Chapter 5. Sample Optimize service workflows
This content in this section is available in this release as a Technology Preview, and therefore is not fully supported by Red Hat. It should only be used for testing, and should not be deployed in a production environment. For more information, see Technology Preview.
Two sample workflows ship with this release of the Optimize service (watcher) in Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO). One workflow uses the OpenStack CLI, and the other workflow uses the OpenStack Dashboard (horizon). The two sample workflows require you to create instances. For information about creating instances, see Creating an instance in Creating and managing instances.
The topics included in this section are:
Prerequisites
- A functional RHOSO 18.0 deployment that contains two or more Compute nodes.
- The Compute service (nova) live migration feature is operational.
- The Optimize service is operational.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
5.1. Consolidating node resources
Use the node resource consolidation strategy to reduce the spread of workloads, and consolidate instances onto a smaller subset of Compute nodes. The Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) administrator can use the Optimize service (watcher) with the node resource consolidation strategy to migrate all running instances from a source Compute node to a destination Compute node without user interruption. Unlike the VM workload consolidation strategy, the node resource consolidation strategy does not set the status of the source Compute node to disabled.
| Goal | Strategy |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Prerequisites
- You have an operational RHOSO 18.0 on which the Optimize service (watcher) is running.
- Your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Access the remote shell for the OpenStackClient pod from your workstation:
oc rsh -n openstack openstackclient
$ oc rsh -n openstack openstackclientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node:
openstack server list --long -c Name -c Host
$ openstack server list --long -c Name -c HostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, instances
test01andtest02that are running oncompute1andcompute2, respectively:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an audit template that uses the strategy,
node_resource_consolidation, and the goal,server_consolidation.Example
In this example, the audit template is named
NodeResourceConsolidation:openstack optimize audittemplate create -s node_resource_consolidation NodeResourceConsolidation server_consolidation
$ openstack optimize audittemplate create -s node_resource_consolidation NodeResourceConsolidation server_consolidationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the audit template has been created:
openstack optimize audittemplate list
$ openstack optimize audittemplate listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
+----------------------+-----------------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+-----------------------------+ | server_consolidation | node_resource_consolidation | +----------------------+-----------------------------+
+----------------------+-----------------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+-----------------------------+ | server_consolidation | node_resource_consolidation | +----------------------+-----------------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run an audit that uses an audit template based on the strategy,
node_resource_consolidation, and the goal,server_consolidation.Example
In this audit the
NodeResourceConsolidationaudit template is used, and checks the resource usage of both Compute nodes. The strategy parameterhost_choice=specifyis set, which means that the strategy will specify the node where the instances will be migrated:openstack optimize audit create -a NodeResourceConsolidation \ -p host_choice=specify
$ openstack optimize audit create -a NodeResourceConsolidation \ -p host_choice=specifyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information about the parameters this strategy uses, see Node resource consolidation strategy.
Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the Optimize service ran the audit:
openstack optimize audit list
$ openstack optimize audit listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
If the audit
Statehas a value ofSUCCEEDEDthen the audit ran and has created an action plan:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit 7984626e-cc14-4b87-ab96-f0127f2da51e
$ openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit 7984626e-cc14-4b87-ab96-f0127f2da51eCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example,
Global efficacyisReleased_nodes_ratio: 50.00 %.This value indicates that if you execute the action plan, the Compute service will live migrate the instances so that half of the Compute nodes in the environment will be freed up, and host no running instances:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the actions contained in the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71fc5c0c-5890-4cd8-b919-f06eb94da94b
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71fc5c0c-5890-4cd8-b919-f06eb94da94bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan contains one action,
migrate:+--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | UUID | State | Action | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | bda5053b-2489-49fe-bc04-5b2ad3bc5075 | PENDING | migrate | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+
+--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | UUID | State | Action | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | bda5053b-2489-49fe-bc04-5b2ad3bc5075 | PENDING | migrate | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can view more detail about the action:
Example
openstack optimize action show bda5053b-2489-49fe-bc04-5b2ad3bc5075
$ openstack optimize action show bda5053b-2489-49fe-bc04-5b2ad3bc5075Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan will live migrate all of the instances running on one of the Compute nodes, to free up the node:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan start \ 71fc5c0c-5890-4cd8-b919-f06eb94da94b
$ openstack optimize actionplan start \ 71fc5c0c-5890-4cd8-b919-f06eb94da94bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the action succeeded.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71fc5c0c-5890-4cd8-b919-f06eb94da94
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71fc5c0c-5890-4cd8-b919-f06eb94da94Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that one of the Compute nodes no longer hosts any instances:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, both instances,
test01andtest02, are now running on the same Compute node,compute2. This means that thecompute1node is freed up:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Exit the
openstackclientpod:exit
$ exitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2. Consolidating VM instances
Use the Optimize service (watcher) with VM workload consolidation strategy to move a VM instance workload when the physical host CPU or RAM utilization percentage exceeds the specified threshold. The instance that is migrated should cause the workload for the host to approximate the average workload of all the Compute nodes in the Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) cluster. Unlike the node resource consolidation strategy, the VM workload consolidation strategy sets the status of the source Compute node to disabled.
