Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 3. JBoss Security Model
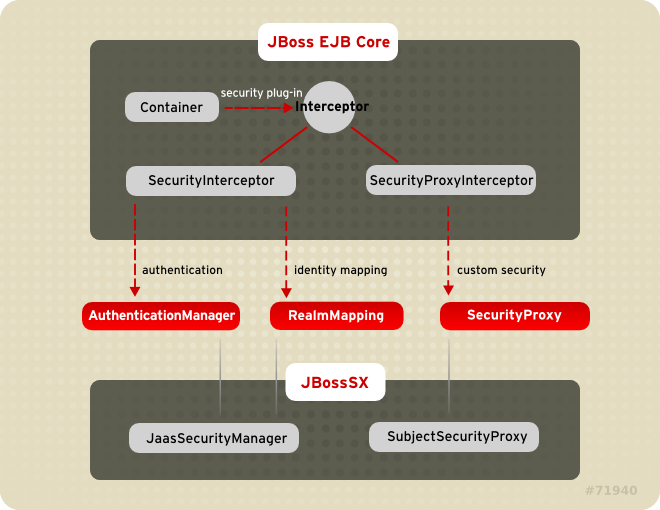
org.jboss.security.AuthenticationManagerorg.jboss.security.RealmMappingorg.jboss.security.SecurityProxyorg.jboss.security.AuthorizationManagerorg.jboss.security.AuditManagerorg.jboss.security.MappingManager
Figure 3.1. Security Model Interface Relationships to JBoss Enterprise Application Platform EJB Container Elements.
org.jboss.ejb.Container, org.jboss.SecurityInterceptor and org.jboss.SecurityProxyInterceptor. The other classes are interfaces and classes provided by the JBoss security subsystem.
org.jboss.security.AuthenticationManagerorg.jboss.security.AuthorizationManager
Security Interface Roles
- AuthenticationManager
- This interface is responsible for validating credentials associated with Principals . Principals are identities, such as user names, employee numbers, and social security numbers. Credentials are proof of the identity, such as passwords, session keys, and digital signatures. The
isValidmethod is invoked to determine whether a user identity and associated credentials as known in the operational environment are valid proof of the user's identity. - AuthorizationManager
- This interface is responsible for the access control mandated by the Java EE specifications. The implementation of this interface provides the ability to stack a set of Policy Providers useful for pluggable authorization.
- SecurityProxy
- This interface describes the requirements for a custom
SecurityProxyInterceptorplug-in. ASecurityProxyallows for the externalization of custom security checks on a per-method basis for both the EJB home and remote interface methods. - AuditManager
- This interface is responsible for providing an audit trail of security events.
- MappingManager
- This interface is responsible for providing mapping of Principal, Role, and Attributes. The implementation of AuthorizationManager may internally call the mapping manager to map roles before performing access control.
- SecurityDomain
- This is an extension of the
AuthenticationManager, RealmMapping , andSubjectSecurityManagerinterfaces.SecurityDomainis the recommended way to implement security in components, because of the advantages the JAAS Subject offers, and the increased support offered to ASP-style application and resource deployments. Ajava.security.KeyStore, and the Java Secure Socket Extension (JSSE)com.sun.net.ssl.KeyManagerFactoryandcom.sun.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactoryinterfaces are included in the class. - RealmMapping
- This interface is responsible for principal mapping and role mapping. The
getPrincipalmethod takes a user identity as known in the operational environment and returns the application domain identity. ThedoesUserHaveRolemethod validates that the user identity in the operation environment has been assigned the indicated role from the application domain.
AuthenticationManager , RealmMapping and SecurityProxy interfaces have no association to JAAS related classes. Although the JBossSX framework is heavily dependent on JAAS, the basic security interfaces required for implementation of the Java EE security model are not. The JBossSX framework is simply an implementation of the basic security plug-in interfaces that are based on JAAS.
Figure 3.2. JBossSX Framework Implementation Classes and the EAP EJB Container Layer.
3.1. Enabling Declarative Security Revisited
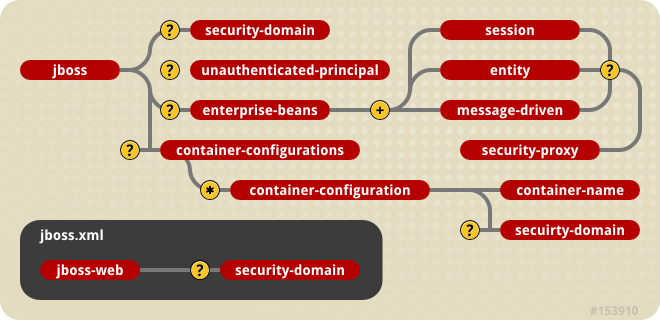
Figure 3.3. jboss.xml and jboss-web.xml Security Element Subsets.
AuthenticationManager and RealmMapping interfaces. When specified as a top-level element, it defines what security domain is specified for all EJBs in the deployment unit. This is the typical usage because mixing security managers within a deployment unit complicates inter-component operation and administration.
Principal object returned by the EJBContext.getUserPrincipal method when an unauthenticated user invokes an EJB. Note that this conveys no special permissions to an unauthenticated caller. Its primary purpose is to allow unsecured servlets and JSP pages to invoke unsecured EJBs and allow the target EJB to obtain a non-null Principal for the caller using the getUserPrincipal method. This is a J2EE specification requirement.
org.jboss.security.SecurityProxy interface. Alternatively, you can use a common interface that uses an object to implement methods in the home, remote, local home, or local interfaces of the EJB. If the given class does not implement the SecurityProxy interface, the instance must be wrapped in a SecurityProxy implementation that delegates the method invocations to the object. The org.jboss.security.SubjectSecurityProxy is an example SecurityProxy implementation used by the default JBossSX installation.
SecurityProxy in the context of a trivial stateless session bean. The custom SecurityProxy validates that no one invokes the bean's echo method with a four-letter word as its argument. This is a check that is not possible with role-based security; you cannot define a FourLetterEchoInvoker role because the security context is the method argument, not a property of the caller. The code for the custom SecurityProxy is given in Example 3.1, “Custom EchoSecurityProxy Implementation.”
Example 3.1. Custom EchoSecurityProxy Implementation.
EchoSecurityProxy checks that the method to be invoked on the bean instance corresponds to the echo(String) method loaded the init method. If there is a match, the method argument is obtained and its length compared against 4 or null. Either case results in a SecurityException being thrown.
jboss.xml descriptor that installs the EchoSecurityProxy as the custom proxy for the EchoBean is given in Example 3.2, “jboss.xml descriptor”.
Example 3.2. jboss.xml descriptor
EchoBean.echo method with the arguments Hello and Four as illustrated in this fragment:
Four is a four-letter word. Run the client as follows using Ant from the examples directory:
echo('Hello') method call succeeds as expected and the echo('Four') method call results in a rather messy looking exception, which is also expected. The above output has been truncated to fit in the book. The key part to the exception is that the SecurityException("No 4 letter words") generated by the EchoSecurityProxy was thrown to abort the attempted method invocation as desired.