Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 3. Using system-wide cryptographic policies
The system-wide cryptographic policies is a system component that configures the core cryptographic subsystems, covering the TLS, IPsec, SSH, DNSSec, and Kerberos protocols. It provides a small set of policies, which the administrator can select.
3.1. System-wide cryptographic policies
The RHEL system-wide cryptographic policies configure core subsystems, such as TLS and SSH, which ensures that applications reject weak algorithms by default. The four predefined policies are DEFAULT, LEGACY, FUTURE, and FIPS.
When a system-wide policy is set up, applications in RHEL follow it and deny using algorithms and protocols that do not meet the policy, unless you explicitly request the application to do so. That is, the policy applies to the default behavior of applications when running with the system-provided configuration but you can override it if required.
3.1.1. Predefined cryptographic policies
RHEL 9 contains the following predefined policies:
DEFAULT- The default system-wide cryptographic policy level offers secure settings for current threat models. It allows the TLS 1.2 and 1.3 protocols, as well as the IKEv2 and SSH2 protocols. The RSA keys and Diffie-Hellman parameters are accepted if they are at least 2048 bits long. TLS ciphers that use the RSA key exchange are rejected.
LEGACY- Ensures maximum compatibility with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and earlier; it is less secure due to an increased attack surface. SHA-1 is allowed to be used as TLS hash, signature, and algorithm. CBC-mode ciphers are allowed to be used with SSH. Applications using GnuTLS allow certificates signed with SHA-1. It allows the TLS 1.2 and 1.3 protocols, as well as the IKEv2 and SSH2 protocols. The RSA keys and Diffie-Hellman parameters are accepted if they are at least 2048 bits long.
FUTUREA stricter forward-looking security level intended for testing a possible future policy. This policy does not allow the use of SHA-1 in DNSSec or as an HMAC. SHA2-224 and SHA3-224 hashes are rejected. 128-bit ciphers are disabled. CBC-mode ciphers are disabled except in Kerberos. It allows the TLS 1.2 and 1.3 protocols, as well as the IKEv2 and SSH2 protocols. The RSA keys and Diffie-Hellman parameters are accepted if they are at least 3072 bits long. If your system communicates on the public internet, you might face interoperability problems.
ImportantBecause a cryptographic key used by a certificate on the Customer Portal API does not meet the requirements by the
FUTUREsystem-wide cryptographic policy, theredhat-support-toolutility does not work with this policy level at the moment.To work around this problem, use the
DEFAULTcryptographic policy while connecting to the Customer Portal API.FIPSConforms with the FIPS 140 requirements. The
fips-mode-setuptool, which switches the RHEL system into FIPS mode, uses this policy internally. Switching to theFIPSpolicy does not guarantee compliance with the FIPS 140 standard. You also must re-generate all cryptographic keys after you set the system to FIPS mode. This is not possible in many scenarios.RHEL also provides the
FIPS:OSPPsystem-wide subpolicy, which contains further restrictions for cryptographic algorithms required by the Common Criteria (CC) certification. The system becomes less interoperable after you set this subpolicy. For example, you cannot use RSA and DH keys shorter than 3072 bits, additional SSH algorithms, and several TLS groups. SettingFIPS:OSPPalso prevents connecting to Red Hat Content Delivery Network (CDN) structure. Furthermore, you cannot integrate Active Directory (AD) into the IdM deployments that useFIPS:OSPP, communication between RHEL hosts usingFIPS:OSPPand AD domains might not work, or some AD accounts might not be able to authenticate.NoteYour system is not CC-compliant after you set the
FIPS:OSPPcryptographic subpolicy. The only correct way to make your RHEL system compliant with the CC standard is by following the guidance provided in thecc-configpackage. See Common Criteria section on the Product compliance Red Hat Customer Portal page for a list of certified RHEL versions, validation reports, and links to CC guides.
