1.5. Network
The Red Hat Virtualization network architecture facilitates connectivity between the different elements of the Red Hat Virtualization environment. The network architecture not only supports network connectivity, it also allows for network segregation.
Figure 1.3. Network Architecture
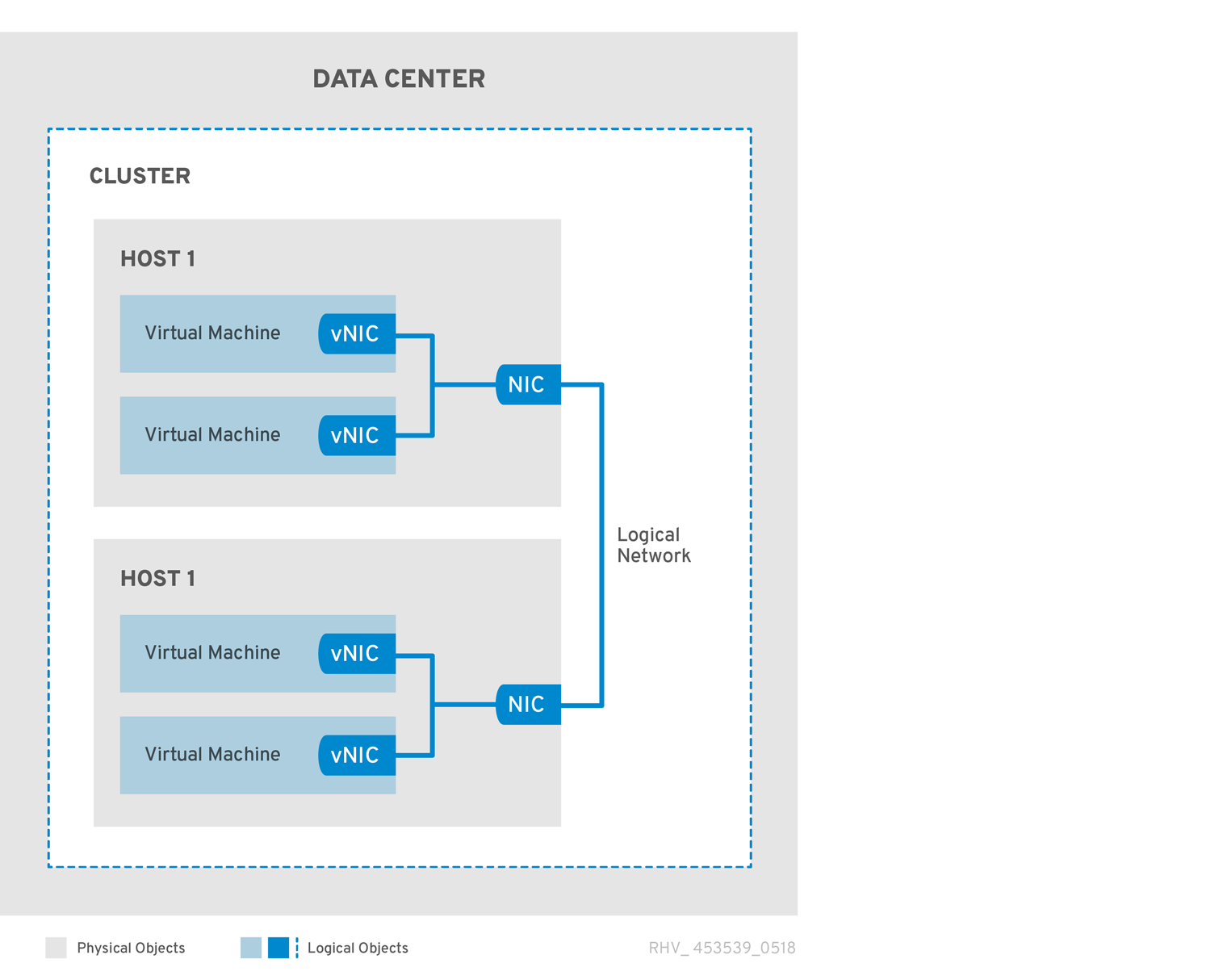
Networking is defined in Red Hat Virtualization in several layers. The underlying physical networking infrastructure must be in place and configured to allow connectivity between the hardware and the logical components of the Red Hat Virtualization environment.
- Networking Infrastructure Layer
The Red Hat Virtualization network architecture relies on some common hardware and software devices:
- Network Interface Controllers (NICs) are physical network interface devices that connect a host to the network.
- Virtual NICs (VNICs) are logical NICs that operate using the host’s physical NICs. They provide network connectivity to virtual machines.
- Bonds bind multiple NICs into a single interface.
- Bridges are a packet-forwarding technique for packet-switching networks. They form the basis of virtual machine logical networks.
- Logical Networks
Logical networks allow segregation of network traffic based on environment requirements. The types of logical network are:
- logical networks that carry virtual machine network traffic,
- logical networks that do not carry virtual machine network traffic,
- optional logical networks,
- and required networks.
All logical networks can either be required or optional.
A logical network that carries virtual machine network traffic is implemented at the host level as a software bridge device. By default, one logical network is defined during the installation of the Red Hat Virtualization Manager: the ovirtmgmt management network.
Other logical networks that can be added by an administrator are: a dedicated storage logical network, and a dedicated display logical network. Logical networks that do not carry virtual machine traffic do not have an associated bridge device on hosts. They are associated with host network interfaces directly.
Red Hat Virtualization segregates management-related network traffic from migration-related network traffic. This makes it possible to use a dedicated network (without routing) for live migration, and ensures that the management network (ovirtmgmt) does not lose its connection to hypervisors during migrations.
- Explanation of logical networks on different layers
- Logical networks have different implications for each layer of the virtualization environment.
Data Center Layer
Logical networks are defined at the data center level. Each data center has the ovirtmgmt management network by default. Further logical networks are optional but recommended. Designation as a VM Network and a custom MTU can be set at the data center level. A logical network that is defined for a data center must also be added to the clusters that use the logical network.
Cluster Layer
Logical networks are made available from a data center, and must be added to the clusters that will use them. Each cluster is connected to the management network by default. You can optionally add to a cluster logical networks that have been defined for the cluster’s parent data center. When a required logical network has been added to a cluster, it must be implemented for each host in the cluster. Optional logical networks can be added to hosts as needed.
Host Layer
Virtual machine logical networks are implemented for each host in a cluster as a software bridge device associated with a given network interface. Non-virtual machine logical networks do not have associated bridges, and are associated with host network interfaces directly. Each host has the management network implemented as a bridge using one of its network devices as a result of being included in a Red Hat Virtualization environment. Further required logical networks that have been added to a cluster must be associated with network interfaces on each host to become operational for the cluster.
Virtual Machine Layer
Logical networks can be made available to virtual machines in the same way that a network can be made available to a physical machine. A virtual machine can have its virtual NIC connected to any virtual machine logical network that has been implemented on the host that runs it. The virtual machine then gains connectivity to any other devices or destinations that are available on the logical network it is connected to.
Example 1.1. Management Network
The management logical network, named ovirtmgmt, is created automatically when the Red Hat Virtualization Manager is installed. The ovirtmgmt network is dedicated to management traffic between the Red Hat Virtualization Manager and hosts. If no other specifically purposed bridges are set up, ovirtmgmt is the default bridge for all traffic.