Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 10. Self-tests
Red Hat Certificate System has the added functionality to allow self-tests of the server. The self-tests are run at start up and can also be run on demand. The startup self-tests run when the server starts and keep the server from starting if a critical self-test fails. The on-demand self-tests are run by clicking the self-tests button in the subsystem console.
10.1. Running self-tests
You can run the on-demand self-tests using the CLI on all CS subsystems (CA, OCSP, KRA, TKS, and TPS).
The console also provides on-demand self-tests services, however only for the CA, OCSP, KRA, and TKS subsystems - not for the TPS. As the pkiconsole tool is also being deprecated, we encourage using the CLI.
10.1.1. Running self-tests from the console
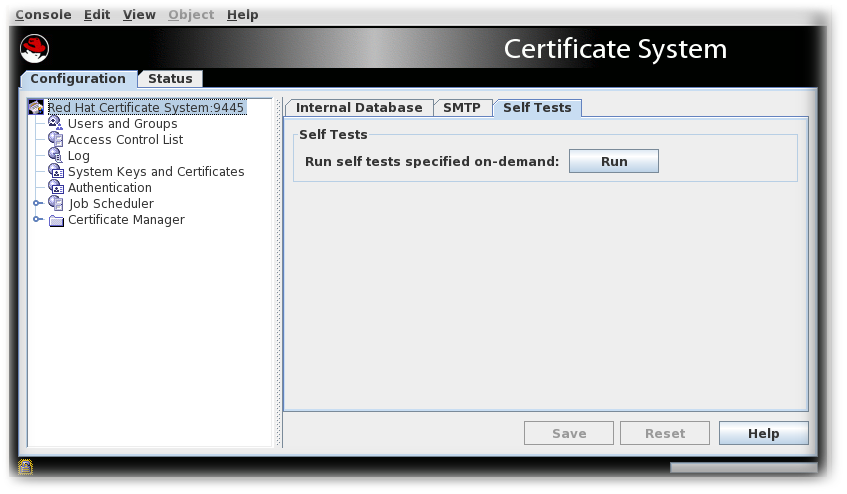
Log into the Console.
pkiconsole -d nssdb -n 'optional client cert nickname' https://server.example.com:admin_port/subsystem_type
# pkiconsole -d nssdb -n 'optional client cert nickname' https://server.example.com:admin_port/subsystem_typeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated and will be replaced by a new browser-based UI in a future major release. Althoughpkiconsolewill continue to be available until the replacement UI is released, we encourage using the command line equivalent ofpkiconsoleat this time, as the pki CLI will continue to be supported and improved upon even when the new browser-based UI becomes available in the future.Select the subsystem name at the top of the left pane.
- Select the Self Tests tab.
Click .
The self-tests that are configured for the subsystem will run. If any critical self-tests fail, the server will stop.
- The On-Demand Self Tests Results window appears, showing the logged events for this run of the self-tests.
10.1.2. Running self-tests using the CLI
The following command-line interfaces (CLIs) are available for self-tests for all subsystems. Where <subsystem> can be “ca”, “kra”, “ocsp”, “tks”, or “tps”
To view all the self-tests enabled for a subsystem:
pki -d nssdb -n 'cert-nickname' -p subsystem_port <subsystem>-selftest-find
# pki -d nssdb -n 'cert-nickname' -p subsystem_port <subsystem>-selftest-findCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To run on demand self-tests:
pki -d nssdb -n ‘cert-nickname’ -p subsystem_port <subsystem>-selftest-run
# pki -d nssdb -n ‘cert-nickname’ -p subsystem_port <subsystem>-selftest-runCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To show the details of a self-test:
pki -d nssdb -n ‘cert-nickname’ -p subsystem_port <subsystem>-selftest-show
# pki -d nssdb -n ‘cert-nickname’ -p subsystem_port <subsystem>-selftest-showCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2. Debugging self-tests failures
In the event of self-test failure, the Certificate System instance will stop completely and will not respond to any HTTP or HTTPS requests.
To diagnose a manually run self-test failure, refer to the various logs described in Section 10.2.1, “Self-Test logging”. Often other logs are useful as well, including debug logs. For more information on subsystem logs, refer to Chapter 12, Configuring subsystem logs. For more information on debug logs, refer to 2.3.14 Logs section under Chapter 2 Certificate System Architecture Overview in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition).
Common causes of self-test failures are services (such as LDAP) are down or unreachable, certificates are expired, or the system configuration is wrong. A precise cause of self-test failure is given in the logs.
After the cause of the self-test failure is identified and fixed, please restart the Certificate System server to resume normal operations:
systemctl restart pki-tomcatd-nuxwdog@instance_name.service
# systemctl restart pki-tomcatd-nuxwdog@instance_name.service10.2.1. Self-Test logging
A separate log, selftests.log, is added to the log directory that contains reports for both the start up self-tests and the on-demand self-tests. This log is configured by changing the setting for the log in the CS.cfg file. See the Modifying Self-Test Configuration in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition) for details.