Red Hat continuously adjusts all policy levels so that all libraries provide secure defaults, except when using the LEGACY policy. Even though the LEGACY profile does not provide secure defaults, it does not include any algorithms that are easily exploitable. As such, the set of enabled algorithms or acceptable key sizes in any provided policy may change during the lifetime of Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Such changes reflect new security standards and new security research. If you must ensure interoperability with a specific system for the whole lifetime of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, opt out from the system-wide cryptographic policies for components that interact with that system or re-enable specific algorithms by using custom cryptographic policies.
The specific algorithms and ciphers described as allowed in the policy levels are available only if an application supports them:
LEGACY | DEFAULT | FIPS | FUTURE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IKEv1 | no | no | no | no |
| 3DES | no | no | no | no |
| RC4 | no | no | no | no |
| DH | min. 2048-bit | min. 2048-bit | min. 2048-bit | min. 3072-bit |
| RSA | min. 2048-bit | min. 2048-bit | min. 2048-bit | min. 3072-bit |
| DSA | no | no | no | no |
| TLS v1.1 and older | no | no | no | no |
| TLS v1.2 and newer | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| SHA-1 in digital signatures and certificates | yes | no | no | no |
| CBC mode ciphers | yes | no[a] | no[b] | no[c] |
| Symmetric ciphers with keys < 256 bits | yes | yes | yes | no |
[a]
CBC ciphers are disabled for SSH
[b]
CBC ciphers are disabled for all protocols except Kerberos
[c]
CBC ciphers are disabled for all protocols except Kerberos
| ||||
You can find further details about cryptographic policies and covered applications in the crypto-policies(7) man page on your system.
3.1.2. Post-quantum cryptography
RHEL 9.7 crypto-policies introduced the new PQ subpolicy. You can apply the PQ subpolicy on all cryptographic policies: LEGACY, DEFAULT, FUTURE, and FIPS. For example, after you use the update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:PQ command, hybrid Module-Lattice-Based Key-Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM) and pure Module-Lattice-Based Digital Signature Standard (ML-DSA) post-quantum cryptographic algorithms are enabled on top of the DEFAULT cryptographic policy with the highest priorities.
The purpose of PQC is to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of digital communication and stored data against future attacks that use cryptographically relevant quantum computers (CRQCs).
While CRQCs are not currently operational, continued advances in quantum computing might render classic cryptographic algorithms such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography computationally feasible to break. PQC algorithms mitigate this anticipated long-term security risk by providing quantum-resistant equivalents. You can prevent the current risk of "harvest now, decrypt later" attacks by configuring RHEL with PQC.
3.2. Changing the system-wide cryptographic policy
You can change the system-wide cryptographic policy on your system by using the update-crypto-policies tool and restarting your system.
Prerequisites
- You have root privileges on the system.
Procedure
Optional: Display the current cryptographic policy:
update-crypto-policies --show DEFAULT
$ update-crypto-policies --show DEFAULTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the new cryptographic policy:
update-crypto-policies --set <POLICY> <POLICY>
# update-crypto-policies --set <POLICY> <POLICY>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<POLICY>with the policy or subpolicy you want to set, for exampleFUTURE,LEGACYorFIPS:OSPP.Restart the system:
reboot
# rebootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Display the current cryptographic policy:
update-crypto-policies --show <POLICY>
$ update-crypto-policies --show <POLICY>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.3. Switching the system-wide cryptographic policy to mode compatible with earlier releases
The default system-wide cryptographic policy in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 does not allow communication using older, insecure protocols. For environments that require to be compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and in some cases also with earlier releases, the less secure LEGACY policy level is available.
Switching to the LEGACY policy level results in a less secure system and applications.
Procedure
To switch the system-wide cryptographic policy to the
LEGACYlevel, enter the following command asroot:update-crypto-policies --set LEGACY Setting system policy to LEGACY
# update-crypto-policies --set LEGACY Setting system policy to LEGACYCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.4. Re-enabling SHA-1
The use of the SHA-1 algorithm for creating and verifying signatures is restricted in the DEFAULT cryptographic policy. If your scenario requires the use of SHA-1 for verifying existing or third-party cryptographic signatures, you can enable it by applying the SHA1 subpolicy, which RHEL 9 provides by default. Note that it weakens the security of the system.
