Chapter 8. Automatially build Dockerfiles with build workers
Red Hat Quay supports building Dockerfiles using a set of worker nodes. Build triggers, such as GitHub webhooks (Setup Instructions), can be configured to automatically build new versions of your repositories when new code is committed. This document will walk you through enabling the feature flag and setting up multiple build workers to enable this feature.
8.1. Enable building
-
Visit the management panel: Sign in to a superuser account and visit
http://yourregister/superuserto view the management panel: Enable Dockerfile Build Support:
-
Click the configuration tab and scroll down to the section entitled Dockerfile Build Support.
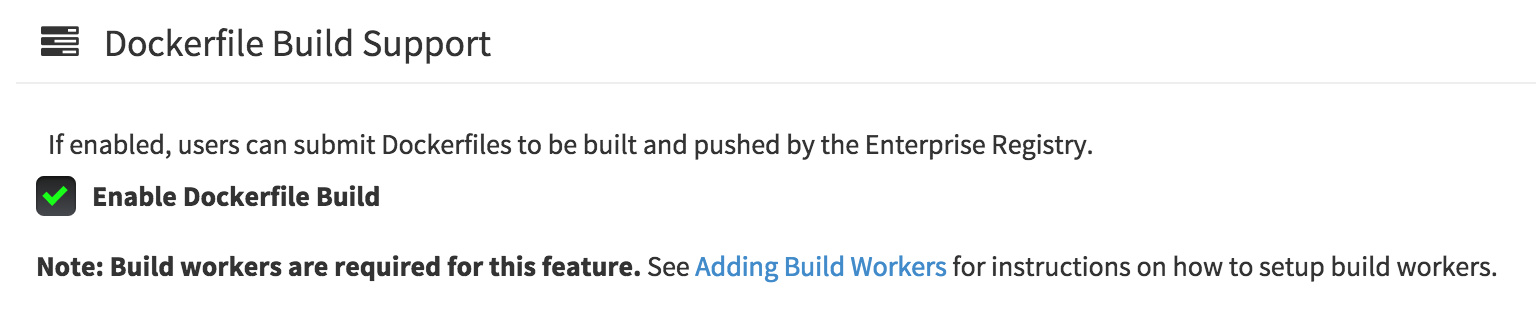
- Check the "Enable Dockerfile Build" box
- Click "Save Configuration Changes"
- Restart the container (you will be prompted)
-
Click the configuration tab and scroll down to the section entitled Dockerfile Build Support.
8.2. Set up the build workers
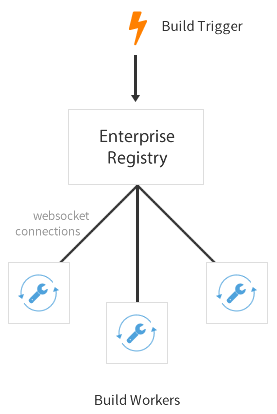
One or more build workers will communicate with Red Hat Quay to build new containers when triggered. The machines must have Docker installed and must not be used for any other work. The following procedure needs to be done every time a new worker needs to be added, but it can be automated fairly easily.
8.2.1. Pull the build worker image
Pull down the latest copy of the image. Make sure to pull the version tagged matching your Red Hat Quay version.
# docker pull quay.io/redhat/quay-builder:v3.2.2
8.2.2. Run the build worker image
Run this container on each build worker. Since the worker will be orchestrating docker builds, we need to mount in the docker socket. This orchestration will use a large amount of CPU and need to manipulate the docker images on disk — we recommend that dedicated machines be used for this task.
Use the environment variable SERVER to tell the worker the hostname at which Red Hat Quay is accessible:
| Security | Websocket Address |
|---|---|
| Using SSL | wss://your.quayenterprise.dnsname |
| Without SSL | ws://your.quayenterprise.dnsname |
Here’s what the full command looks like:
docker run --restart on-failure \ -e SERVER=ws://myquayenterprise \ --privileged=true \ -v /mnt/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ quay.io/redhat/quay-builder:v3.2.2
# docker run --restart on-failure \
-e SERVER=ws://myquayenterprise \
--privileged=true \
-v /mnt/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
quay.io/redhat/quay-builder:v3.2.2When the container starts, each build worker will auto-register and start building containers once a job is triggered and it is assigned to a worker.
If Red Hat Quay is setup to use a SSL certificate that is not globally trusted, for example a self-signed certificate, Red Hat Quay’s public SSL certificates must be mounted onto the quay-builder container’s SSL trust store. An example command to mount a certificate found at the host’s /path/to/ssl/rootCA.pem looks like:
8.3. Set up GitHub build (optional)
If your organization plans to have builds be conducted via pushes to GitHub (or GitHub Enterprise), please continue with the Setting up GitHub Build.