Este contenido no está disponible en el idioma seleccionado.
Chapter 1. Overview
The Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) 2.3 on Red Hat OpenShift reference architecture provides an opinionated setup of deploying an Ansible Automation Platform environment. It provides a step-by-step deployment procedure with the latest best practices to install and configure Ansible Automation Platform 2.3. It is best suited for system and platform administrators looking to deploy Ansible Automation Platform on Red Hat OpenShift.
By utilizing the power of Red Hat OpenShift, we can streamline the deployment of Ansible Automation Platform and significantly reduce the time and effort required to set it up.
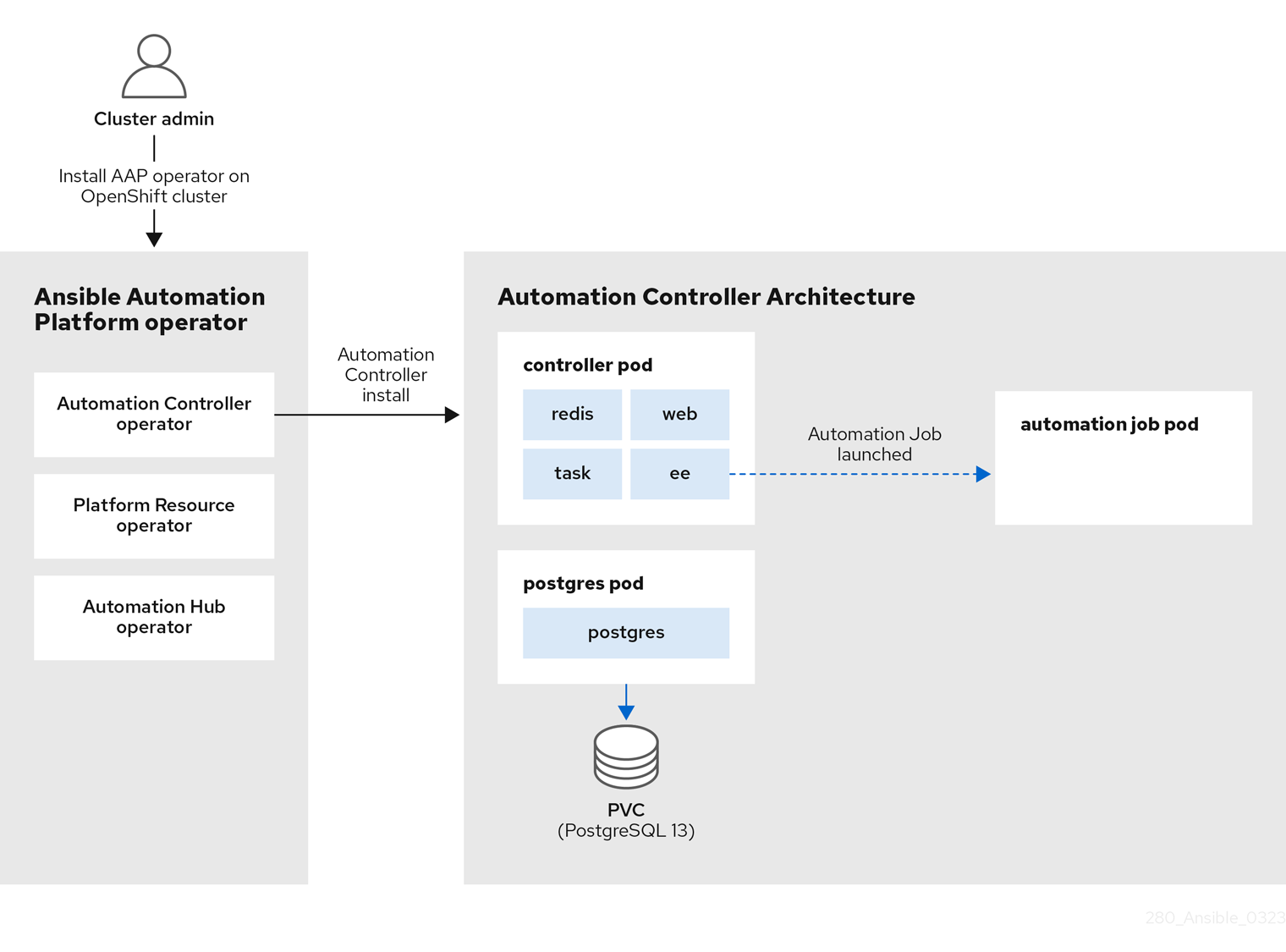
Figure 1.1. automation controller architecture
The Figure 1.1, “automation controller architecture”, shows the deployment process flow of the Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) operator deploying the automation controller component. The automation controller operator, one of the three operators that comprise the larger Ansible Automation Platform operator, is responsible for deploying the various pods including the controller, postgres and automation job pods.
