Este contenido no está disponible en el idioma seleccionado.
4.2. Link Elements
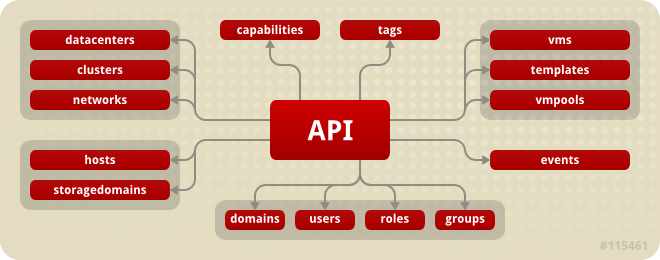
Access to the Entry Point provides
link elements and URIs for all of the resource collections the API exposes. Each collection uses a relation type to identify the URI a client needs.
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
capabilities | Supported capabilities of the Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization Manager. |
datacenters | Data centers. |
clusters | Host clusters. |
networks | Virtual networks. |
storagedomains | Storage domains. |
hosts | Hosts. |
vms | Virtual machines. |
disks | Virtual machine disks. |
templates | Templates. |
vmpools | Virtual machine pools. |
domains | Identity service domains. |
groups | Imported identity service groups. |
roles | Roles. |
users | Users. |
tags | Tags. |
events | Events. |
Figure 4.1. The relationship between the API entry point and the resource collections exposed by the API
Note
All URIs shown in example responses are illustrative. The format of all URIs returned by the server is opaque. Clients navigate to specific resources through the entry point URI and use the relationship types to access the URIs.
The server chooses to include absolute URIs or absolute paths [3] in the
link element's href attribute, so clients are required to handle either form.
The
link elements also contain a set of search URIs for certain collections. These URIs use URI templates [4] to integrate search queries. The purpose of the URI template is to accept a search expression using the natural HTTP pattern of a query parameter. The client does not require prior knowledge of the URI structure. Thus clients should treat these templates as being opaque and access them with a URI template library.
Each search query URI template is identified with a relation type using the convention
"collection/search".
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
datacenters/search | Query data centers. |
clusters/search | Query host clusters. |
storagedomains/search | Query storage domains. |
hosts/search | Query hosts. |
vms/search | Query virtual machines. |
disks/search | Query disks. |
templates/search | Query templates. |
vmpools/search | Query virtual machine pools. |
events/search | Query events. |
users/search | Query users. |
[3]
The RFC describing Uniform Resource Locator Generic Syntax provides a Collected ABNF for URI that explains the difference between these forms.
[4]
The Internet-Draft describing the format of a URI Template is available at http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-gregorio-uritemplate-03.