Chapter 2. Adding TLS Certificates to the Red Hat Quay Container
To add custom TLS certificates to Red Hat Quay, you can use either the command line interface or the Red Hat Quay user interface. From the command line, you need to create a new directory named extra_ca_certs/ beneath the Red Hat Quay config directory and copy any required site-specific TLS certificates to this new directory.
2.1. Add Custom/SSL certificates from the Red Hat Quay UI
To add custom or self-signed SSL certificates to Red Hat Quay from the web UI, do the following:
- Navigate to the Red Hat Quay config UI.
- Scroll to the Custom SSL Certificates section.
-
In the Upload certificates box, select the filename of the certificate. The following figure shows the result of uploading a file named ca.crt.
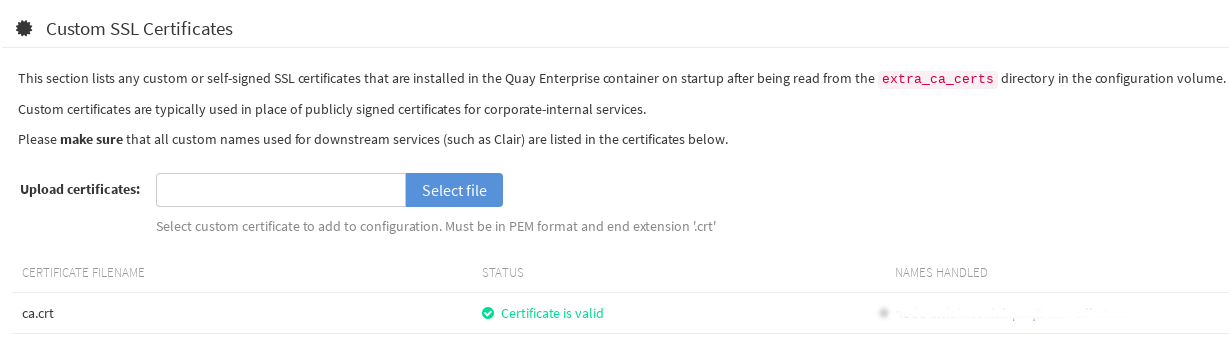
2.2. Add TLS certificates to Red Hat Quay
View certificate to be added to the container
cat storage.crt -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDTTCCAjWgAwIBAgIJAMVr9ngjJhzbMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMD0xCzAJBgNV [...] -----END CERTIFICATE-----
$ cat storage.crt -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDTTCCAjWgAwIBAgIJAMVr9ngjJhzbMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMD0xCzAJBgNV [...] -----END CERTIFICATE-----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create certs directory and copy certificate there
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Obtain the quay container’s
CONTAINER IDwithdocker ps:docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS 5a3e82c4a75f quay.io/coreos/quay:v2.9.5 "/sbin/my_init" 24 hours ago Up 18 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp, 8443/tcp grave_keller
$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS 5a3e82c4a75f quay.io/coreos/quay:v2.9.5 "/sbin/my_init" 24 hours ago Up 18 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp, 8443/tcp grave_kellerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the container with that ID:
docker restart 5a3e82c4a75f
$ docker restart 5a3e82c4a75fCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Examine the certificate copied into the container namespace:
docker exec -it 5a3e82c4a75f cat /etc/ssl/certs/storage.pem -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDTTCCAjWgAwIBAgIJAMVr9ngjJhzbMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMD0xCzAJBgNV
$ docker exec -it 5a3e82c4a75f cat /etc/ssl/certs/storage.pem -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDTTCCAjWgAwIBAgIJAMVr9ngjJhzbMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMD0xCzAJBgNVCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.3. Add certs when deployed on Kubernetes
When deployed on Kubernetes, Red Hat Quay mounts in a secret as a volume to store config assets. Unfortunately, this currently breaks the upload certificate function of the Red Hat Quay config UI.
To get around this error, a base64 encoded certificate can be added to the secret after Quay has been deployed. Here’s how:
Begin by base64 encoding the contents of the certificate:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
kubectltool to edit the quay-enterprise-config-secret.kubectl --namespace quay-enterprise edit secret/quay-enterprise-config-secret
$ kubectl --namespace quay-enterprise edit secret/quay-enterprise-config-secretCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add an entry for the cert and paste the full base64 encoded string under the entry:
custom-cert.crt: c1psWGpqeGlPQmNEWkJPMjJ5d0pDemVnR2QNCnRsbW9JdEF4YnFSdVd3PT0KLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUtLS0tLQo=
custom-cert.crt: c1psWGpqeGlPQmNEWkJPMjJ5d0pDemVnR2QNCnRsbW9JdEF4YnFSdVd3PT0KLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUtLS0tLQo=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Finally, recycle all Red Hat Quay pods. Use
kubectl deleteto remove all Red Hat Quay pods. The Red Hat Quay Deployment will automatically schedule replacement pods with the new certificate data.