Prerequisites
-
The system uses the
DEFAULTsystem-wide cryptographic policy.
Procedure
Apply the
SHA1subpolicy to theDEFAULTcryptographic policy:update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:SHA1 Setting system policy to DEFAULT:SHA1 Note: System-wide crypto policies are applied on application start-up. It is recommended to restart the system for the change of policies to fully take place.
# update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:SHA1 Setting system policy to DEFAULT:SHA1 Note: System-wide crypto policies are applied on application start-up. It is recommended to restart the system for the change of policies to fully take place.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the system:
reboot
# rebootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Display the current cryptographic policy:
update-crypto-policies --show DEFAULT:SHA1
# update-crypto-policies --show DEFAULT:SHA1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Switching to the LEGACY cryptographic policy by using the update-crypto-policies --set LEGACY command also enables SHA-1 for signatures. However, the LEGACY cryptographic policy makes your system much more vulnerable by also enabling other weak cryptographic algorithms. Use this workaround only for scenarios that require the enablement of other legacy cryptographic algorithms than SHA-1 signatures.
3.5. Setting up system-wide cryptographic policies in the web console
You can set one of system-wide cryptographic policies and subpolicies directly in the RHEL web console interface. Besides the four predefined system-wide cryptographic policies, you can also apply the following combinations of policies and subpolicies through the graphical interface now:
DEFAULT:SHA1-
The
DEFAULTpolicy with theSHA-1algorithm enabled. LEGACY:AD-SUPPORT-
The
LEGACYpolicy with less secure settings that improve interoperability for Active Directory services. FIPS:OSPP-
The
FIPSpolicy with further restrictions required by the Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation standard.
Because the FIPS:OSPP system-wide subpolicy contains further restrictions for cryptographic algorithms required by the Common Criteria (CC) certification, the system is less interoperable after you set it. For example, you cannot use RSA and DH keys shorter than 3072 bits, additional SSH algorithms, and several TLS groups. Setting FIPS:OSPP also prevents connecting to Red Hat Content Delivery Network (CDN) structure. Furthermore, you cannot integrate Active Directory (AD) into the IdM deployments that use FIPS:OSPP, communication between RHEL hosts using FIPS:OSPP and AD domains might not work, or some AD accounts might not be able to authenticate.
Note that your system is not CC-compliant after you set the FIPS:OSPP cryptographic subpolicy. The only correct way to make your RHEL system compliant with the CC standard is by following the guidance provided in the cc-config package. See the Common Criteria section on the Product compliance Red Hat Customer Portal page for a list of certified RHEL versions, validation reports, and links to CC guides hosted at the National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP) website.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the RHEL 9 web console.
- You have enabled the cockpit service.
Your user account is allowed to log in to the web console.
For instructions, see Installing and enabling the web console.
-
You have
rootprivileges or permissions to enter administrative commands withsudo.
Procedure
Log in to the RHEL 9 web console.
For details, see Logging in to the web console.
In the Configuration card of the Overview page, click your current policy value next to Crypto policy.
In the Change crypto policy dialog window, click on the policy you want to start using on your system.
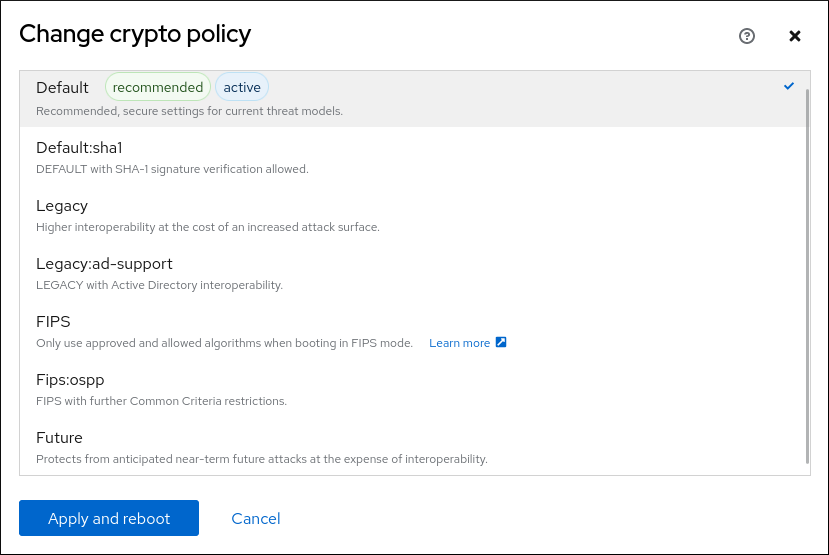
- Click the button.
