Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 2. Optimizing systemd to shorten the boot time
As a system administrator, you can optimize performance of your system and shorten the boot time. You can review the services that systemd starts during boot and evaluate their necessity. Disabling certain services to start at boot can improve the boot time of your system.
2.1. Examining system boot performance
To examine system boot performance, you can use the systemd-analyze command. By using certain options, you can tune systemd to shorten the boot time.
Prerequisites
Optional: Before you examine
systemdto tune the boot time, list all enabled services:systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled
$ systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure
Choose the information you want to analyze:
Analyze the information about the time that the last successful boot took:
systemd-analyze
$ systemd-analyzeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Analyze the unit initialization time of each
systemdunit:systemd-analyze blame
$ systemd-analyze blameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output lists the units in descending order according to the time they took to initialize during the last successful boot.
Identify critical units that took the longest time to initialize at the last successful boot:
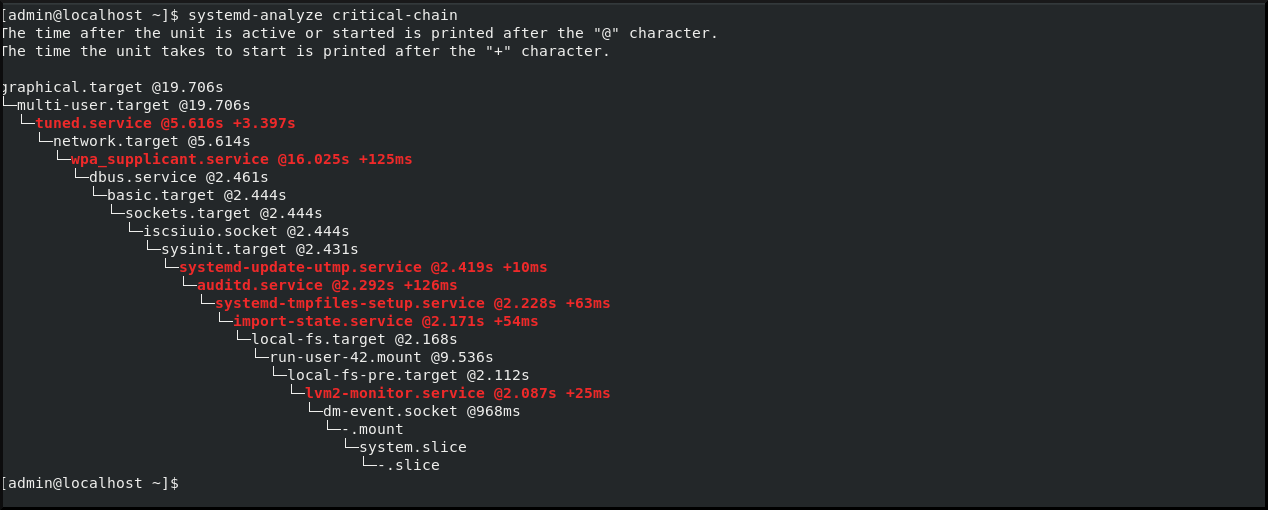
systemd-analyze critical-chain
$ systemd-analyze critical-chainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output highlights the units that critically slow down the boot with the red color.
Figure 2.1. The output of the systemd-analyze critical-chain command
2.2. A guide to selecting services that can be safely disabled
You can shorten the boot time of your system by disabling certain services that are enabled on boot by default.
List enabled services:
systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled
$ systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable a service:
systemctl disable <service_name>
# systemctl disable <service_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Certain services must stay enabled so that your operating system is safe and functions in the way you need.
Refer to the following table as a guide to selecting the services that you can safely disable. The table lists all services enabled by default on a minimal installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
| Service name | Can it be disabled? | More information |
|---|---|---|
| auditd.service | yes |
Disable |
| autovt@.service | no | This service runs only when it is really needed, so it does not need to be disabled. |
| crond.service | yes | Be aware that no items from crontab will run if you disable crond.service. |
| dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service | yes |
A symlink to |
| dbus-org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.service | yes |
A symlink to |
| dbus-org.freedesktop.nm-dispatcher.service | yes |
A symlink to |
| firewalld.service | yes |
Disable |
| getty@.service | no | This service runs only when it is really needed, so it does not need to be disabled. |
| import-state.service | yes |
Disable |
| irqbalance.service | yes |
Disable |
| kdump.service | yes |
Disable |
| loadmodules.service | yes |
This service is not started unless the |
| lvm2-monitor.service | yes |
Disable |
| microcode.service | no | Do not disable the service because it provides updates of the microcode software in the CPU. |
| NetworkManager-dispatcher.service | yes |
Disable |
| NetworkManager-wait-online.service | yes |
Disable |
| NetworkManager.service | yes |
Disable |
| nis-domainname.service | yes |
Disable |
| rhsmcertd.service | no | |
| rngd.service | yes |
Disable |
| rsyslog.service | yes |
Disable |
| selinux-autorelabel-mark.service | yes |
Disable |
| sshd.service | yes |
Disable |
| sssd.service | yes |
Disable |
| syslog.service | yes |
An alias for |
| tuned.service | yes |
Disable |
| lvm2-lvmpolld.socket | yes |
Disable |
| dnf-makecache.timer | yes |
Disable |
| unbound-anchor.timer | yes |
Disable |
To find more information about a service, use one of the following commands:
systemctl cat <service_name>
$ systemctl cat <service_name>systemctl help <service_name>
$ systemctl help <service_name>
The systemctl cat command provides the content of the respective /usr/lib/systemd/system/<service> service file, as well as all applicable overrides. The applicable overrides include unit file overrides from the /etc/systemd/system/<service> file or drop-in files from a corresponding unit.type.d directory.