| Goal | Strategy |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Prerequisites
- You have an operational RHOSO 18.0 on which the Optimize service (watcher) is running.
- Your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Access the remote shell for the OpenStackClient pod from your workstation:
oc rsh -n openstack openstackclient
$ oc rsh -n openstack openstackclientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, instances
test01andtest03that are running oncompute1have a heavy RAM load. We want to use the Optimize service with the workload balance strategy to migrate at least one of these instances to a Compute node that has more capacity without user interruption:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an audit template that uses the strategy,
vm_workload_consolidation, and the goalserver_consolidation.Example
In this example, the audit template is named
WorkLoadConsolidation:openstack optimize audittemplate create -s vm_workload_consolidation \ WorkLoadConsolidation server_consolidation
$ openstack optimize audittemplate create -s vm_workload_consolidation \ WorkLoadConsolidation server_consolidationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the audit template has been created:
openstack optimize audittemplate list
$ openstack optimize audittemplate listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
+----------------------+-----------------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+-----------------------------+ | server_consolidation | vm_workload_consolidation | +----------------------+-----------------------------+
+----------------------+-----------------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+-----------------------------+ | server_consolidation | vm_workload_consolidation | +----------------------+-----------------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run an audit that uses an audit template based on the strategy,
vm_workload_consolidation, and the goalserver_consolidation. Update the strategy parameters with values appropriate for your environment.Example
In this audit the
WorkLoadConsolidationaudit template is used, and checks for CPU usage using theworkload_balancestrategy:openstack optimize audit create -a WorkLoadConsolidation
$ openstack optimize audit create -a WorkLoadConsolidationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information about the parameters this strategy uses, see VM workload consolidation strategy.
Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the Optimize service ran the audit:
openstack optimize audit list
$ openstack optimize audit listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
If the audit
Statehas a value ofSUCCEEDEDthen the audit ran and has created an action plan:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit bdb0edfa-344a-4897-a7fd-3b1994d87db7
$ openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit bdb0edfa-344a-4897-a7fd-3b1994d87db7Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example,
Global efficacyisLive_migrations_count: 50.00 %.This value indicates that if you execute the action plan, the Compute service will migrate 50 percent of the currently running instances:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the actions contained in the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71bb6d02-50a9-4e18-b030-c070d5b36cde
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71bb6d02-50a9-4e18-b030-c070d5b36cdeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan contains one action,
migrate:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can view more detail about an action:
Example
openstack optimize action show 7207af7a-569f-4d72-9a9a-0be7f9c9b175
$ openstack optimize action show 7207af7a-569f-4d72-9a9a-0be7f9c9b175Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan will live migrate one of the instances with a heavy CPU usage to a Compute node where the instance CPU usage is lower.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan start \ 71bb6d02-50a9-4e18-b030-c070d5b36cde
$ openstack optimize actionplan start \ 71bb6d02-50a9-4e18-b030-c070d5b36cdeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the action succeeded.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71bb6d02-50a9-4e18-b030-c070d5b36cde
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 71bb6d02-50a9-4e18-b030-c070d5b36cdeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that one of the instances with a heavy CPU usage has been migrated to a different Compute node:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the instances
test01andtest03are now running on a different node,compute2:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Exit the
openstackclientpod:exit
$ exitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.3. Stabilizing multiple workloads
Use the Optimize service (watcher) with the workload stabilization strategy to move VM instance workloads when the physical host CPU or RAM utilization percentage exceeds the specified threshold. The instances that are migrated should cause the workload for the host to approximate the average workload of all the Compute nodes in the Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) cluster.
This topic also demonstrates how to use the OpenStack Dashboard (horizon) when stabilizing multiple workloads.
| Goal | Strategy |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Prerequisites
- You have an operational RHOSO 18.0 on which the Optimize service (watcher) is running.
- You have created at least two instances that run on different nodes.
- You have the Dashboard service (horizon) installed on your workstation.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Ensure that you are in the project where you have the
Adminrole assigned:
Click the
Computemenu, and chooseInstances.
Verify that your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node:
In this example, instances
test01andtest03that are running oncompute1have a heavy CPU load. Use the Optimize service with the workload stabilization strategy to live migrate at least one of these instances to a Compute node that has more capacity without user interruption:
Click the
Admintab:
Click the
Optimizationmenu, and selectAudit Templates:
In the
Audit Templatespanel, clickCreate Template.
The
Create Audit Templatedialog box displays.Create an
Audit TemplatenamedWorkLoadStabilization, select the goalWorkload Balancing, and select the strategyWorkload stabilization. When you are finished, click theCreate Audit Templatebutton.
Click the
Auditssub tab, and then click theCreate Auditbutton.
The
Create Auditdialog box displays.Select the following values, and then click the
Create Auditbutton:-
In
Audit Template, chooseWorkLoadStabilization. -
In
Audit Type, chooseCONTINUOUS. In
Interval, enter180.
-
In
Click the UUID for the
Auditto see the action plans created for the new audit.
Click the UUID for the action plan to see more detail.

Click the UUID under
Related Actions.
In the
Actionspanel, you can see more information about the recommended action.In this example, the
test01instance, an instance that has a heavy CPU load, will be live migrated from thecompute1node to thecompute2node.
When you are finished reviewing the action, click the
Action planssub menu:
In the
Action Planspanel, for theRECOMMENDEDaction plan, click theStart Action Planbutton: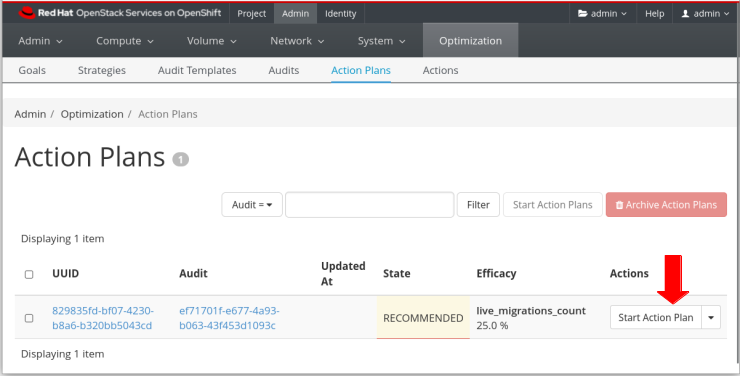
The value of
Statechanges toONGOING.Monitor the Action Plans panel, until the
Stateshows a value ofSUCCEEDED.Click the
Computemenu, and chooseInstances.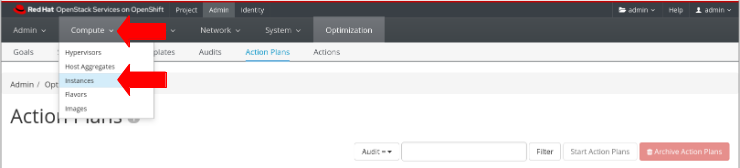
Confirm that one of the instances with a heavy CPU usage has been migrated to a different Compute node.
In this example, instance
test01now is running on a different node,compute2:
Click the
Optimizationmenu, and chooseAudits.
In the
Auditspanel, from theGo to Action Plandrop-down, selectCancel Auditto stop theCONTINUOUSaudit.
5.4. Balancing single instance workloads
Use the Optimize service (watcher) with the workload balance strategy to move a VM instance workload when the physical host CPU or RAM utilization percentage exceeds the specified threshold. The instance that is migrated should cause the workload for the host to approximate the average workload of all the Compute nodes in the Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift (RHOSO) cluster.
| Goal | Strategy |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Prerequisites
- You have an operational RHOSO 18.0 on which the Optimize service (watcher) is running.
- Your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Access the remote shell for the OpenStackClient pod from your workstation:
oc rsh -n openstack openstackclient
$ oc rsh -n openstack openstackclientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, instances
test01andtest03that are running oncompute1have a heavy CPU load. We want to use the Optimize service with the workload balance strategy to live migrate at least one of these instances to a Compute node that has more capacity without user interruption:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an audit template that uses the strategy,
workload_balance, and the goalworkload_balancing.Example
In this example, the audit template is named
WorkLoadBalance:openstack optimize audittemplate create -s workload_balance \ WorkLoadBalance workload_balancing
$ openstack optimize audittemplate create -s workload_balance \ WorkLoadBalance workload_balancingCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the audit template has been created:
openstack optimize audittemplate list
$ openstack optimize audittemplate listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
+----------------------+------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+------------------+ | workload_balancing | workload_balance | +----------------------+------------------+
+----------------------+------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+------------------+ | workload_balancing | workload_balance | +----------------------+------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run an audit that uses an audit template based on the strategy,
workload_balance, and the goalworkload_balancing. Update the strategy parameters with values appropriate for your environment.Example
In this audit the
WorkLoadBalanceaudit template is used, and checks for CPU usage usingworkload_balancestrategy parameters with various values:openstack optimize audit create -a WorkLoadBalance -p granularity=30 \ -p threshold=20 -p period=300 -p metrics=instance_cpu_usage
$ openstack optimize audit create -a WorkLoadBalance -p granularity=30 \ -p threshold=20 -p period=300 -p metrics=instance_cpu_usageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information about the parameters this strategy uses, see Workload balance migration strategy.
Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the Optimize service ran the audit:
openstack optimize audit list
$ openstack optimize audit listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
If the audit
Statehas a value ofSUCCEEDEDthen the audit ran and has created an action plan:+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | UUID | State | Strategy | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | ad815d54-5b7d-4562-aa12-17e1b64d0868 | SUCCEEDED | workload_balance | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | UUID | State | Strategy | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | ad815d54-5b7d-4562-aa12-17e1b64d0868 | SUCCEEDED | workload_balance | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit ad815d54-5b7d-4562-aa12-17e1b64d0868
$ openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit ad815d54-5b7d-4562-aa12-17e1b64d0868Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example,
Global efficacyisLive_migrations_count: 25.00 %.This value indicates that if you execute the action plan, the Compute service will migrate 25% of the currently running instances:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the actions contained in the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan f40dfa4e-1b96-4883-b85f-3bfa73554359
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan f40dfa4e-1b96-4883-b85f-3bfa73554359Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan contains one action,
migrate:+--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | UUID | State | Action | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | 9a510bf9-ebac-450d-a4ea-a10b66d6d869 | PENDING | migrate | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+
+--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | UUID | State | Action | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+ | 9a510bf9-ebac-450d-a4ea-a10b66d6d869 | PENDING | migrate | +--------------------------------------+---------+---------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can view more detail about the action:
Example
openstack optimize action show 9a510bf9-ebac-450d-a4ea-a10b66d6d869
$ openstack optimize action show 9a510bf9-ebac-450d-a4ea-a10b66d6d869Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan will live migrate one of the instances with a heavy CPU usage to a Compute node where the instance CPU usage is lower.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan start \ f40dfa4e-1b96-4883-b85f-3bfa73554359
$ openstack optimize actionplan start \ f40dfa4e-1b96-4883-b85f-3bfa73554359Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the action succeeded.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan dfdcb491-89c5-4c07-a5ed-65d2085c488c
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan dfdcb491-89c5-4c07-a5ed-65d2085c488cCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that one of the instances with a heavy CPU usage has been migrated to a different Compute node:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, instance
test03now is running on a different node,compute2:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Exit the
openstackclientpod:exit
$ exitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.5. Streamlining workload migrations
Use the Optimize service (watcher) with the zone migration strategy to migrate many instances efficiently without user interruption and with minimum downtime for hardware maintenance.
The term zone in the zone migration strategy refers to a user-defined set of Compute nodes and storage pools. Zone does not a refer to Openstack availability zones.
| Goal | Strategy |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Prerequisites
- You have an operational RHOSO 18.0 on which the Optimize service (watcher) is running.
- Your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Access the remote shell for the OpenStackClient pod from your workstation:
oc rsh -n openstack openstackclient
$ oc rsh -n openstack openstackclientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that your RHOSO environment contains at least two Compute nodes that run at least one instance on each node:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, two instances are running on
compute1and one instance is running oncompute2. Thecompute1node is scheduled for maintenance, so we want to use the Optimize service with the zone migration strategy to live migrate the instances to the other Compute node without user interruption:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an audit template that uses the strategy,
zone_migration, and the goal,hardware_maintenance.Example
In this example, the audit template is named
ZoneMigration:openstack optimize audittemplate create -s zone_migration ZoneMigration hardware_maintenance
$ openstack optimize audittemplate create -s zone_migration ZoneMigration hardware_maintenanceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information about the parameters this strategy uses, see Zone migration.
Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the audit template has been created:
openstack optimize audittemplate list
$ openstack optimize audittemplate listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
+----------------------+------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+------------------+ | hardware_maintenance | zone_migration | +----------------------+------------------+
+----------------------+------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+------------------+ | hardware_maintenance | zone_migration | +----------------------+------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run an audit that uses an audit template based on the strategy,
zone_migration, and the goal,hardware_maintenance. Update the strategy parameters with values appropriate for your environment.Example
The
ZoneMigrationaudit template is used in this example with the following strategy parameter values:-
src_node: contains the value,compute1, which is the node where maintenance will be performed. dst_node: contains the value,compute2, which is the node where the instances running oncompute1will be migrated.openstack optimize audit create -a ZoneMigration -p compute_nodes=\ '[{"src_node":"compute1.ctlplane.localdomain", "dst_node":"compute2.ctlplane.localdomain"}]'$ openstack optimize audit create -a ZoneMigration -p compute_nodes=\ '[{"src_node":"compute1.ctlplane.localdomain", "dst_node":"compute2.ctlplane.localdomain"}]'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Confirm that the Optimize service created the audit:
openstack optimize audit list
$ openstack optimize audit listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
If
Statehas a value ofSUCCEEDEDthen the audit ran and has created an action plan:+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | UUID | State | Strategy | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | 9e9eeb70-63bd-427e-a5a6-a2f049f1bc73 | SUCCEEDED | zone_migration | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | UUID | State | Strategy | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | 9e9eeb70-63bd-427e-a5a6-a2f049f1bc73 | SUCCEEDED | zone_migration | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit 9e9eeb70-63bd-427e-a5a6-a2f049f1bc73 \ -c UUID -c State -c "Global efficacy"
$ openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit 9e9eeb70-63bd-427e-a5a6-a2f049f1bc73 \ -c UUID -c State -c "Global efficacy"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the
Live_instance_migrate_ratiorepresents the percentage of instances that are live migrated in the action plan: the number of live migrations in the action plan divided by the number of instances that could be migrated according to user input. For example, if thesrc_nodehad 4 active instances but 2 are migrated in the action plan, the ratio would be 50%Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the actions contained in the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40305df2-c240-464b-ac56-62e51bf139ef \ -c 'UUID' -c 'State' -c 'Action'
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40305df2-c240-464b-ac56-62e51bf139ef \ -c 'UUID' -c 'State' -c 'Action'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan contains two actions to migrate two instances:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can view more detail about an action:
Example
In this example, more detail is requested for the migrate action,
680e6152-e163-443d-9bd4-178b73494aa4:openstack optimize action show 680e6152-e163-443d-9bd4-178b73494aa4
$ openstack optimize action show 680e6152-e163-443d-9bd4-178b73494aa4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan will migrate the
test01instance from thecompute1node to thecompute2node:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan start \ 40305df2-c240-464b-ac56-62e51bf139ef
$ openstack optimize actionplan start \ 40305df2-c240-464b-ac56-62e51bf139efCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, both instances are being live migrated from
compute1tocompute2:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the actions succeeded.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40305df2-c240-464b-ac56-62e51bf139ef
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40305df2-c240-464b-ac56-62e51bf139efCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that all of the instances have been migrated to a different Compute node:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the two instances that were running on
compute1are now running oncompute2:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Exit the
openstackclientpod:exit
$ exitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.6. Preparing Compute nodes for planned maintenance
Use the Optimize service (watcher) with the host maintenance strategy to migrate all of the instances off a Compute node in your Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP) environment to perform host maintenance, without user interruption. If the backup node is not provided, the Optimize service migrates all instances by relying on nova-scheduler. In both use cases, the Compute maintenance node will be disabled.
Use the host maintenance strategy in a planned maintenance window where the load is low to minimize impact on the workloads. When you run the audit, ensure that do not change the default audit_type value, ONESHOT.
| Goal | Strategy |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Prerequisites
- You have an operational RHOSO 18.0 on which the Optimize service (watcher) is running.
You have at least two Compute nodes:
- One Compute node with at least one instance running.
- A second Compute node that serves as a back-up node.
-
You have the
occommand line tool installed on your workstation. -
You are logged on to a workstation that has access to the RHOSO control plane as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges.
Procedure
Access the remote shell for the OpenStackClient pod from your workstation:
oc rsh -n openstack openstackclient
$ oc rsh -n openstack openstackclientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that there are at least two compute nodes and at least one instance.
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, one instance is running on
compute1and one instance running oncompute2. Thecompute1node is scheduled for maintenance, so we want to use the Optimize service with the host maintenance strategy to migrate the instances fromcompute1tocompute2without user interruption:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an audit template that uses the strategy,
host_maintenance, and the goal,cluster_maintaining.Example
In this example, the audit template is named
HostMaintenance:openstack optimize audittemplate create -s host_maintenance \ HostMaintenance cluster_maintaining
$ openstack optimize audittemplate create -s host_maintenance \ HostMaintenance cluster_maintainingCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the audit template has been created:
openstack optimize audittemplate list
$ openstack optimize audittemplate listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
+----------------------+------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+------------------+ | cluster_maintaining | host_maintenance | +----------------------+------------------+
+----------------------+------------------+ | Goal | Strategy | +----------------------+------------------+ | cluster_maintaining | host_maintenance | +----------------------+------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run an audit that uses an audit template based on the strategy,
host_maintenance, and the goal,cluster_maintaining. Update the strategy parameters with values appropriate for your environment.Example
The
HostMaintenanceaudit template is used in this example, with thecompute1host scheduled for maintenance:openstack optimize audit create -a HostMaintenance \ -p maintenance_node=compute1.ctlplane.localdomain
$ openstack optimize audit create -a HostMaintenance \ -p maintenance_node=compute1.ctlplane.localdomainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information about the parameters this strategy uses, see Host maintenance strategy.
Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the Optimize service created the audit:
openstack optimize audit list
$ openstack optimize audit listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
If
Statehas a value ofSUCCEEDEDthen the audit ran and has created an action plan:+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | UUID | State | Strategy | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | 8cfb4abe-3720-4af2-a8a9-fba8fff1f442 | SUCCEEDED | host_maintenance | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+
+--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | UUID | State | Strategy | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+ | 8cfb4abe-3720-4af2-a8a9-fba8fff1f442 | SUCCEEDED | host_maintenance | +--------------------------------------+-----------+------------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit 8cfb4abe-3720-4af2-a8a9-fba8fff1f442
$ openstack optimize actionplan list \ --audit 8cfb4abe-3720-4af2-a8a9-fba8fff1f442Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
+--------------------------------------+-------------+-----------------+ | UUID | State | Global efficacy | +--------------------------------------+-------------+-----------------+ | 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08 | RECOMMENDED | | +--------------------------------------+-------------+-----------------+
+--------------------------------------+-------------+-----------------+ | UUID | State | Global efficacy | +--------------------------------------+-------------+-----------------+ | 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08 | RECOMMENDED | | +--------------------------------------+-------------+-----------------+Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List the actions contained in the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan contains two actions:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can view more detail about an action.
Example
openstack optimize action show \ 6e3154ac-279a-4b26-b993-9a6eea70309b
$ openstack optimize action show \ 6e3154ac-279a-4b26-b993-9a6eea70309bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan will migrate the one instance currently running on the
compute1node to thecompute2node:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
openstack optimize action show \ 19afe53e-4cf4-4b67-b910-92bca5f40186
$ openstack optimize action show \ 19afe53e-4cf4-4b67-b910-92bca5f40186Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the action plan will change the
compute1node state todisabled.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the action plan.
Example
openstack optimize actionplan start \ 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08
$ openstack optimize actionplan start \ 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the action succeeded.
Example
openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08
$ openstack optimize action list \ --action-plan 40017617-7698-4ce7-b5ce-2917ec522a08Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information about the parameters this strategy uses, see Host maintenance strategy.
Sample output
In this example, the instance was migrated from the
compute1node, and the state ofcompute1was set to disabled:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that all instances running on the maintenance node have been migrated:
openstack server list --long
$ openstack server list --longCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the instance that was running on the
compute1node,test01now is running on thecompute2node:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the maintenance node has been disabled.
openstack compute service list
$ openstack compute service listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample output
In this example, the
compute1node has aStatusofdisabled:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Exit the
openstackclientpod:exit
$ exitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow