Chapter 11. Provisioning virtual machines in VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere is an enterprise-level virtualization platform from VMware. Red Hat Satellite can interact with the vSphere platform, including creating new virtual machines and controlling their power management states.
11.1. Prerequisites for VMware provisioning
The requirements for VMware vSphere provisioning include:
A supported version of VMware vCenter Server. The following versions have been fully tested with Satellite:
- vCenter Server 7.0
- vCenter Server 6.7 (EOL)
- vCenter Server 6.5 (EOL)
- A Capsule Server managing a network on the vSphere environment. Ensure no other DHCP services run on this network to avoid conflicts with Capsule Server. For more information, see Chapter 3, Configuring networking.
- An existing VMware template if you want to use image-based provisioning.
- You can use synchronized content repositories for Red Hat Enterprise Linux. For more information, see Syncing Repositories in Managing content.
- Provide an activation key for host registration. For more information, see Creating An Activation Key in Managing content.
11.2. Creating a VMware user
The VMware vSphere server requires an administration-like user for Satellite Server communication. For security reasons, do not use the administrator user for such communication. Instead, create a user with the following permissions:
For VMware vCenter Server version 6.7, set the following permissions:
-
All Privileges
Datastore Allocate Space, Browse datastore, Update Virtual Machine files, Low level file operations -
All Privileges
Network Assign Network -
All Privileges
Resource Assign virtual machine to resource pool -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Change Config (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Interaction (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Edit Inventory (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Provisioning (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Guest Operations (All)
Note that the same steps also apply to VMware vCenter Server version 7.0.
For VMware vCenter Server version 6.5, set the following permissions:
-
All Privileges
Datastore Allocate Space, Browse datastore, Update Virtual Machine files, Low level file operations -
All Privileges
Network Assign Network -
All Privileges
Resource Assign virtual machine to resource pool -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Configuration (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Interaction (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Inventory (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Provisioning (All) -
All Privileges
Virtual Machine Guest Operations (All)
11.3. Adding a VMware connection to Satellite Server
Use this procedure to add a VMware vSphere connection in Satellite Server’s compute resources. To use the CLI instead of the Satellite web UI, see the CLI procedure.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that the host and network-based firewalls are configured to allow communication from Satellite Server to vCenter on TCP port 443.
- Verify that Satellite Server and vCenter can resolve each other’s host names.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Resources, and in the Compute Resources window, click Create Compute Resource.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the resource.
- From the Provider list, select VMware.
- In the Description field, enter a description for the resource.
- In the VCenter/Server field, enter the IP address or host name of the vCenter server.
- In the User field, enter the user name with permission to access the vCenter’s resources.
- In the Password field, enter the password for the user.
- Click Load Datacenters to populate the list of data centers from your VMware vSphere environment.
- From the Datacenter list, select a specific data center to manage from this list.
- In the Fingerprint field, ensure that this field is populated with the fingerprint from the data center.
- From the Display Type list, select a console type, for example, VNC or VMRC. Note that VNC consoles are unsupported on VMware ESXi 6.5 and later.
Optional: In the VNC Console Passwords field, select the Set a randomly generated password on the display connection checkbox to secure console access for new hosts with a randomly generated password. You can retrieve the password for the VNC console to access guest virtual machine console from the
libvirtdhost from the output of the following command:# virsh edit your_VM_name <graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport='yes' listen='0.0.0.0' passwd='your_randomly_generated_password'>
The password randomly generates every time the console for the virtual machine opens, for example, with virt-manager.
- From the Enable Caching list, you can select whether to enable caching of compute resources. For more information, see Section 11.10, “Caching of compute resources”.
- Click the Locations and Organizations tabs and verify that the values are automatically set to your current context. You can also add additional contexts.
- Click Submit to save the connection.
CLI procedure
Create the connection with the
hammer compute-resource createcommand. SelectVmwareas the--providerand set the instance UUID of the data center as the--uuid:# hammer compute-resource create \ --datacenter "My_Datacenter" \ --description "vSphere server at vsphere.example.com" \ --locations "My_Location" \ --name "My_vSphere" \ --organizations "My_Organization" \ --password "My_Password" \ --provider "Vmware" \ --server "vsphere.example.com" \ --user "My_User"
11.4. Adding VMware images to Satellite Server
VMware vSphere uses templates as images for creating new virtual machines. If using image-based provisioning to create new hosts, you need to add VMware template details to your Satellite Server. This includes access details and the template name.
To use the CLI instead of the Satellite web UI, see the CLI procedure.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Resources.
- Select your Vmware compute resource.
