_IP/nova"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the Compute scheduler service on the Compute controller nodes:
systemctl restart openstack-nova-scheduler.service
# systemctl restart openstack-nova-scheduler.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the compute service on the compute nodes:
systemctl restart openstack-nova-compute.service
# systemctl restart openstack-nova-compute.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.3.3. Configure the OpenStack Networking DHCP Agent to Tag iPXE Requests
OpenStack Networking DHCP requests from iPXE need to have a DHCP tag called ipxe to let the DHCP server know that the client needs to perform an HTTP operation to get the boot.ipxe script. You can do this by adding a dhcp-userclass entry to the dnsmasq configuration file used by the OpenStack Networking DHCP Agent service.
On your overcloud controller, verify which
dnsmasqfile the DHCP Agent is using:grep ^dnsmasq_config_file /etc/neutron/dhcp_agent.ini
# grep ^dnsmasq_config_file /etc/neutron/dhcp_agent.ini dnsmasq_config_file =/etc/neutron/dnsmasq-neutron.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit this file and add the following lines at the end of the file:
Create the "ipxe" tag if request comes from iPXE user class
# Create the "ipxe" tag if request comes from iPXE user class dhcp-userclass=set:ipxe,iPXECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save the file and restart the OpenStack Networking DHCP Agent service:
systemctl restart neutron-dhcp-agent.service
# systemctl restart neutron-dhcp-agent.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4. Configure the Compute Node for Bare Metal Provisioning
The following instructions here apply ONLY to the Compute node that is also running the Bare Metal Provisioning service. You need to perform these steps as a root user on the Compute node.
On the Compute node, you have the Bare Metal Provisioning NIC, for example, eth6. The goals with this procedure are as follows:
-
To connect the Bare Metal Provisioning NIC,
eth6in this example, to Open vSwitch. - To assign an IP address on this connection as the Bare Metal server needs to pull down the boot images from the bare metal node as a part of the iPXE process.
Connecting eth6 to Open vSwitch
As with the Controller node in Section 1.3, “Configure the Controller Nodes for Bare Metal Provisioning Service”, create a bridge within Open vSwitch on the Compute node running the Bare Metal Provisioning service:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-ironic ovs-vsctl add-port br-ironic IRONIC_PROVISIONING_NIC
# ovs-vsctl add-br br-ironic # ovs-vsctl add-port br-ironic IRONIC_PROVISIONING_NICCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Here,
br-ironicis the name of the bridge andIRONIC_PROVISIONING NICis the NIC connected to the Bare Metal Provisioning Network, for example,eth6.NoteThe only difference between this and Section 1.3, “Configure the Controller Nodes for Bare Metal Provisioning Service” is that you do not restart the OpenStack Networking service on the Compute node.
This adds the bridge and port to the Open vSwitch, which you can verify using the
ovs-vsctl showcommand. However, it does not connect it to the integration bridge (br-int) for use by OpenStack.To create the connection, you need to update the OpenStack Networking plugin files as follows:
Update the ML2 configuration file,
/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.inias follows:-
For the
type_driversparameter, make sureflatis listed among the drivers, for example,type_drivers = vxlan,vlan,flat,gre. This is a comma delimited list. -
For the
mechanism_driversparameter, make sureopenvswitchoption is listed among the drivers, for example,mechanism_drivers =openvswitch. This is a comma delimited list. -
For the
flat_networksparameters, create a name to refer to the Bare Metal Provisioning Network, for example,ironicnet. Make sure this name is listed among theflat_networkslisted, for example,flat_networks =datacentre,ironicnet. This is a comma delimited list. -
If you are using a VLAN for the Bare Metal Provisioning Network, add the
network_vlan_rangesparameter with the following format:ironicnet:VLAN_START:VLAN_END, for example,network_vlan_ranges =datacentre:1:1000. This is a comma delimited list. -
The
enable_security_groupparameter should already be enabled. But if it is not set, change the value toTrue, for example,enable_security_group = True.
-
For the
In the
/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/openvswitch_agent.inifile, find thebridge_mappingsparameter and update as follows:bridge_mappings =datacentre:br-ex,ironicnet:br-ironic
bridge_mappings =datacentre:br-ex,ironicnet:br-ironicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The value of this comma delimited key-value pair maps the name of the Bare Metal Provisioning Network to the physical device which is connected to the network.
Restart the OpenStack Networking Open vSwitch Agent service:
systemctl restart neutron-openvswitch-agent.service
# systemctl restart neutron-openvswitch-agent.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You have now achieved your first goal from this procedure. Next, you need to assign an IP address to your br-ironic bridge and make sure it persists after a reboot.