Verification
After the restart, log back in to web console, and check that the Crypto policy value corresponds to the one you selected.
Alternatively, you can enter the
update-crypto-policies --showcommand to display the current system-wide cryptographic policy in your terminal.
3.6. Enabling post-quantum algorithms system-wide
You can enable post-quantum cryptography (PQC) system-wide by applying the PQ subpolicy.
Prerequisites
- You have root privileges on the system.
Procedure
Enable the
TEST-PQcryptographic subpolicy on top of your current system-wide policy, for example:update-crypto-policies --show DEFAULT update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:PQ
$ update-crypto-policies --show DEFAULT # update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:PQCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To make your cryptographic settings effective for already running services and applications, restart the system:
reboot
# rebootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check that the
/etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.polfile contains PQC, for example:cat /etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.pol | grep MLKEM group = MLKEM768-X25519 P256-MLKEM768 P384-MLKEM1024 MLKEM1024-X448 X25519 SECP256R1 X448 SECP521R1 SECP384R1 FFDHE-2048 FFDHE-3072 FFDHE-4096 FFDHE-6144 FFDHE-8192
$ cat /etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.pol | grep MLKEM group = MLKEM768-X25519 P256-MLKEM768 P384-MLKEM1024 MLKEM1024-X448 X25519 SECP256R1 X448 SECP521R1 SECP384R1 FFDHE-2048 FFDHE-3072 FFDHE-4096 FFDHE-6144 FFDHE-8192Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.7. Excluding an application from following system-wide cryptographic policies
You can customize cryptographic settings used by your application preferably by configuring supported cipher suites and protocols directly in the application.
You can also remove a symlink related to your application from the /etc/crypto-policies/back-ends directory and replace it with your customized cryptographic settings. This configuration prevents the use of system-wide cryptographic policies for applications that use the excluded back end. Furthermore, this modification is not supported by Red Hat.
3.7.1. Examples of opting out of the system-wide cryptographic policies
wget
To customize cryptographic settings used by the wget network downloader, use --secure-protocol and --ciphers options. For example:
wget --secure-protocol=TLSv1_1 --ciphers="SECURE128" https://example.com
$ wget --secure-protocol=TLSv1_1 --ciphers="SECURE128" https://example.com
See the HTTPS (SSL/TLS) Options section of the wget(1) man page for more information.
curl
To specify ciphers used by the curl tool, use the --ciphers option and provide a colon-separated list of ciphers as a value. For example:
curl https://example.com --ciphers '@SECLEVEL=0:DES-CBC3-SHA:RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA'
$ curl https://example.com --ciphers '@SECLEVEL=0:DES-CBC3-SHA:RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA'
See the curl(1) man page for more information.
Firefox
Even though you cannot opt out of system-wide cryptographic policies in the Firefox web browser, you can further restrict supported ciphers and TLS versions in Firefox’s Configuration Editor. Type about:config in the address bar and change the value of the security.tls.version.min option as required. Setting security.tls.version.min to 1 allows TLS 1.0 as the minimum required, security.tls.version.min 2 enables TLS 1.1, and so on.
OpenSSH
To opt out of the system-wide cryptographic policies for your OpenSSH server, specify the cryptographic policy in a drop-in configuration file located in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/ directory, with a two-digit number prefix smaller than 50, so that it lexicographically precedes the 50-redhat.conf file, and with a .conf suffix, for example, 49-crypto-policy-override.conf.