- Click Create Image.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the image.
- From the Operating System list, select the base operating system of the image.
- From the Architecture list, select the operating system architecture.
-
In the Username field, enter the SSH user name for image access. By default, this is set to
root. -
If your image supports user data input such as
cloud-initdata, click the User data checkbox. - Optional: In the Password field, enter the SSH password to access the image.
- From the Image list, select an image from VMware.
- Click Submit to save the image details.
CLI procedure
Create the image with the
hammer compute-resource image createcommand. Use the--uuidfield to store the relative template path on the vSphere environment:# hammer compute-resource image create \ --architecture "My_Architecture" \ --compute-resource "My_VMware" --name "My_Image" \ --operatingsystem "My_Operating_System" \ --username root \ --uuid "My_UUID"
11.5. Adding VMware details to a compute profile
You can predefine certain hardware settings for virtual machines on VMware vSphere. You achieve this through adding these hardware settings to a compute profile. To use the CLI instead of the Satellite web UI, see the CLI procedure.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Profiles.
- Select a compute profile.
- Select a Vmware compute resource.
- In the CPUs field, enter the number of CPUs to allocate to the host.
- In the Cores per socket field, enter the number of cores to allocate to each CPU.
- In the Memory field, enter the amount of memory in MiB to allocate to the host.
- In the Firmware checkbox, select either BIOS or UEFI as firmware for the host. By default, this is set to automatic.
- In the Cluster list, select the name of the target host cluster on the VMware environment.
- From the Resource pool list, select an available resource allocations for the host.
- In the Folder list, select the folder to organize the host.
- From the Guest OS list, select the operating system you want to use in VMware vSphere.
- From the Virtual H/W version list, select the underlying VMware hardware abstraction to use for virtual machines.
- If you want to add more memory while the virtual machine is powered on, select the Memory hot add checkbox.
- If you want to add more CPUs while the virtual machine is powered on, select the CPU hot add checkbox.
- If you want to add a CD-ROM drive, select the CD-ROM drive checkbox.
- From the Boot order list, define the order in which the virtual machines tried to boot.
- Optional: In the Annotation Notes field, enter an arbitrary description.
- If you use image-based provisioning, select the image from the Image list.
- From the SCSI controller list, select the disk access method for the host.
- If you want to use eager zero thick provisioning, select the Eager zero checkbox. By default, the disk uses lazy zero thick provisioning.
- From the Network Interfaces list, select the network parameters for the host’s network interface. At least one interface must point to a Capsule-managed network.
- Optional: Click Add Interface to create another network interfaces.
- Click Submit to save the compute profile.
CLI procedure
Create a compute profile:
# hammer compute-profile create --name "My_Compute_Profile"Set VMware details to a compute profile:
# hammer compute-profile values create \ --compute-attributes "cpus=1,corespersocket=2,memory_mb=1024,cluster=MyCluster,path=MyVMs,start=true" \ --compute-profile "My_Compute_Profile" \ --compute-resource "My_VMware" \ --interface "compute_type=VirtualE1000,compute_network=mynetwork \ --volume "size_gb=20G,datastore=Data,name=myharddisk,thin=true"
11.6. Creating hosts on VMware
The VMware vSphere provisioning process provides the option to create hosts over a network connection or using an existing image.
For network-based provisioning, you must create a host to access either Satellite Server’s integrated Capsule or an external Capsule Server on a VMware vSphere virtual network, so that the host has access to PXE provisioning services. The new host entry triggers the VMware vSphere server to create the virtual machine. If the virtual machine detects the defined Capsule Server through the virtual network, the virtual machine boots to PXE and begins to install the chosen operating system.
DHCP conflicts
If you use a virtual network on the VMware vSphere server for provisioning, ensure that you select a virtual network that does not provide DHCP assignments. This causes DHCP conflicts with Satellite Server when booting new hosts.
For image-based provisioning, use the pre-existing image as a basis for the new volume.
To use the CLI instead of the Satellite web UI, see the CLI procedure.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Hosts > Create Host.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the host.
- Optional: Click the Organization tab and change the organization context to match your requirement.
- Optional: Click the Location tab and change the location context to match your requirement.
- From the Host Group list, select a host group that you want to assign your host to. That host group will populate the form.
- From the Deploy on list, select the VMware vSphere connection.
- From the Compute Profile list, select a profile to use to automatically populate virtual machine-based settings.
- Click the Interfaces tab, and on the interface of the host, click Edit.
Verify that the fields are populated with values. Note in particular:
- Satellite automatically assigns an IP address for the new host.
