Este contenido no está disponible en el idioma seleccionado.
Chapter 5. Network ports and protocols
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform uses several ports to communicate with its services. These ports must be open and available for incoming connections to the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform server in order for it to work. Ensure that these ports are available and are not blocked by the server firewall.
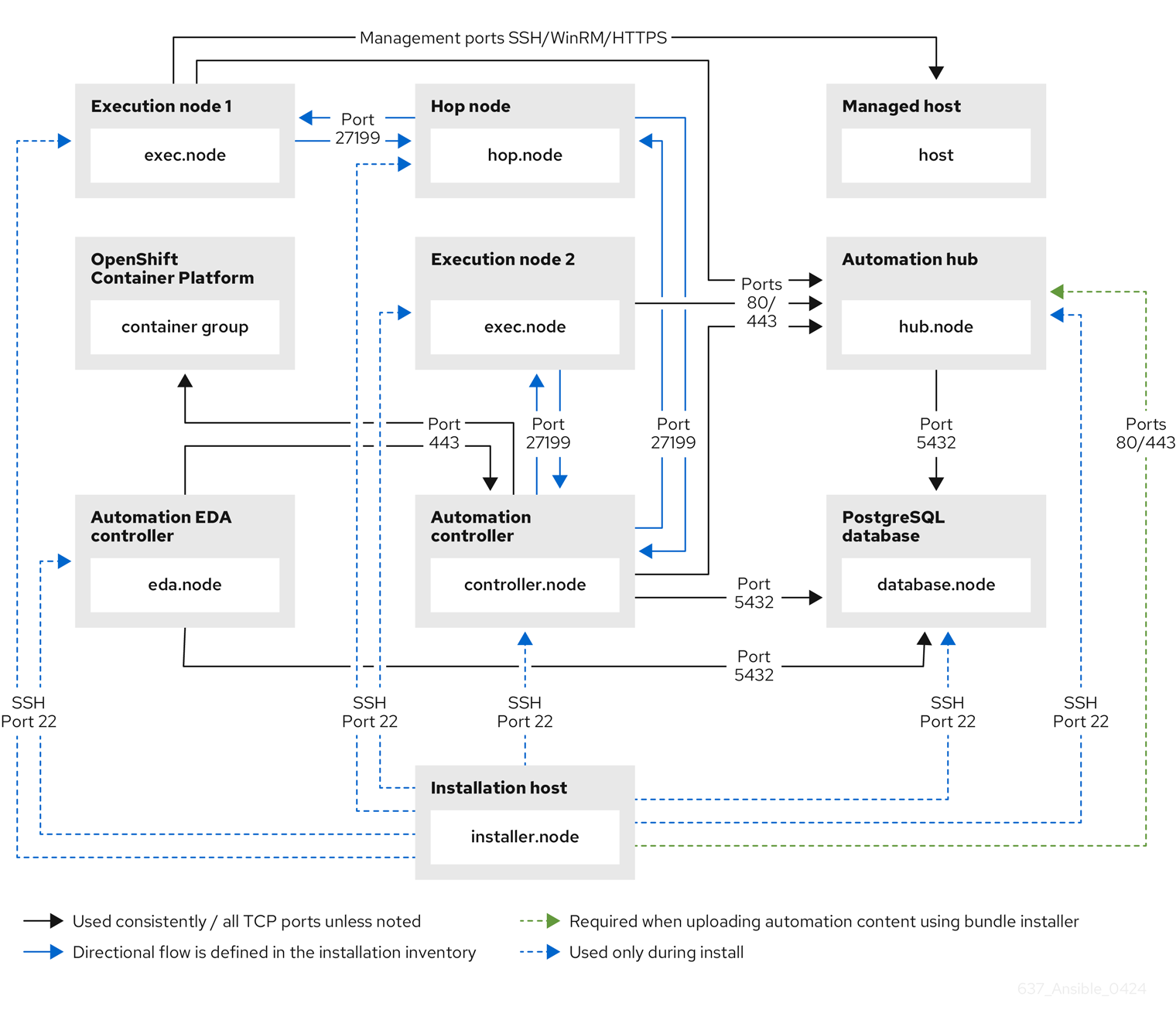
The following architectural diagram is an example of a fully deployed Ansible Automation Platform with all possible components.