See the sshd_config(5) man page for more information.
To opt out of system-wide cryptographic policies for your OpenSSH client, perform one of the following tasks:
-
For a given user, override the global
ssh_configwith a user-specific configuration in the~/.ssh/configfile. -
For the entire system, specify the cryptographic policy in a drop-in configuration file located in the
/etc/ssh/ssh_config.d/directory, with a two-digit number prefix smaller than 50, so that it lexicographically precedes the50-redhat.conffile, and with a.confsuffix, for example,49-crypto-policy-override.conf.
See the ssh_config(5) man page for more information.
Libreswan
See the Enabling legacy ciphers and algorithms in Libreswan section in the Securing networks document for detailed information.
3.8. Customizing system-wide cryptographic policies with subpolicies
Use this procedure to adjust the set of enabled cryptographic algorithms or protocols.
You can either apply custom subpolicies on top of an existing system-wide cryptographic policy or define such a policy from scratch.
The concept of scoped policies allows enabling different sets of algorithms for different back ends. You can limit each configuration directive to specific protocols, libraries, or services.
Furthermore, directives can use asterisks for specifying multiple values using wildcards.
The /etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.pol file lists all settings in the currently applied system-wide cryptographic policy after wildcard expansion. To make your cryptographic policy more strict, consider using values listed in the /usr/share/crypto-policies/policies/FUTURE.pol file.
You can find example subpolicies in the /usr/share/crypto-policies/policies/modules/ directory. The subpolicy files in this directory contain also descriptions in lines that are commented out.
Procedure
Checkout to the
/etc/crypto-policies/policies/modules/directory:cd /etc/crypto-policies/policies/modules/
# cd /etc/crypto-policies/policies/modules/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create subpolicies for your adjustments, for example:
touch MYCRYPTO-1.pmod touch SCOPES-AND-WILDCARDS.pmod
# touch MYCRYPTO-1.pmod # touch SCOPES-AND-WILDCARDS.pmodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUse upper-case letters in file names of policy modules.
Open the policy modules in a text editor of your choice and insert options that modify the system-wide cryptographic policy, for example:
vi MYCRYPTO-1.pmod
# vi MYCRYPTO-1.pmodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow min_rsa_size = 3072 hash = SHA2-384 SHA2-512 SHA3-384 SHA3-512
min_rsa_size = 3072 hash = SHA2-384 SHA2-512 SHA3-384 SHA3-512Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow vi SCOPES-AND-WILDCARDS.pmod
# vi SCOPES-AND-WILDCARDS.pmodCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the changes in the module files.
Apply your policy adjustments to the
DEFAULTsystem-wide cryptographic policy level:update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:MYCRYPTO-1:SCOPES-AND-WILDCARDS
# update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:MYCRYPTO-1:SCOPES-AND-WILDCARDSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To make your cryptographic settings effective for already running services and applications, restart the system:
reboot
# rebootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Check that the
/etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.polfile contains your changes, for example:cat /etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.pol | grep rsa_size min_rsa_size = 3072
$ cat /etc/crypto-policies/state/CURRENT.pol | grep rsa_size min_rsa_size = 3072Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.9. Creating and setting a custom system-wide cryptographic policy
For specific scenarios, you can customize the system-wide cryptographic policy by creating and using a complete policy file.
Procedure
Create a policy file for your customizations:
cd /etc/crypto-policies/policies/ touch MYPOLICY.pol
# cd /etc/crypto-policies/policies/ # touch MYPOLICY.polCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, start by copying one of the four predefined policy levels:
cp /usr/share/crypto-policies/policies/DEFAULT.pol /etc/crypto-policies/policies/MYPOLICY.pol
# cp /usr/share/crypto-policies/policies/DEFAULT.pol /etc/crypto-policies/policies/MYPOLICY.polCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the file with your custom cryptographic policy in a text editor of your choice to fit your requirements, for example:
vi /etc/crypto-policies/policies/MYPOLICY.pol
# vi /etc/crypto-policies/policies/MYPOLICY.polCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Switch the system-wide cryptographic policy to your custom level:
update-crypto-policies --set MYPOLICY
# update-crypto-policies --set MYPOLICYCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To make your cryptographic settings effective for already running services and applications, restart the system:
reboot
# rebootCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.10. Enhancing security with the FUTURE cryptographic policy using the crypto_policies RHEL system role
You can use the crypto_policies RHEL system role to configure the FUTURE cryptographic policy on your managed nodes.