- Ensure that the MAC address field is blank. VMware assigns a MAC address to the host during provisioning.
- The Name from the Host tab becomes the DNS name.
- Ensure that Satellite automatically selects the Managed, Primary, and Provision options for the first interface on the host. If not, select them.
- In the interface window, review the VMware-specific fields that are populated with settings from our compute profile. Modify these settings to suit your needs.
- Click OK to save. To add another interface, click Add Interface. You can select only one interface for Provision and Primary.
- Click the Operating System tab, and confirm that all fields automatically contain values.
Select the Provisioning Method that you want:
- For network-based provisioning, click Network Based.
- For image-based provisioning, click Image Based.
- For boot-disk provisioning, click Boot disk based.
- Click Resolve in Provisioning templates to check the new host can identify the right provisioning templates to use.
- Click the Virtual Machine tab and confirm that these settings are populated with details from the host group and compute profile. Modify these settings to suit your requirements.
- Click the Parameters tab and ensure that a parameter exists that provides an activation key. If a parameter does not exist, click + Add Parameter. In the field Name, enter kt_activation_keys. In the field Value, enter the name of the activation key used to register the Content Hosts.
- Click Submit to provision your host on VMware.
CLI procedure
Create the host from a network with the
hammer host createcommand and include--provision-method buildto use network-based provisioning:# hammer host create \ --build true \ --compute-attributes="cpus=1,corespersocket=2,memory_mb=1024,cluster=MyCluster,path=MyVMs,start=true" \ --compute-resource "My_VMware" \ --enabled true \ --hostgroup "My_Host_Group" \ --interface "managed=true,primary=true,provision=true,compute_type=VirtualE1000,compute_network=mynetwork" \ --location "My_Location" \ --managed true \ --name "My_Host" \ --organization "My_Organization" \ --provision-method build \ --volume="size_gb=20G,datastore=Data,name=myharddisk,thin=true"
Create the host from an image with the
hammer host createcommand and include--provision-method imageto use image-based provisioning:# hammer host create \ --compute-attributes="cpus=1,corespersocket=2,memory_mb=1024,cluster=MyCluster,path=MyVMs,start=true" \ --compute-resource "My_VMware" \ --enabled true \ --hostgroup "My_Host_Group" \ --image "My_VMware_Image" \ --interface "managed=true,primary=true,provision=true,compute_type=VirtualE1000,compute_network=mynetwork" \ --location "My_Location" \ --managed true \ --name "My_Host" \ --organization "My_Organization" \ --provision-method image \ --volume="size_gb=20G,datastore=Data,name=myharddisk,thin=true"
For more information about additional host creation parameters for this compute resource, enter the hammer host create --help command.
11.7. Using VMware cloud-init and userdata templates for provisioning
