Chapter 1. Introduction to the Load-balancing service
The Load-balancing service (octavia) provides a load balancing as a service API version 2 implementation for Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) environments. The Load-balancing service manages multiple virtual machines, containers, or bare metal servers—collectively known as amphorae—which it launches on demand. The ability to provide on-demand, horizontal scaling makes the Load-balancing service a fully-featured load balancer that is appropriate for large RHOSO enterprise deployments.
1.1. Load-balancing service components
The Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) Load-balancing service (octavia) uses a set of VM instances referred to as amphorae that reside on the Compute nodes. The Load-balancing service controllers communicate with the amphorae over a load-balancing management network (lb-mgmt-net).
When using octavia, you can create load-balancer virtual IPs (VIPs) that do not require floating IPs (FIPs). Not using FIPs has the advantage of improving performance through the load balancer.
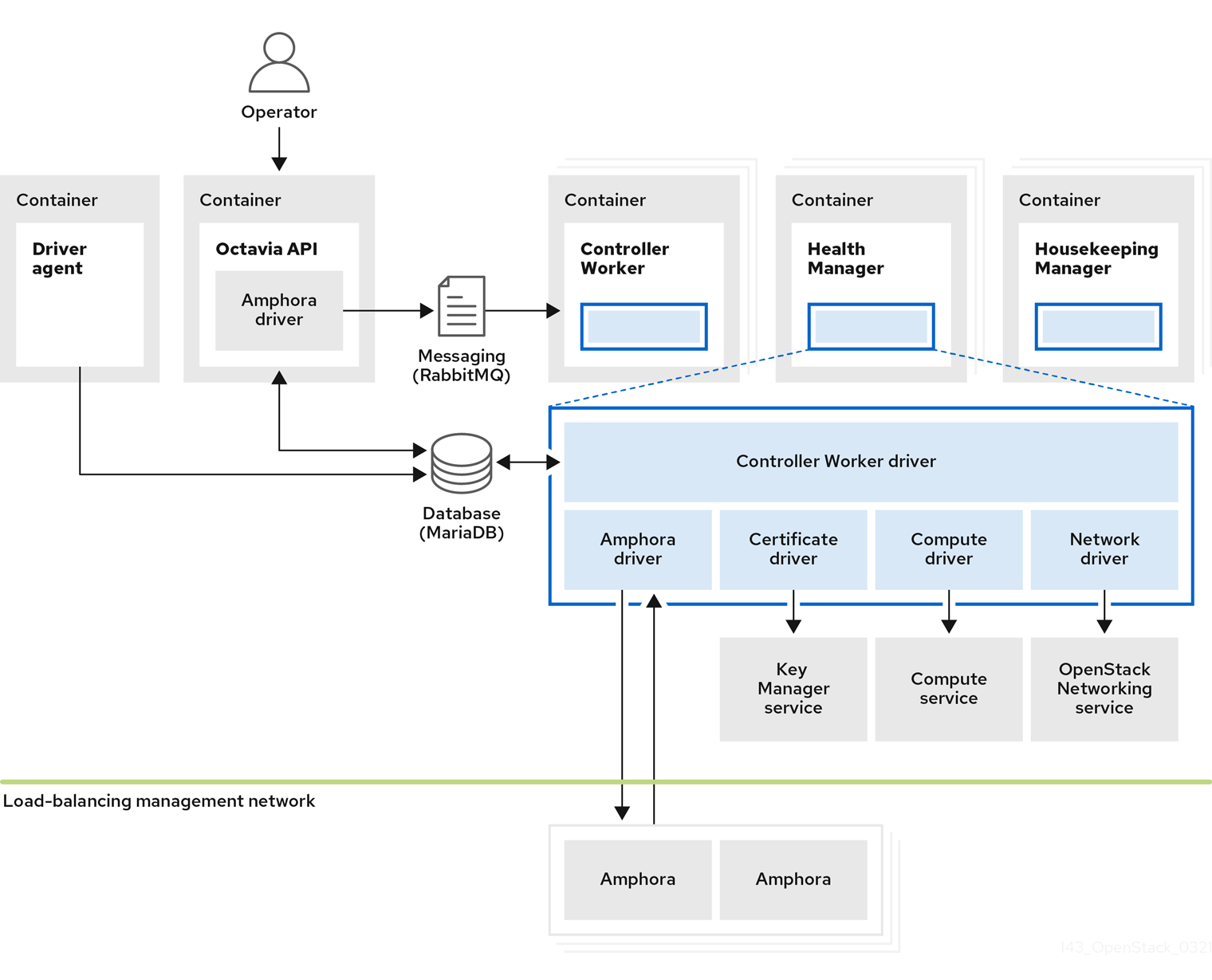
Figure 1.1. Load-balancing service components
Figure 1.1 shows the components of the Load-balancing service are hosted on the same nodes as the Networking API server, which by default, is on the Red Hat OpenShift worker nodes that host the RHOSO control plane. The Load-balancing service consists of the following components:
- Octavia API (
octavia-apipods) - Provides the REST API for users to interact with octavia.