The FUTURE policy helps to achieve, for example:
- Future-proofing against emerging threats: anticipates advancements in computational power.
- Enhanced security: stronger encryption standards require longer key lengths and more secure algorithms.
- Compliance with high-security standards: for example in healthcare, telco, and finance the data sensitivity is high, and availability of strong cryptography is critical.
Typically, FUTURE is suitable for environments handling highly sensitive data, preparing for future regulations, or adopting long-term security strategies.
Legacy systems or software does not have to support the more modern and stricter algorithms and protocols enforced by the FUTURE policy. For example, older systems might not support TLS 1.3 or larger key sizes. This could lead to compatibility problems.
Also, using strong algorithms usually increases the computational workload, which could negatively affect your system performance.
Because the FIPS:OSPP system-wide subpolicy contains further restrictions for cryptographic algorithms required by the Common Criteria (CC) certification, the system is less interoperable after you set it. For example, you cannot use RSA and DH keys shorter than 3072 bits, additional SSH algorithms, and several TLS groups. Setting FIPS:OSPP also prevents connecting to Red Hat Content Delivery Network (CDN) structure. Furthermore, you cannot integrate Active Directory (AD) into the IdM deployments that use FIPS:OSPP, communication between RHEL hosts using FIPS:OSPP and AD domains might not work, or some AD accounts might not be able to authenticate.
Note that your system is not CC-compliant after you set the FIPS:OSPP cryptographic subpolicy. The only correct way to make your RHEL system compliant with the CC standard is by following the guidance provided in the cc-config package. See the Common Criteria section on the Product compliance Red Hat Customer Portal page for a list of certified RHEL versions, validation reports, and links to CC guides hosted at the National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP) website.
Prerequisites
- You have prepared the control node and the managed nodes.
-
The account you use to connect to the managed nodes has
sudopermissions for these nodes.
Procedure
Create a playbook file, for example,
~/playbook.yml, with the following content:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The settings specified in the example playbook include the following:
crypto_policies_policy: FUTURE-
Configures the required cryptographic policy (
FUTURE) on the managed node. It can be either the base policy or a base policy with some sub-policies. The specified base policy and sub-policies have to be available on the managed node. The default value isnull. It means that the configuration is not changed and thecrypto_policiesRHEL system role will only collect the Ansible facts. crypto_policies_reboot_ok: true-
Causes the system to reboot after the cryptographic policy change to make sure all of the services and applications will read the new configuration files. The default value is
false.
For details about all variables used in the playbook, see the
/usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.crypto_policies/README.mdfile on the control node.Validate the playbook syntax:
ansible-playbook --syntax-check ~/playbook.yml
$ ansible-playbook --syntax-check ~/playbook.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that this command only validates the syntax and does not protect against a wrong but valid configuration.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook ~/playbook.yml
$ ansible-playbook ~/playbook.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
On the control node, create another playbook named, for example,
verify_playbook.yml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The settings specified in the example playbook include the following:
crypto_policies_active-
An exported Ansible fact that contains the currently active policy name in the format as accepted by the
crypto_policies_policyvariable.
Validate the playbook syntax:
ansible-playbook --syntax-check ~/verify_playbook.yml
$ ansible-playbook --syntax-check ~/verify_playbook.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook ~/verify_playbook.yml TASK [debug] ************************** ok: [host] => { "crypto_policies_active": "FUTURE" }$ ansible-playbook ~/verify_playbook.yml TASK [debug] ************************** ok: [host] => { "crypto_policies_active": "FUTURE" }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
crypto_policies_activevariable shows the active policy on the managed node.