You can use VMware with the Cloud-init and Userdata templates to insert user data into the new virtual machine, to make further VMware customization, and to enable the VMware-hosted virtual machine to call back to Satellite.
You can use the same procedures to set up a VMware compute resource within Satellite, with a few modifications to the workflow.
Figure 11.1. VMware cloud-init provisioning overview
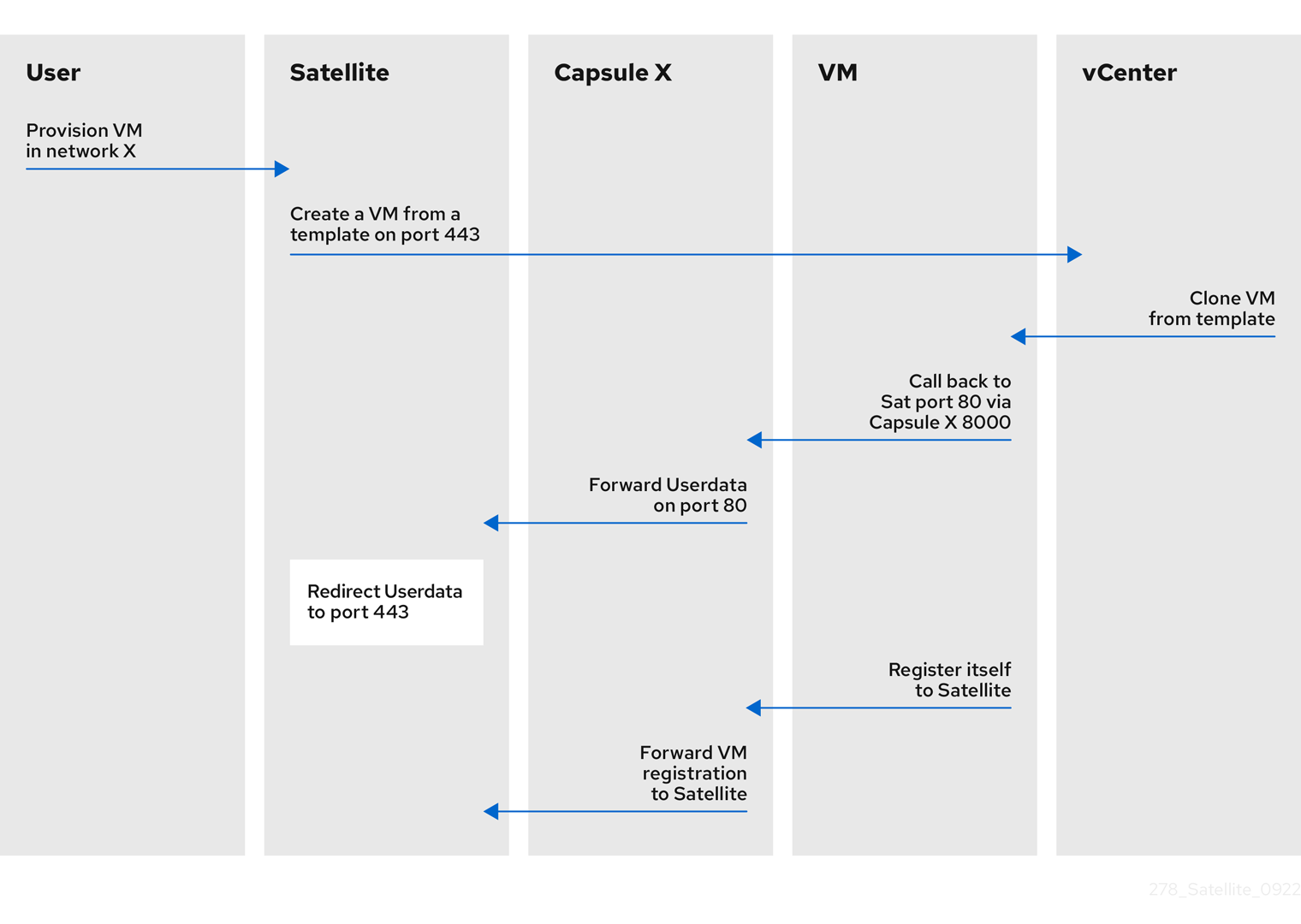
When you set up the compute resource and images for VMware provisioning in Satellite, the following sequence of provisioning events occurs:
- The user provisions one or more virtual machines using the Satellite web UI, API, or hammer
- Satellite calls the VMware vCenter to clone the virtual machine template
-
Satellite
userdataprovisioning template adds customized identity information -
When provisioning completes, the
Cloud-initprovisioning template instructs the virtual machine to call back to Capsule whencloud-initruns - VMware vCenter clones the template to the virtual machine
- VMware vCenter applies customization for the virtual machine’s identity, including the host name, IP, and DNS
-
The virtual machine builds,
cloud-initis invoked and calls back Satellite on port80, which then redirects to443
Prerequisites
-
Configure port and firewall settings to open any necessary connections. Because of the
cloud-initservice, the virtual machine always calls back to Satellite even if you register the virtual machine to Capsule. For more information, see Port and firewall requirements in Installing Satellite Server in a connected network environment and Port and firewall requirements in Installing Capsule Server. - If you want to use Capsule Servers instead of your Satellite Server, ensure that you have configured your Capsule Servers accordingly. For more information, see Configuring Capsule for Host Registration and Provisioning in Installing Capsule Server.
Back up the following configuration files:
-
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/01_network.cfg -
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/10_datasource.cfg -
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
-
Associating the Userdata and Cloud-init templates with the operating system
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Hosts > Templates > Provisioning Templates.
- Search for the CloudInit default template and click its name.
- Click the Association tab.
- Select all operating systems to which the template applies and click Submit.
- Repeat the steps above for the UserData open-vm-tools template.
- Navigate to Hosts > Provisioning Setup > Operating Systems.
- Select the operating system that you want to use for provisioning.
- Click the Templates tab.
- From the Cloud-init template list, select CloudInit default.
- From the User data template list, select UserData open-vm-tools.
- Click Submit to save the changes.
Preparing an image to use the cloud-init template
To prepare an image, you must first configure the settings that you require on a virtual machine that you can then save as an image to use in Satellite.
To use the cloud-init template for provisioning, you must configure a virtual machine so that cloud-init is installed, enabled, and configured to call back to Satellite Server.
