Este contenido no está disponible en el idioma seleccionado.
Chapter 3. Automation mesh design patterns
The automation mesh topologies in this section provide examples you can use to design a mesh deployment in your environment. Examples range from a simple, hydrid node deployment to a complex pattern that deploys numerous automation controller instances, employing several execution and hop nodes.
Prerequisites
- You reviewed conceptual information on node types and relationsips
The following examples include images that illustrate the mesh topology. The arrows in the images indicate the direction of peering. After peering is established, the connection between the nodes allows bidirectional communication.
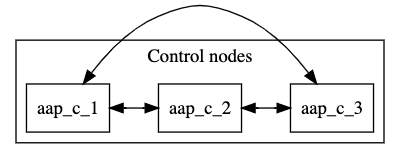
3.1. Multiple hybrid nodes inventory file example
This example inventory file deploys a control plane consisting of multiple hybrid nodes. The nodes in the control plane are automatically peered to one another.
[automationcontroller] aap_c_1.example.com aap_c_2.example.com aap_c_3.example.com
[automationcontroller]
aap_c_1.example.com
aap_c_2.example.com
aap_c_3.example.comThe following image displays the topology of this mesh network.
The default node_type for nodes in the control plane is hybrid. You can explicitly set the node_type of individual nodes to hybrid in the [automationcontroller group]:
[automationcontroller] aap_c_1.example.com node_type=hybrid aap_c_2.example.com node_type=hybrid aap_c_3.example.com node_type=hybrid
[automationcontroller]
aap_c_1.example.com node_type=hybrid
aap_c_2.example.com node_type=hybrid
aap_c_3.example.com node_type=hybrid
Alternatively, you can set the node-type of all nodes in the [automationcontroller] group. When you add new nodes to the control plane they are automatically set to hybrid nodes.
If you think that you might add control nodes to your control plane in future, it is better to define a separate group for the hybrid nodes, and set the node-type for the group:
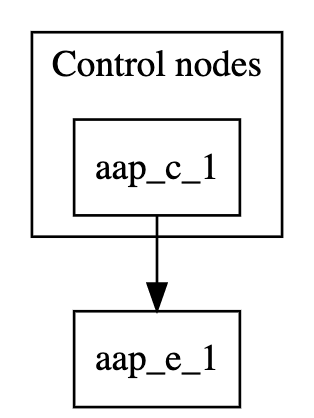
3.2. Single node control plane with single execution node
This example inventory file deploys a single-node control plane and establishes a peer relationship to an execution node.
The following image displays the topology of this mesh network.
The [automationcontroller] stanza defines the control nodes. If you add a new node to the automationcontroller group, it will automatically peer with the aap_c_1.example.com node.
The [automationcontroller:vars] stanza sets the node type to control for all nodes in the control plane and defines how the nodes peer to the execution nodes:
-
If you add a new node to the
execution_nodesgroup, the control plane nodes automatically peer to it. -
If you add a new node to the
automationcontrollergroup, the node type is set tocontrol.
The [execution_nodes] stanza lists all the execution and hop nodes in the inventory. The default node type is execution. You can specify the node type for an individual node:
[execution_nodes] aap_e_1.example.com node_type=execution
[execution_nodes]
aap_e_1.example.com node_type=execution
Alternatively, you can set the node_type of all execution nodes in the [execution_nodes] group. When you add new nodes to the group, they are automatically set to execution nodes.
[execution_nodes] aap_e_1.example.com [execution_nodes:vars] node_type=execution
[execution_nodes]
aap_e_1.example.com
[execution_nodes:vars]
node_type=execution
If you plan to add hop nodes to your inventory in future, it is better to define a separate group for the execution nodes, and set the node_type for the group:
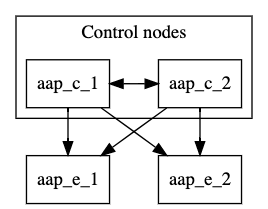
3.3. Minimum resilient configuration
This example inventory file deploys a control plane consisting of two control nodes, and two execution nodes. All nodes in the control plane are automatically peered to one another. All nodes in the control plane are peered with all nodes in the execution_nodes group. This configuration is resilient because the execution nodes are reachable from all control nodes.
The capacity algorithm determines which control node is chosen when a job is launched. Refer to Automation controller Capacity Determination and Job Impact in the Automation Controller User Guide for more information.
The following inventory file defines this configuration.
The [automationcontroller] stanza defines the control nodes. All nodes in the control plane are peered to one another. If you add a new node to the automationcontroller group, it will automatically peer with the original nodes.
The [automationcontroller:vars] stanza sets the node type to control for all nodes in the control plane and defines how the nodes peer to the execution nodes:
-
If you add a new node to the
execution_nodesgroup, the control plane nodes automatically peer to it. -
If you add a new node to the
automationcontrollergroup, the node type is set tocontrol.
The following image displays the topology of this mesh network.
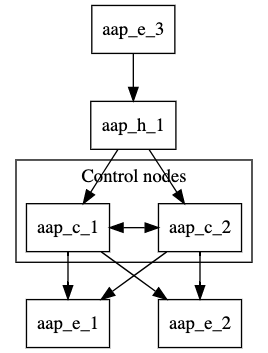
3.4. Segregated local and remote execution configuration
This configuration adds a hop node and a remote execution node to the resilient configuration. The remote execution node is reachable from the hop node.
You can use this setup if you are setting up execution nodes in a remote location, or if you need to run automation in a DMZ network.
The following image displays the topology of this mesh network.
The [automationcontroller:vars] stanza sets the node types for all nodes in the control plane and defines how the control nodes peer to the local execution nodes:
- All nodes in the control plane are automatically peered to one another.
- All nodes in the control plane are peered with all local execution nodes.
If the name of a group of nodes begins with instance_group_, the installer recognises it as an instance group and adds it to the Ansible Automation Platform user interface.
3.5. Multi-hopped execution node
In this configuration, resilient controller nodes are peered with resilient local execution nodes. Resilient local hop nodes are peered with the controller nodes. A remote execution node and a remote hop node are peered with the local hop nodes.
You can use this setup if you need to run automation in a DMZ network from a remote network.
The following image displays the topology of this mesh network.
The [automationcontroller:vars] stanza sets the node types for all nodes in the control plane and defines how the control nodes peer to the local execution nodes:
- All nodes in the control plane are automatically peered to one another.
- All nodes in the control plane are peered with all local execution nodes.
The [local_hop:vars] stanza peers all nodes in the [local_hop] group with all the control nodes.
If the name of a group of nodes begins with instance_group_, the installer recognises it as an instance group and adds it to the Ansible Automation Platform user interface.