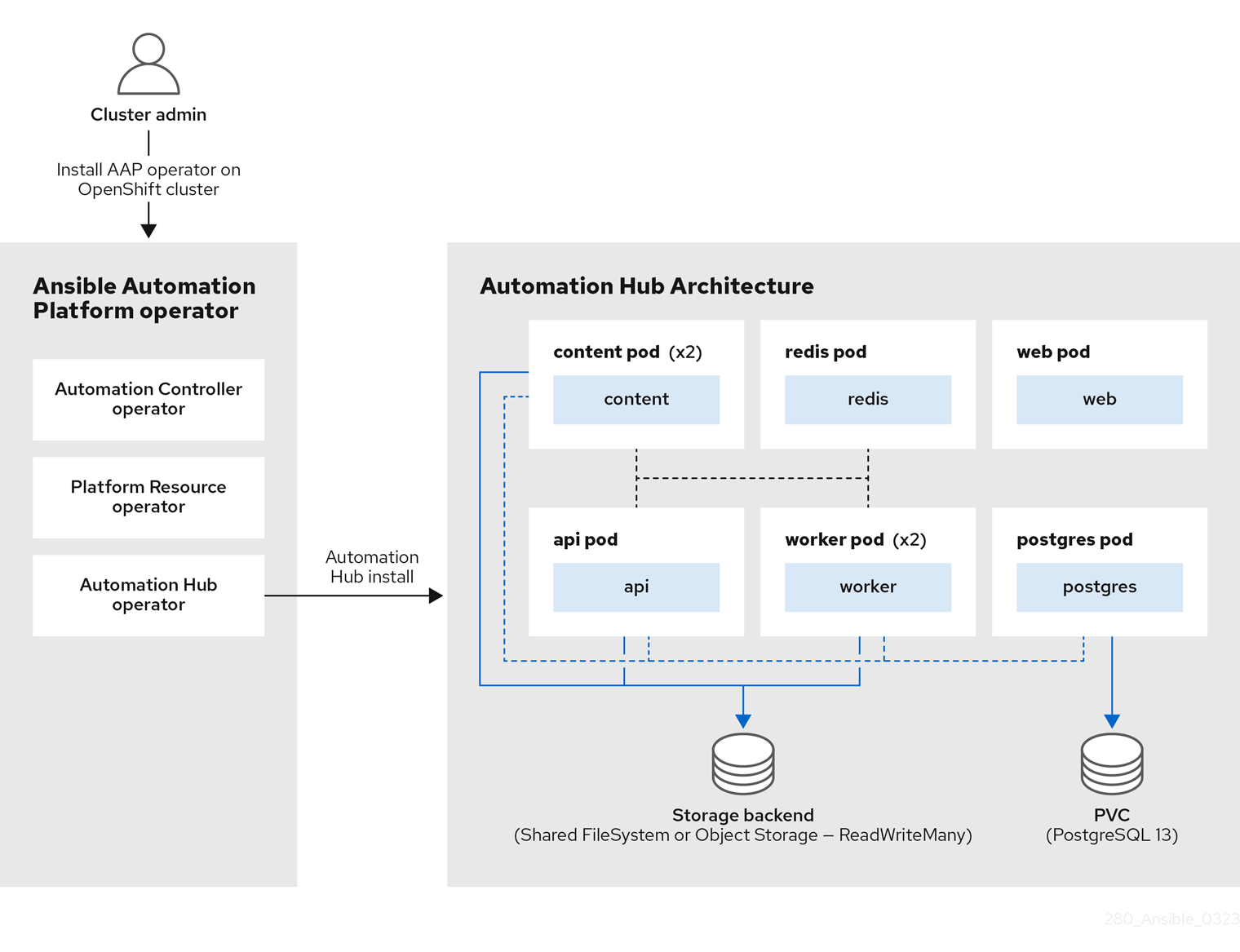
Figure 1.2. automation hub architecture
Similarly, the Figure 1.2, “automation hub architecture” shows the AAP operator deploying the automation hub component. The automation hub operator deploys various pods that communicate with each other to deliver automation hub to share internally generated content, Red Hat Ansible Certified Content, execution environments, and Ansible Validated Content with your teams.
In addition, this reference architecture highlights key steps involved in providing an efficient and scalable environment delivered by a solid foundation for any of your automation efforts.