Assigning an IP address to the Bare Metal server
Create standard configuration files in the
/etc/sysconfig/network-scriptslocation. You can copy theifcfg*files already available in the tenant network and edit the following values:device,ipaddr,ovs_bridge,bridge nameandMACaddresses for thebr-ironicandeth6. When you have completed updating the new files, they should have the following values:ifcfg-br-ironicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ifcfg-eth6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the network bridge to make your IP address pingable.
ifup br-ironic
# ifup br-ironicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you get disconnected from the node when you restart the network services, reboot the server.
1.4.1. Subscribe to the Required Channels
To install the Bare Metal Provisioning packages, you must register the server or servers with Red Hat Subscription Manager, and subscribe to the required channels. If you are installing Bare Metal Provisioning on a compute node, your server may already be appropriately subscribed. Run yum repolist to check whether the channels in the procedure below have been enabled.
Subscribing to the Required Channels
Register your system with the Content Delivery Network, entering your Customer Portal user name and password when prompted:
subscription-manager register
# subscription-manager registerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find entitlement pools containing the channels required to install Bare Metal Provisioning:
subscription-manager list --available | grep -A13 "Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server" subscription-manager list --available | grep -A13 "Red Hat OpenStack Platform"
# subscription-manager list --available | grep -A13 "Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server" # subscription-manager list --available | grep -A13 "Red Hat OpenStack Platform"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the pool identifiers located in the previous step to attach the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Server and Red Hat OpenStack Platform entitlements:
subscription-manager attach --pool=POOL_ID
# subscription-manager attach --pool=POOL_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable the required channels:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-openstack-8-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-rh-common-rpms --enable=rhel-7-server-optional-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-openstack-8-optools-rpms
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-openstack-8-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-rh-common-rpms --enable=rhel-7-server-optional-rpms \ --enable=rhel-7-server-openstack-8-optools-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4.2. Install the Bare Metal Provisioning Packages
Bare Metal Provisioning requires the following packages:
openstack-ironic-api
Provides the Bare Metal Provisioning API service.
openstack-ironic-conductor
Provides the Bare Metal Provisioning conductor service. The conductor allows adding, editing, and deleting nodes, powering on or off nodes with IPMI or SSH, and provisioning, deploying, and decommissioning bare metal nodes.
python-ironicclient
Provides a command-line interface for interacting with the Bare Metal Provisioning services.
Install the packages:
yum install openstack-ironic-api openstack-ironic-conductor python-ironicclient ipxe-bootimgs
# yum install openstack-ironic-api openstack-ironic-conductor python-ironicclient ipxe-bootimgs1.4.3. Configure iPXE
Create the necessary directories for iPXE, map-files and copy the
undionly.kpxeboot image, iPXE andmap-fileinto place:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, the Compute node deployed by the director runs SELinux in
Enforcingmode. To avoid getting permission errors when trying iPXE boot, make sure you set the appropriate labels on these directories. To apply these labels, run the following commands as arootuser:semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "/httpboot(/.*)?" restorecon -Rv /httpboot semanage fcontext -a -t tftpdir_t "/tftpboot(/.*)?" restorecon -Rv /tftpboot
# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "/httpboot(/.*)?" # restorecon -Rv /httpboot # semanage fcontext -a -t tftpdir_t "/tftpboot(/.*)?" # restorecon -Rv /tftpbootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure HTTP so that it can serve requests for the images. The
httpdpackage is already installed, so it is a matter of creating the appropriate virtual host entry and starting the service.NoteThe
/etc/httpd/conf.dcontains number of files. As Red Hat utilizes a single overcloud full image for all the nodes, it includes these files on all the nodes even though it is only used on the Controller node. You can delete the contents of/etc/httpd/conf.dor copy them somewhere else as they are not used.Create a new file in for iPXE configuration. You can name this file anything, making sure it is in the
.confformat and has the following contents:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The above virtual host configuration configures HTTPD to listed on all addresses on port 8088 and sets the document root for all requests to that port to go to
/httpboot.Save this file and enable and restart HTTPD service on the Compute node:
systemctl enable httpd.service systemctl start httpd.service
# systemctl enable httpd.service # systemctl start httpd.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4.4. Configure the Bare Metal Provisioning Service
In this section, you will make the necessary changes to the /etc/ironic/ironic.conf file.