For security purposes, you must install a CA certificate to use HTTPS for all communication. This procedure includes steps to clean the virtual machine so that no unwanted information transfers to the image you use for provisioning.
If you have an image with cloud-init, you must still follow this procedure to enable cloud-init to communicate with Satellite because cloud-init is disabled by default.
Procedure
On the virtual machine that you use to create the image, install the required packages:
# dnf install cloud-init open-vm-tools perl-interpreter perl-File-Temp
Disable network configuration by
cloud-init:# cat << EOM > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/01_network.cfg network: config: disabled EOM
Configure
cloud-initto fetch data from Satellite:# cat << EOM > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/10_datasource.cfg datasource_list: [NoCloud] datasource: NoCloud: seedfrom: https://satellite.example.com/userdata/ EOMIf you intend to provision through Capsule Server, use the URL of your Capsule Server in the
seedfromoption, such ashttps://capsule.example.com:9090/userdata/.Configure modules to use in
cloud-init:# cat << EOM > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg cloud_init_modules: - bootcmd - ssh cloud_config_modules: - runcmd cloud_final_modules: - scripts-per-once - scripts-per-boot - scripts-per-instance - scripts-user - phone-home system_info: distro: rhel paths: cloud_dir: /var/lib/cloud templates_dir: /etc/cloud/templates ssh_svcname: sshd EOMEnable the CA certificates for the image:
# update-ca-trust enable
Download the
katello-server-ca.crtfile from Satellite Server:# wget -O /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/cloud-init-ca.crt https://satellite.example.com/pub/katello-server-ca.crtIf you intend to provision through Capsule Server, download the file from your Capsule Server, such as
https://capsule.example.com/pub/katello-server-ca.crt.Update the record of certificates:
# update-ca-trust extract
Clean the image:
# systemctl stop rsyslog # systemctl stop auditd # package-cleanup --oldkernels --count=1 # dnf clean all
Reduce logspace, remove old logs, and truncate logs:
# logrotate -f /etc/logrotate.conf # rm -f /var/log/*-???????? /var/log/*.gz # rm -f /var/log/dmesg.old # rm -rf /var/log/anaconda # cat /dev/null > /var/log/audit/audit.log # cat /dev/null > /var/log/wtmp # cat /dev/null > /var/log/lastlog # cat /dev/null > /var/log/grubby
Remove
udevhardware rules:# rm -f /etc/udev/rules.d/70*
Remove the
ifcfgscripts related to existing network configurations:# rm -f /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens* # rm -f /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth*
Remove the SSH host keys:
# rm -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*
Remove root user’s SSH history:
# rm -rf ~root/.ssh/known_hosts
Remove root user’s shell history:
# rm -f ~root/.bash_history # unset HISTFILE
- Create an image from this virtual machine.
- Add your image to Satellite.
11.8. Deleting a VM on VMware
You can delete VMs running on VMware from within Satellite.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Resources.
- Select your VMware provider.
- On the Virtual Machines tab, click Delete from the Actions menu. This deletes the virtual machine from the VMware compute resource while retaining any associated hosts within Satellite. If you want to delete the orphaned host, navigate to Hosts > All Hosts and delete the host manually.
11.9. Importing a virtual machine from VMware into Satellite
You can import existing virtual machines running on VMware into Satellite.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Resources.
- Select your VMware compute resource.
- On the Virtual Machines tab, click Import as managed Host or Import as unmanaged Host from the Actions menu. The following page looks identical to creating a host with the compute resource being already selected. For more information, see Creating a host in Satellite in Managing hosts.
- Click Submit to import the virtual machine into Satellite.
11.10. Caching of compute resources
Caching of compute resources speeds up rendering of VMware information.
11.10.1. Enabling caching of compute resources
To enable or disable caching of compute resources:
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Resources.
- Click the Edit button to the right of the VMware server you want to update.
- Select the Enable caching checkbox.
11.10.2. Refreshing the compute resources cache
Refresh the cache of compute resources to update compute resources information.
Procedure
- In the Satellite web UI, navigate to Infrastructure > Compute Resources.
- Select a VMware server you want to refresh the compute resources cache for and click Refresh Cache.
CLI procedure
Use this API call to refresh the compute resources cache:
# curl -H "Accept:application/json" \ -H "Content-Type:application/json" -X PUT \ -u username:password -k \ https://satellite.example.com/api/compute_resources/compute_resource_id/refresh_cache
Use
hammer compute-resource listto determine the ID of the VMware server you want to refresh the compute resources cache for.