- Controller Worker (
octavia-workerpods) - Sends configuration and configuration updates to amphorae over the load-balancing management network.
- Health Manager (
octavia-healthmanagerpods) - Monitors the health of individual amphorae and handles failover events if an amphora encounters a failure.
- Housekeeping Manager (
octavia-housekeepingpods) - Cleans up deleted database records, and manages amphora certificate rotation.
- Driver agent (included within the
octavia-apipods) - Supports other provider drivers, such as OVN.
- Amphora
- Performs the load balancing. Amphorae are typically instances that run on Compute nodes that you configure with load balancing parameters according to the listener, pool, health monitor, L7 policies, and members' configuration. Amphorae send a periodic heartbeat to the Health Manager.
1.2. Load-balancing service object model
The Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) Load-balancing service (octavia) uses a typical load-balancing object model.
Figure 1.2. Load-balancing service object model diagram
- Load balancer
- The top API object that represents the load-balancing entity. The VIP address is allocated when you create the load balancer. When you use the amphora provider to create the load balancer one or more amphora instances launch on one or more Compute nodes.
- Listener
- The port on which the load balancer listens, for example, TCP port 80 for HTTP. Listeners also support TLS-terminated HTTPS load balancers.
- Health Monitor
- A process that performs periodic health checks on each back-end member server to pre-emptively detect failed servers and temporarily remove them from the pool.
- Pool
- A group of members that handle client requests from the load balancer. You can associate pools with more than one listener by using the API. You can share pools with L7 policies.
- Member
- Describes how to connect to the back-end instances or services. This description consists of the IP address and network port on which the back end member is available.
- L7 Rule
- Defines the layer 7 (L7) conditions that determine whether an L7 policy applies to the connection.
- L7 Policy
- A collection of L7 rules associated with a listener, and which might also have an association to a back-end pool. Policies describe actions that the load balancer takes if all of the rules in the policy are true.
1.3. Uses of load balancing in RHOSO
Load balancing is essential for enabling simple or automatic delivery scaling and availability for cloud deployments. The Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) Load-balancing service (octavia) depends on other RHOSO services:
- Compute service (nova) - For managing the Load-balancing service VM instance (amphora) lifecycle, and creating compute resources on demand.
- Networking service (neutron) - For network connectivity between amphorae, tenant environments, and external networks.
- Key Manager service (barbican) - For managing TLS certificates and credentials, when TLS session termination is configured on a listener.
- Identity service (keystone) - For authentication requests to the octavia API, and for the Load-balancing service to authenticate with other RHOSO services.
- Image service (glance) - For storing the amphora virtual machine image.
The Load-balancing service interacts with the other RHOSO services through a driver interface. The driver interface avoids major restructuring of the Load-balancing service if an external component requires replacement with a functionally-equivalent service.