1.4.4.1. Configure Bare Metal Provisioning to Communicate with the Database Server
Set the value of the connection configuration key:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ database connection mysql+pymysql://ironic:PASSWORD@IP/ironic
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \
database connection mysql+pymysql://ironic:PASSWORD@IP/ironicHere, PASSWORD is the password of the database server, IP is the IP address or host name of the database server.
The IP address or host name specified in the connection configuration key must match the IP address or host name to which the Bare Metal Provisioning database user was granted access when creating the Bare Metal Provisioning database in Section 1.3.1, “Create the Bare Metal Provisioning Database”. Moreover, if the database is hosted locally and you granted permissions to localhost when creating the database, you must enter localhost.
1.4.4.2. Configure Bare Metal Provisioning Authentication
Configure Bare Metal Provisioning to use Identity for authentication. All steps in this procedure must be performed on the server or servers hosting Bare Metal Provisioning, while logged in as the root user.
Configuring Bare Metal Provisioning to Authenticate Through Identity
Set the Identity public and admin endpoints that Bare Metal Provisioning must use:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken auth_uri http://IP:5000/v2.0 openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken identity_uri http://IP:35357/
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken auth_uri http://IP:5000/v2.0 # openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken identity_uri http://IP:35357/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace IP with the IP address or host name of the Identity server.
Set Bare Metal Provisioning to authenticate as the service tenant:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken admin_tenant_name service
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken admin_tenant_name serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set Bare Metal Provisioning to authenticate using the ironic administrative user account:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken admin_user ironic
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken admin_user ironicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set Bare Metal Provisioning to use the correct ironic administrative user account password:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken admin_password PASSWORD
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ keystone_authtoken admin_password PASSWORDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace PASSWORD with the password set when the ironic user was created.
1.4.4.3. Configure RabbitMQ Message Broker Settings for Bare Metal Provisioning
RabbitMQ is the default (and recommended) message broker. The RabbitMQ messaging service is provided by the rabbitmq-server package. All steps in the following procedure must be performed on the Controller or Compute nodes hosting Bare Metal Provisioning, while logged in as the root user.
This procedure assumes that the RabbitMQ messaging service has been installed and configured, and an ironic user and associated password have been created on the server hosting the messaging service.
Configuring Bare Metal Provisioning to use the RabbitMQ Message Broker
Set RabbitMQ as the RPC back end:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ DEFAULT rpc_backend ironic.openstack.common.rpc.impl_kombu
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ DEFAULT rpc_backend ironic.openstack.common.rpc.impl_kombuCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the Bare Metal Provisioning to connect to the RabbitMQ host:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_host RABBITMQ_HOST
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_host RABBITMQ_HOSTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace RABBITMQ_HOST with the IP address or host name of the server hosting the message broker.
Set the message broker port to 5672:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_port 5672
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_port 5672Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the RabbitMQ user name and password created for Bare Metal Provisioning when RabbitMQ was configured:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_userid guest openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_password RABBIT_GUEST_PASSWORD
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_userid guest # openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_password RABBIT_GUEST_PASSWORDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace RABBIT_GUEST_PASSWORD with the RabbitMQ password for the guest user.
When RabbitMQ was launched, the guest user was granted read and write permissions to all resources: specifically, through the virtual host. Configure Bare Metal Provisioning to connect to this virtual host:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_virtual_host /
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ oslo_messaging_rabbit rabbit_virtual_host /Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4.4.4. Configure Bare Metal Provisioning Drivers
Bare Metal Provisioning supports multiple drivers for deploying and managing bare metal servers. Some drivers have hardware requirements, and require additional configuration or package installation. See Appendix A, Bare Metal Provisioning Drivers for detailed driver information. The first half of a driver’s name specifies its deployment method (e.g. PXE), and the second half specifies its power management method (e.g. IPMI).