Figure 5.1. Ansible Automation Platform Network ports and protocols
The following table indicates the destination port and the direction of network traffic:
The following default destination ports and installer inventory listed are configurable. If you choose to configure them to suit your environment, you might experience a change in behavior.
| Port | Protocol | Service | Source | Destination | Required for | Installer Inventory Variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | Automation hub | Installation (temporary) |
|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | Controller node | Installation (temporary) |
|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | EDA node | Installation (temporary) |
|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | Execution node | Installation (temporary) |
|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | Hop node | Installation (temporary) |
|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | Hybrid node | Installation (temporary) |
|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | Installer node | PostgreSQL database | Remote access during installation (temporary) |
|
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Installer node | Automation hub | Allows installer node to push the execution environment image to automation hub when using the bundle installer. | Fixed value |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Execution node | Automation hub | Allows execution nodes to pull the execution environment image from automation hub. | Fixed value |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Automation controller | Automation hub | For pulling collections and/or container images execution environments. | Fixed value |
| 443 | TCP | HTTPS | Controller node | Client | Web UI/API |
|
| 443 | TCP | HTTPS | Controller node | OpenShift Container Platform | Only required when using container groups to run jobs. | Host name of OpenShift API server |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Controller node | PostgreSQL database | Open only if the internal database is used along with another component. Otherwise, this port should not be open. |
|
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | EDA node | PostgreSQL database | Open only if the internal database is used along with another component. Otherwise, this port should not be open. |
|
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Automation hub | PostgreSQL database | Open only if the internal database is used along with another component. Otherwise, this port should not be open. |
|
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Controller node | Execution node | Configurable Mesh nodes directly peered to controllers. Direct nodes involved. 27199 communication can be both ways (depending on installation inventory) for execution nodes |
|
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Controller node | Hop node | Configurable ENABLE connections from hop nodes to Receptor port if relayed through hop nodes. |
|
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Controller node | Hybrid node | Configurable ENABLE connections from controllers to Receptor port if relayed through non-hop connected nodes. |
|
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Execution node | Hop node | Configurable Mesh 27199 communication can be both ways (depending on installation inventory) for execution nodes ALLOW connection from controller(s) to Receptor port |
|
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Execution node | Controller node | Configurable Mesh 27199 communication can be both ways (depending on installation inventory) for execution nodes ALLOW connection from controller(s) to Receptor port |
|
- Hybrid nodes act as a combination of control and execution nodes, and therefore Hybrid nodes share the connections of both.
-
If
receptor_listener_portis defined, the machine also requires an available open port on which to establish inbound TCP connections, for example, 27199. It might be the case that some servers do not listen on receptor port (the default is 27199)
Suppose you have a Control plane with nodes A, B, C, D
The RPM installer creates a strongly connected peering between the control plane nodes with a least privileged approach and opens the tcp listener only on those nodes where it is required. All the receptor connections are bidirectional, so once the connection is created, the receptor can communicate in both directions.
The following is an example peering set up for three controller nodes:
Controller node A -→ Controller node B
Controller node A -→ Controller node C
Controller node B -→ Controller node C
You can force the listener by setting
receptor_listener=TrueHowever, a connection Controller B -→ A is likely to be rejected as that connection already exists.
This means that nothing connects to Controller A as Controller A is creating the connections to the other nodes, and the following command does not return anything on Controller A:
[root@controller1 ~]# ss -ntlp | grep 27199 [root@controller1 ~]#
| URL | Required for |
|---|---|
| General account services, subscriptions | |
| Insights data upload | |
| Inventory upload and Cloud Connector connection | |
| Access to Insights dashboard |
| URL | Required for |
|---|---|
| General account services, subscriptions | |
| Indexing execution environments | |
| TCP | |
| https://automation-hub-prd.s3.amazonaws.com:443https://automation-hub-prd.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com:443 | Firewall access |
| Ansible Community curated Ansible content | |
| https://ansible-galaxy-ng.s3.dualstack.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:443 | Dual Stack IPv6 endpoint for Community curated Ansible content repository |
| Access to container images provided by Red Hat and partners | |
| Red Hat and partner curated Ansible Collections |
| URL | Required for |
|---|---|
| Access to container images provided by Red Hat and partners | |
|
| Access to container images provided by Red Hat and partners |
|
| Access to container images provided by Red Hat and partners |
|
| Access to container images provided by Red Hat and partners |
|
| Access to container images provided by Red Hat and partners |
As of April 1st, 2025, quay.io is adding three additional endpoints. As a result, customers must adjust allow/block lists within their firewall systems lists to include the following endpoints:
-
cdn04.quay.io -
cdn05.quay.io -
cdn06.quay.io
To avoid problems pulling container images, customers must allow outbound TCP connections (ports 80 and 443) to the following hostnames:
-
cdn.quay.io -
cdn01.quay.io -
cdn02.quay.io -
cdn03.quay.io -
cdn04.quay.io -
cdn05.quay.io -
cdn06.quay.io
This change should be made to any firewall configuration that specifically enables outbound connections to registry.redhat.io or registry.access.redhat.com.
Use the hostnames instead of IP addresses when configuring firewall rules.
After making this change, you can continue to pull images from registry.redhat.io or registry.access.redhat.com. You do not require a quay.io login, or need to interact with the quay.io registry directly in any way to continue pulling Red Hat container images.
For more information, see Firewall changes for container image pulls 2024/2025.