Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
Chapter 8. Configuring a single node RHHI for Virtualization deployment
8.1. Configuring Red Hat Gluster Storage on a single node
Ensure that disks specified as part of this deployment process do not have any partitions or labels.
Log into the Web Console
Browse to the Web Console management interface of the first hyperconverged host, for example, https://node1.example.com:9090/, and log in with the credentials you created in the previous section.
Start the deployment wizard
Click Virtualization
Hosted Engine and click Start underneath Hyperconverged. 
The Gluster Configuration window opens.
Click the Run Gluster Wizard for Single Node button.
The Gluster Deployment window opens in single node mode.
Specify host
If your hosts use IPv6 networking, check the
Select if hosts are using IPv6checkbox. Your host must use FQDNs if you select this option; IPv6 addresses are not supported.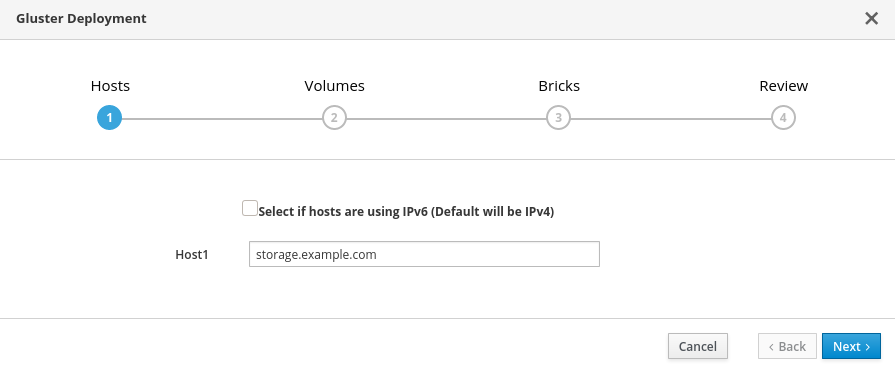
Specify volumes
Specify the volumes to create.
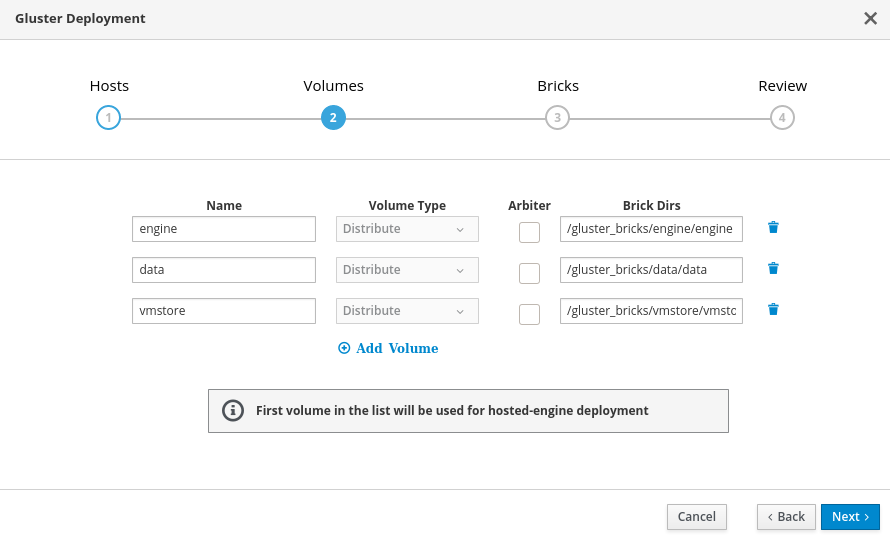
- Name
- Specify the name of the volume to be created.
- Volume Type
- Only distributed volumes are supported for single node deployments.
- Brick Dirs
-
The directory that contains this volume’s bricks. Use a brick path of the format
gluster_bricks/<volname>/<volname>.
The default values are correct for most installations.
If you need more volumes, click Add Volumes to add another row and enter your extra volume details.
Specify bricks
Enter details of the bricks to be created.
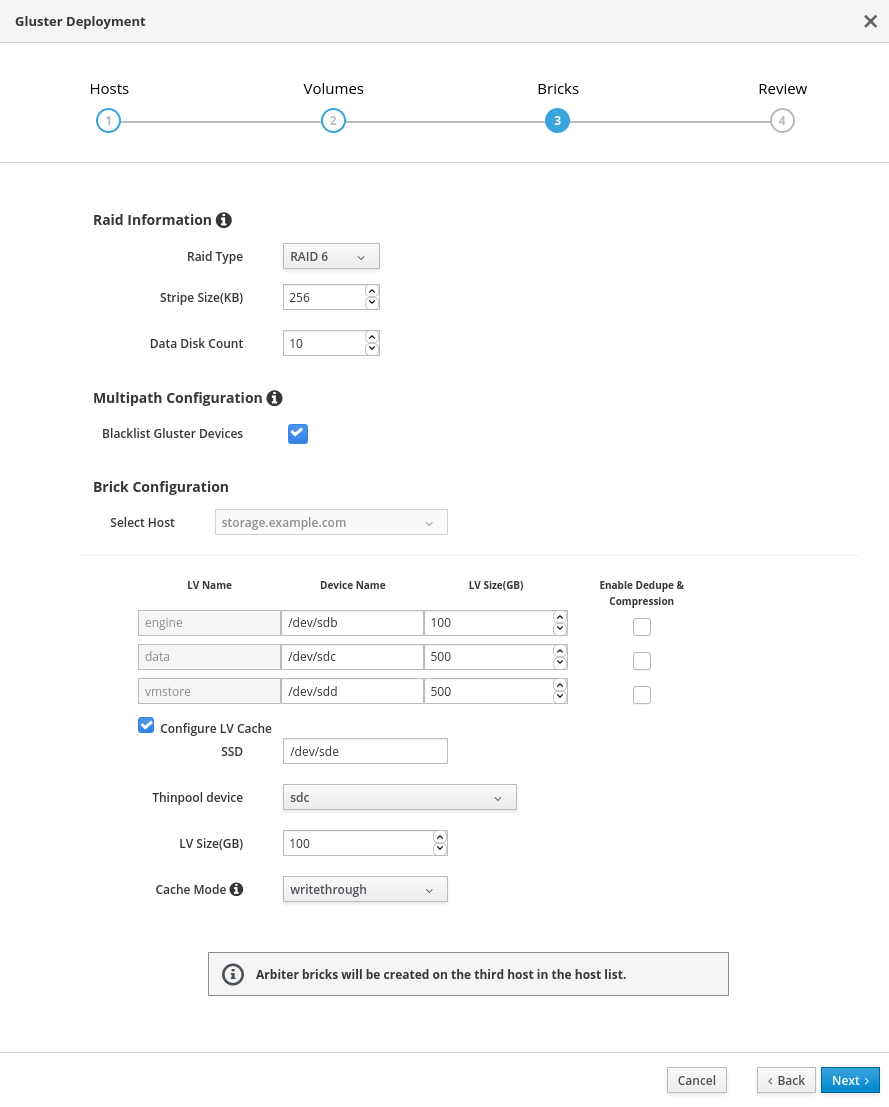
- RAID Type
- Specify the RAID configuration of the host. Supported values are raid5, raid6, and jbod. Setting this option ensures that your storage is correctly tuned for your RAID configuration.
- Stripe Size
- Specify the RAID stripe size in KB. This can be ignored for jbod configurations.
- Data Disk Count
- Specify the number of data disks in your host’s RAID volume. This can be ignored for jbod configurations.
- Blacklist Gluster Devices
-
Prevents the disk that is specified as a Gluster brick from using a multipath device name. If you want to use a multipath device name, uncheck this checkbox and use the
/dev/mapper/<WWID>format to specify your device in theDevicefield. - Select Host
- This option is not valid for single node deployments.
- LV Name
- The name of the logical volume to be created. This is pre-filled with the name that you specified on the previous page of the wizard.
- Device Name
-
Specify the raw device you want to use in the format
/dev/sdc. Use/dev/mapper/<WWID>format for multipath devices. Use/dev/mapper/luks_<name>format for devices using Network-Bound Disk Encryption. - LV Size
- Specify the size of the logical volume to create in GB. Do not enter units, only the number. This number should be the same for all bricks in a replicated set. Arbiter bricks can be smaller than other bricks in their replication set.
- Enable Dedupe & Compression
Specify whether to provision the volume using VDO for compression and deduplication at deployment time. The logical size of the brick is expanded to 10 times the size of physical volume as part of VDO space savings.
NoteEnsure to enable
Dedupe & Compressionon all the bricks which are part of the volume.- Configure LV Cache
Optionally, check this checkbox to configure a small, fast SSD device as a logical volume cache for a larger, slower logical volume.
- Add the device path to the SSD field.
- Specify the Thinpool device to attach the cache device to.
- Add the size to the LV Size (GB) field.
- Set the Cache Mode used by the device.
WarningTo avoid data loss when using write-back mode, Red Hat recommends using two separate SSD/NVMe devices. Configuring the two devices in a RAID-1 configuration (via software or hardware), significantly reduces the potential of data loss from lost writes.
For further information about lvmcache configuration, see LVM cache logical volumes in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 documentation.
Review and edit configuration
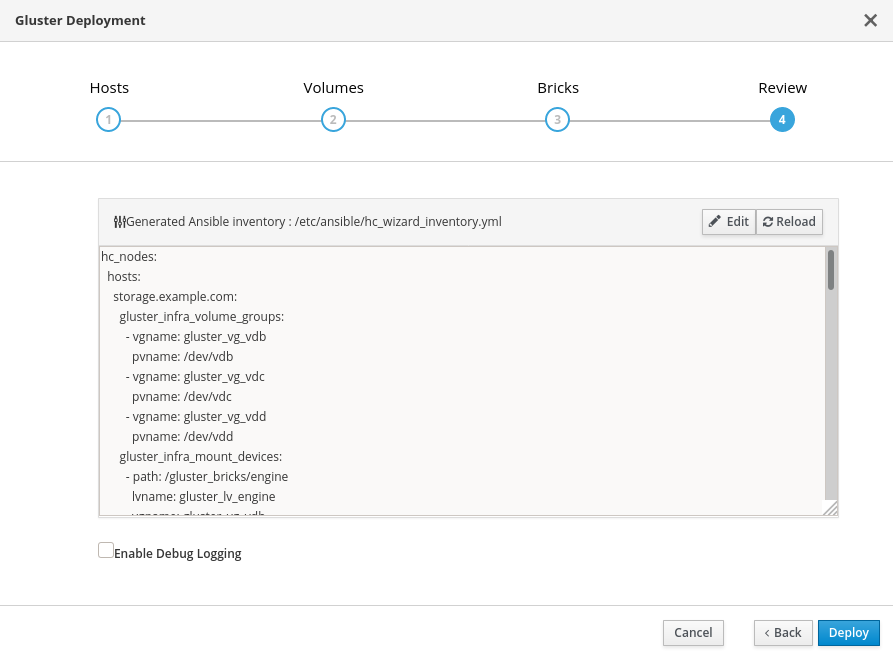
Click Edit to begin editing the generated deployment configuration file.
Make any changes required and click Save.
Review the configuration file.
If all configuration details are correct, click Deploy.
Wait for deployment to complete
You can watch the progress of the deployment in the text field.
The window displays Successfully deployed gluster when complete.
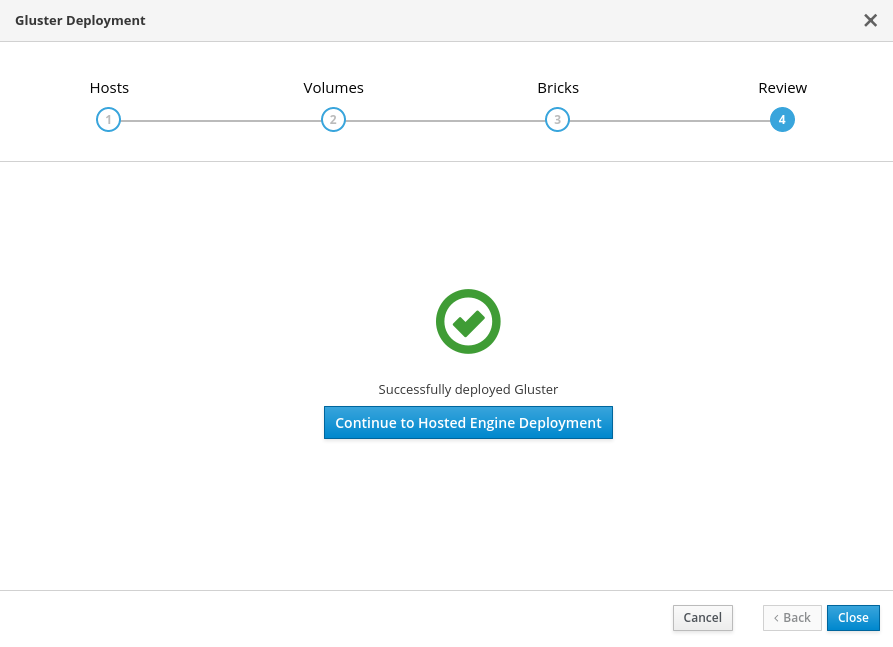
Click Continue to Hosted Engine Deployment and continue the deployment process with the instructions in Section 8.2, “Deploy the Hosted Engine on a single node using the Web Console”.