Configuring Bare Metal Provisioning Drivers
Specify the driver or drivers that you will use to provision bare metal servers. Specify multiple drivers using a comma-separated list:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ DEFAULT enabled_drivers DRIVER1,DRIVER2
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ DEFAULT enabled_drivers DRIVER1,DRIVER2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following drivers are supported:
IPMI with PXE deploy
-
pxe_ipmitool
-
DRAC with PXE deploy
-
pxe_drac
-
iLO with PXE deploy
-
pxe_ilo
-
SSH with PXE deploy
-
pxe_ssh
-
iRMC with PXE
-
pxe_irmc
-
Restart the Bare Metal conductor service:
systemctl restart openstack-ironic-conductor.service
# systemctl restart openstack-ironic-conductor.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4.4.5. Configure the Bare Metal Provisioning Service to use PXE
Set the Bare Metal Provisioning service to use PXE templates:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe pxe_config_template \$pybasedir/drivers/modules/ipxe_config.template
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe pxe_config_template \$pybasedir/drivers/modules/ipxe_config.templateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the Bare Metal Provisioning service to use
tftp_server:openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe tftp_server BARE_METAL_PROVISIONING_NETWORK_IP
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe tftp_server BARE_METAL_PROVISIONING_NETWORK_IPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the PXE
tftp_root:openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe tftp_root /tftpboot
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe tftp_root /tftpbootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the PXE boot file name:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe pxe_bootfile_name undionly.kpxe
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe pxe_bootfile_name undionly.kpxeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable the Bare Metal Provisioning service to use iPXE:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe ipxe_enabled true
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ pxe ipxe_enabled trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the URL for the
httpserver:openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf deploy http_url http://BARE_METAL_PROVISIONING_IP:8088
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf deploy http_url http://BARE_METAL_PROVISIONING_IP:8088Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the Bare Metal conductor service:
systemctl restart openstack-ironic-conductor.service
# systemctl restart openstack-ironic-conductor.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4.4.6. Configure Bare Metal Provisioning to Communicate with OpenStack Networking and OpenStack Image
Bare Metal Provisioning uses OpenStack Networking for DHCP and network configuration, and uses the Image service for managing the images used to boot physical machines. Configure Bare Metal Provisioning to connect to and communicate with OpenStack Networking and the Image service. All steps in this procedure must be performed on the server hosting Bare Metal Provisioning, while logged in as the root user.
Configuring Bare Metal Provisioning to Communicate with OpenStack Networking and OpenStack Image
Set Bare Metal Provisioning to use the OpenStack Networking endpoint:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ neutron url http://NEUTRON_IP:9696
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ neutron url http://NEUTRON_IP:9696Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace NEUTRON_IP with the IP address or host name of the server hosting OpenStack Networking.
Set Bare Metal Provisioning to communicate with the Image service:
openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ glance glance_host GLANCE_IP
# openstack-config --set /etc/ironic/ironic.conf \ glance glance_host GLANCE_IPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace GLANCE_IP with the IP address or host name of the server hosting the Image service.
Start the Bare Metal Provisioning API service, and configure it to start at boot time:
systemctl start openstack-ironic-api.service systemctl enable openstack-ironic-api.service
# systemctl start openstack-ironic-api.service # systemctl enable openstack-ironic-api.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the Bare Metal Provisioning database tables:
ironic-dbsync --config-file /etc/ironic/ironic.conf create_schema
# ironic-dbsync --config-file /etc/ironic/ironic.conf create_schemaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the Bare Metal Provisioning conductor service, and configure it to start at boot time:
systemctl restart openstack-ironic-conductor.service systemctl enable openstack-ironic-conductor.service
# systemctl restart openstack-ironic-conductor.service # systemctl enable openstack-ironic-conductor.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.4.5. Configure OpenStack Compute to Use Bare Metal Provisioning Service
In this section, you will update the /etc/nova/nova.conf file to configure the Compute service to use the Bare Metal Provisioning service:
Configuring OpenStack Compute to Use Bare Metal Provisioning
Set Compute to use the clustered compute manager:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT compute_manager ironic.nova.compute.manager.ClusteredComputeManager
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT compute_manager ironic.nova.compute.manager.ClusteredComputeManagerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the virtual RAM to physical RAM allocation ratio:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT ram_allocation_ratio 1.0
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT ram_allocation_ratio 1.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the amount of disk space in MB to reserve for the host:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT reserved_host_memory_mb 0
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT reserved_host_memory_mb 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set Compute to use the Bare Metal Provisioning driver:
openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT compute_driver nova.virt.ironic.IronicDriver
# openstack-config --set /etc/nova/nova.conf \ DEFAULT compute_driver nova.virt.ironic.IronicDriverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set Compute to use the correct authentication details for Bare Metal Provisioning:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace the following values:
- Replace PASSWORD with the password that Bare Metal Provisioning uses to authenticate with Identity.
- Replace IDENTITY_IP with the IP address or host name of the server hosting Identity.
- Replace IRONIC_API_IP with the IP address or host name of the server hosting the Bare Metal Provisioning API service.
Restart the Compute scheduler service on the Compute controller nodes:
systemctl restart openstack-nova-scheduler.service
# systemctl restart openstack-nova-scheduler.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the compute service on the compute nodes:
systemctl restart openstack-nova-compute.service
# systemctl restart openstack-nova-compute.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow