Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 4. AMQ Streams Operators
AMQ Streams supports Kafka using Operators to deploy and manage the components and dependencies of Kafka to OpenShift.
Operators are a method of packaging, deploying, and managing an OpenShift application. AMQ Streams Operators extend OpenShift functionality, automating common and complex tasks related to a Kafka deployment. By implementing knowledge of Kafka operations in code, Kafka administration tasks are simplified and require less manual intervention.
Operators
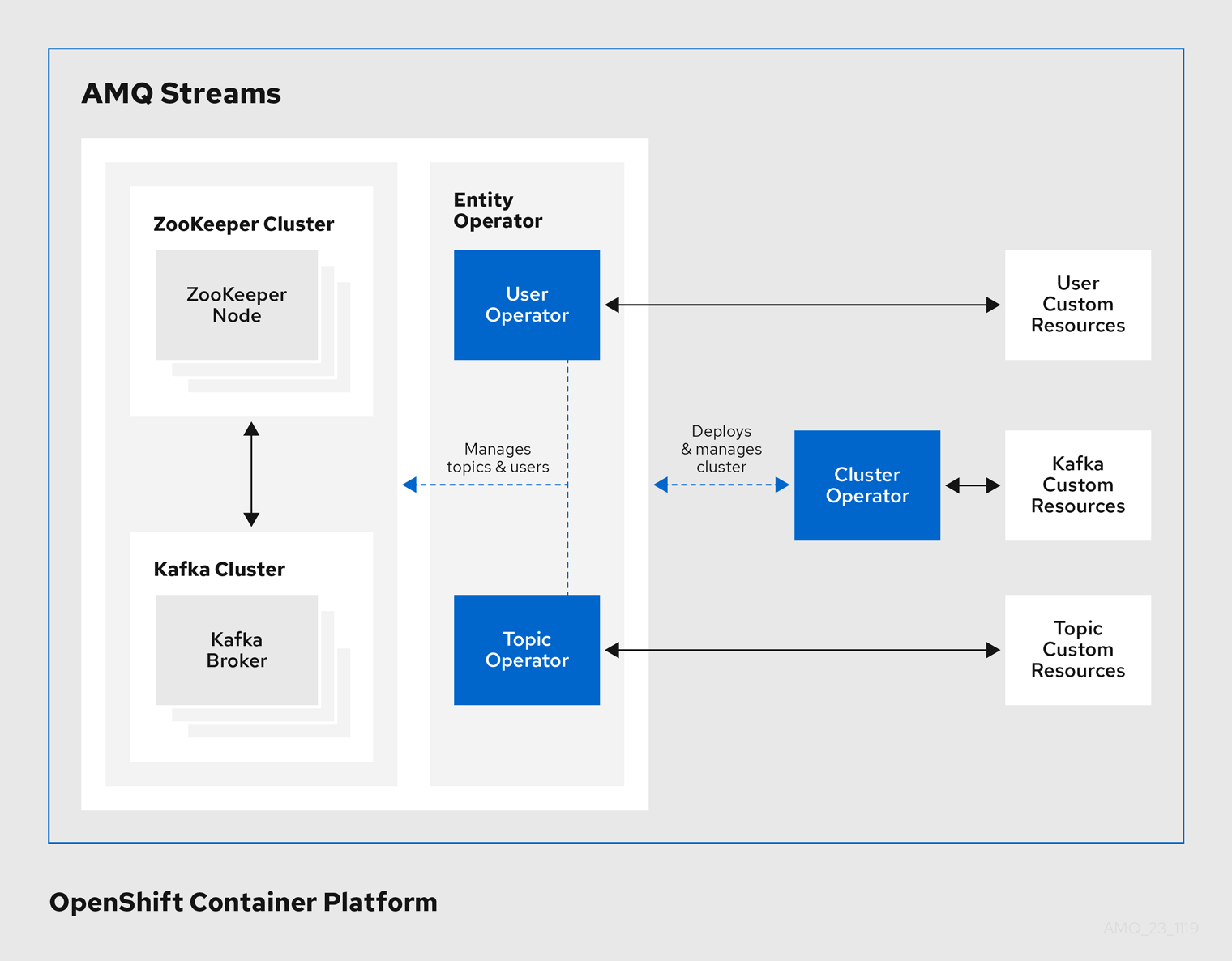
AMQ Streams provides Operators for managing a Kafka cluster running within an OpenShift cluster.
- Cluster Operator
- Deploys and manages Apache Kafka clusters, Kafka Connect, Kafka MirrorMaker, Kafka Bridge, Kafka Exporter, and the Entity Operator
- Entity Operator
- Comprises the Topic Operator and User Operator
- Topic Operator
- Manages Kafka topics
- User Operator
- Manages Kafka users
The Cluster Operator can deploy the Topic Operator and User Operator as part of an Entity Operator configuration at the same time as a Kafka cluster.
Operators within the AMQ Streams architecture
4.1. Cluster Operator
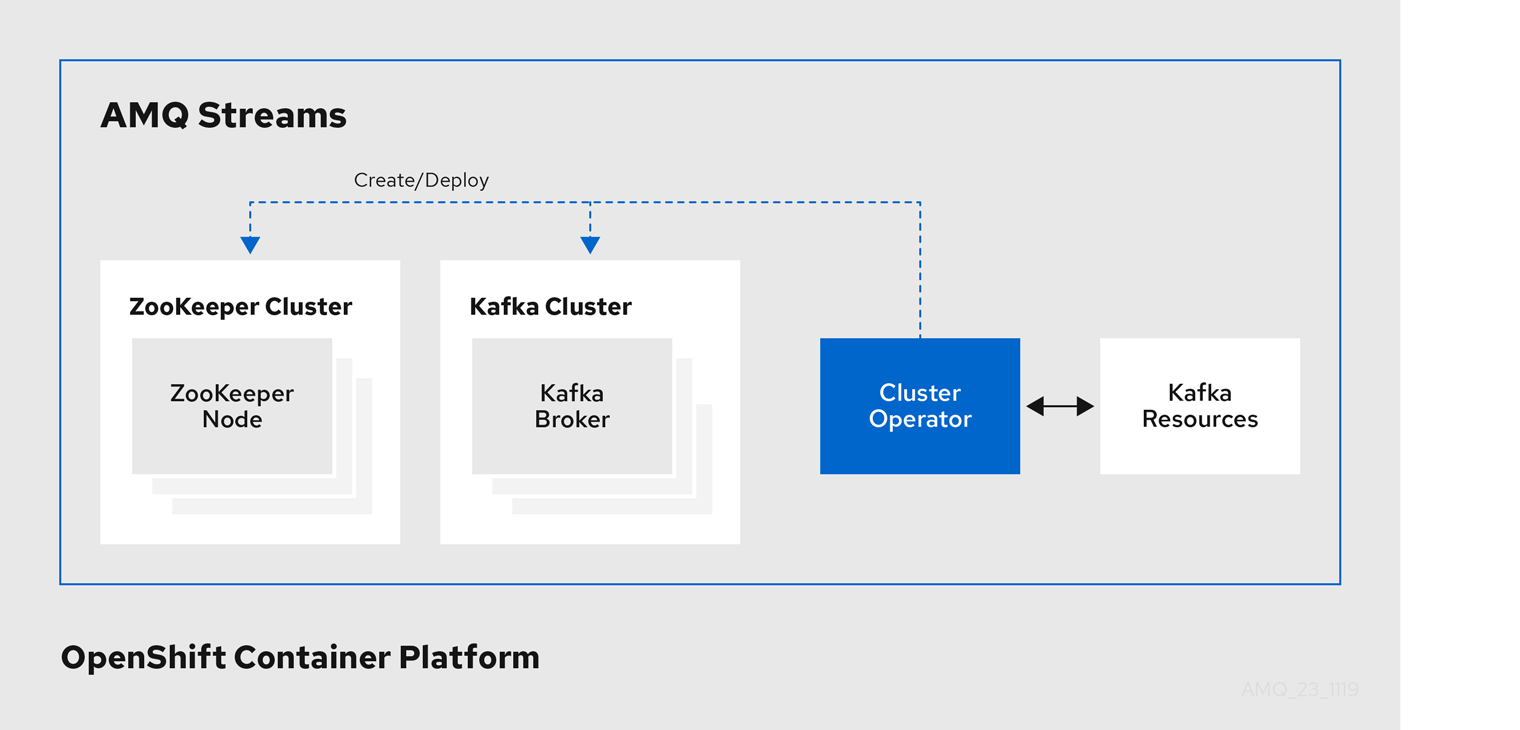
AMQ Streams uses the Cluster Operator to deploy and manage clusters for:
- Kafka (including ZooKeeper, Entity Operator, Kafka Exporter, and Cruise Control)
- Kafka Connect
- Kafka MirrorMaker
- Kafka Bridge
Custom resources are used to deploy the clusters.
