Este contenido no está disponible en el idioma seleccionado.
Chapter 7. Architecture
7.1. Data Structures Within The Cache
Copiar enlaceEnlace copiado en el portapapeles!
A
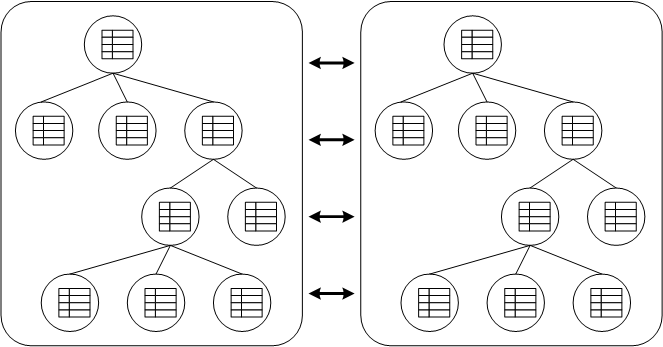
Cache consists of a collection of Node instances, organized in a tree structure. Each Node contains a Map which holds the data objects to be cached. It is important to note that the structure is a mathematical tree, and not a graph; each Node has one and only one parent, and the root node is denoted by the constant fully qualified name, Fqn.ROOT.
Figure 7.1. Data structured as a tree
Any modifications (see Chapter 2, User API) in one cache instance will be replicated to the other cache. Naturally, you can have more than 2 caches in a cluster. Depending on the transactional settings, this replication will occur either after each modification or at the end of a transaction, at commit time. When a new cache is created, it can optionally acquire the contents from one of the existing caches on start up.