Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 4. Tuna
You can use the Tuna tool to adjust scheduler tunables, tune thread priority, IRQ handlers, and isolate CPU cores and sockets. Tuna aims to reduce the complexity of performing tuning tasks.
After installing the tuna package, use the
tuna command without any arguments to start the Tuna graphical user interface (GUI). Use the tuna -h command to display available command-line interface (CLI) options. Note that the tuna(8) manual page distinguishes between action and modifier options.
The Tuna GUI and CLI provide equivalent functionality. The GUI displays the CPU topology on one screen to help you identify problems. The Tuna GUI also allows you to make changes to the running threads, and see the results of those changes immediately. In the CLI, Tuna accepts multiple command-line parameters and processes them sequentially. You can use such commands in application initialization scripts as configuration commands.
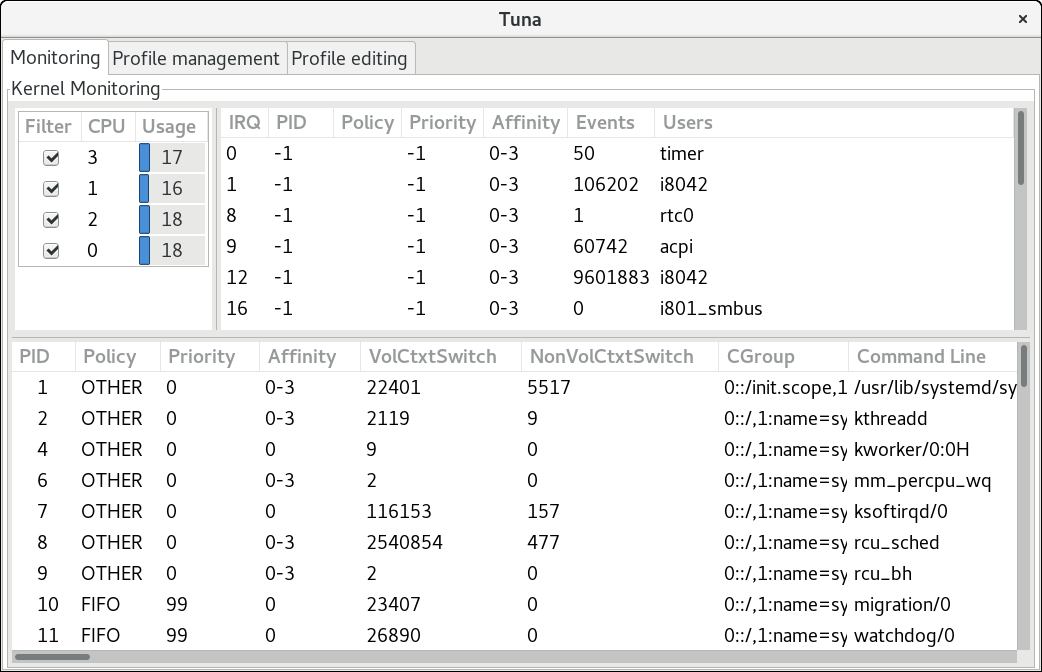
The Monitoring tab of the Tuna GUI
Important
Use the
tuna --save=filename command with a descriptive file name to save the current configuration. Note that this command does not save every option that Tuna can change, but saves the kernel thread changes only. Any processes that are not currently running when they are changed are not saved.
4.1. Reviewing the System with Tuna
Copier lienLien copié sur presse-papiers!
Before you make any changes, you can use Tuna to show you what is currently happening on the system.
To view the current policies and priorities, use the
tuna --show_threads command:
To show only a specific thread corresponding to a PID or matching a command name, add the
--threads option before --show_threads:
tuna --threads=pid_or_cmd_list --show_threads
# tuna --threads=pid_or_cmd_list --show_threads
The pid_or_cmd_list argument is a list of comma-separated PIDs or command-name patterns.
To view the current interrupt requests (IRQs) and their affinity, use the
tuna --show_irqs command:
To show only a specific interrupt request corresponding to an IRQ number or matching an IRQ user name, add the
--irqs option before --show_irqs:
tuna --irqs=number_or_user_list --show_irqs
# tuna --irqs=number_or_user_list --show_irqs
The number_or_user_list argument is a list of comma-separated IRQ numbers or user-name patterns.