For example, to deploy a Kafka cluster:
-
A
Kafkaresource with the cluster configuration is created within the OpenShift cluster. -
The Cluster Operator deploys a corresponding Kafka cluster, based on what is declared in the
Kafkaresource.
The Cluster Operator can also deploy (through configuration of the Kafka resource):
-
A Topic Operator to provide operator-style topic management through
KafkaTopiccustom resources -
A User Operator to provide operator-style user management through
KafkaUsercustom resources
The Topic Operator and User Operator function within the Entity Operator on deployment.
Example architecture for the Cluster Operator
4.2. Topic Operator
The Topic Operator provides a way of managing topics in a Kafka cluster through OpenShift resources.
Example architecture for the Topic Operator

The role of the Topic Operator is to keep a set of KafkaTopic OpenShift resources describing Kafka topics in-sync with corresponding Kafka topics.
Specifically, if a KafkaTopic is:
- Created, the Topic Operator creates the topic
- Deleted, the Topic Operator deletes the topic
- Changed, the Topic Operator updates the topic
Working in the other direction, if a topic is:
-
Created within the Kafka cluster, the Operator creates a
KafkaTopic -
Deleted from the Kafka cluster, the Operator deletes the
KafkaTopic -
Changed in the Kafka cluster, the Operator updates the
KafkaTopic
This allows you to declare a KafkaTopic as part of your application’s deployment and the Topic Operator will take care of creating the topic for you. Your application just needs to deal with producing or consuming from the necessary topics.
The Topic Operator maintains information about each topic in a topic store, which is continually synchronized with updates from Kafka topics or OpenShift KafkaTopic custom resources. Updates from operations applied to a local in-memory topic store are persisted to a backup topic store on disk. If a topic is reconfigured or reassigned to other brokers, the KafkaTopic will always be up to date.
4.3. User Operator
The User Operator manages Kafka users for a Kafka cluster by watching for KafkaUser resources that describe Kafka users, and ensuring that they are configured properly in the Kafka cluster.
For example, if a KafkaUser is:
- Created, the User Operator creates the user it describes
- Deleted, the User Operator deletes the user it describes
- Changed, the User Operator updates the user it describes
Unlike the Topic Operator, the User Operator does not sync any changes from the Kafka cluster with the OpenShift resources. Kafka topics can be created by applications directly in Kafka, but it is not expected that the users will be managed directly in the Kafka cluster in parallel with the User Operator.
The User Operator allows you to declare a KafkaUser resource as part of your application’s deployment. You can specify the authentication and authorization mechanism for the user. You can also configure user quotas that control usage of Kafka resources to ensure, for example, that a user does not monopolize access to a broker.
When the user is created, the user credentials are created in a Secret. Your application needs to use the user and its credentials for authentication and to produce or consume messages.
In addition to managing credentials for authentication, the User Operator also manages authorization rules by including a description of the user’s access rights in the KafkaUser declaration.
4.4. Feature gates in AMQ Streams Operators
You can enable and disable some features of operators using feature gates.
Feature gates are set in the operator configuration and have three stages of maturity: alpha, beta, or General Availability (GA).
For more information, see Feature gates.