If deployment fails, click Clean up to remove any potentially incorrect changes to the system.
When cleanup is complete, click Redeploy. This returns you to the Review and edit configuration tab so that you can correct any issues in the generated configuration file before reattempting deployment.
8.2. Deploy the Hosted Engine on a single node using the Web Console
This section shows you how to deploy the Hosted Engine on a single node using the Web Console. Following this process results in Red Hat Virtualization Manager running in a virtual machine on your node, and managing that virtual machine. It also configures a Default cluster consisting only of that node, and enables Red Hat Gluster Storage functionality and the virtual-host tuned performance profile for the cluster of one.
Prerequisites
- The RHV-M Appliance is installed during the deployment process; however, if required, you can install it on the deployment host before starting the installation:
# yum install rhvm-appliance
Manually installing the Manager virtual machine is not supported.
- Configure Red Hat Gluster Storage on a single node
Gather the information you need for Hosted Engine deployment
Have the following information ready before you start the deployment process.
- IP address for a pingable gateway to the hyperconverged host
- IP address of the front-end management network
- Fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the Hosted Engine virtual machine
- MAC address that resolves to the static FQDN and IP address of the Hosted Engine
Procedure
Open the Hosted Engine Deployment wizard
If you continued directly from the end of Configure Red Hat Gluster Storage on a single node, the wizard is already open.
Otherwise:
-
Click Virtualization
Hosted Engine. - Click Start underneath Hyperconverged.
Click Use existing configuration.
ImportantIf the previous deployment attempt failed, click Clean up instead of Use existing configuration to discard the previous attempt and start from scratch. If your deployment uses Network-Bound Disk Encryption, you must then follow the process in Cleaning up Network-Bound Disk Encryption after a failed deployment.
-
Click Virtualization
Specify virtual machine details
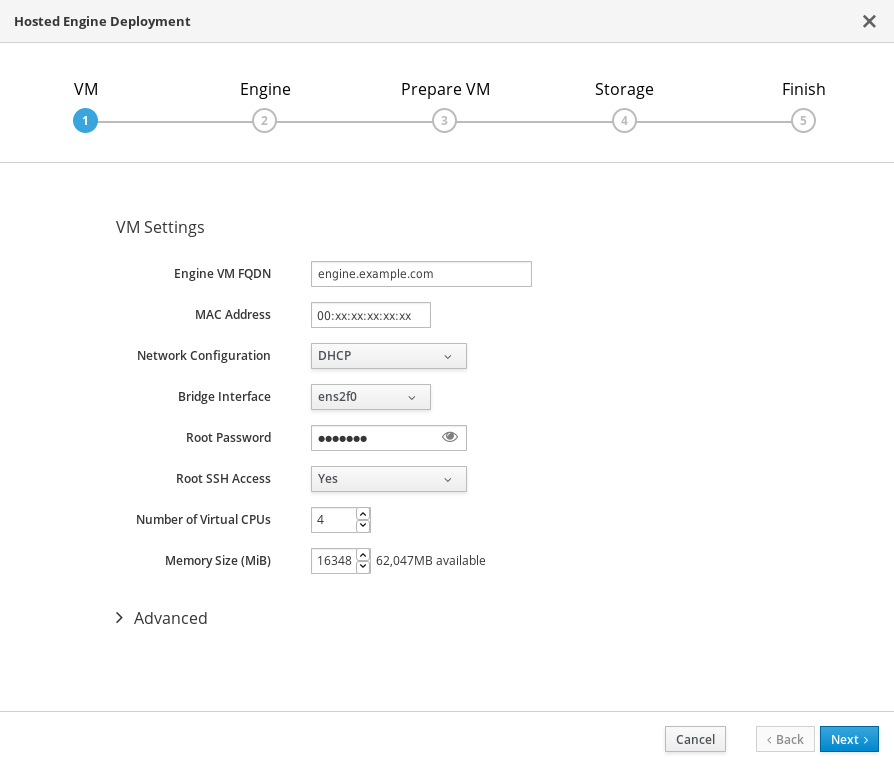
Enter the following details:
- Engine VM FQDN
-
The fully qualified domain name to be used for the Hosted Engine virtual machine, for example,
engine.example.com. - MAC Address
The MAC address associated with the Engine VM FQDN.
ImportantThe pre-populated MAC address must be replaced.
- Network Configuration
Choose either DHCP or Static from the Network Configuration drop-down list.
- If you choose DHCP, you must have a DHCP reservation for the Hosted Engine virtual machine so that its host name resolves to the address received from DHCP. Specify its MAC address in the MAC Address field.
If you choose Static, enter the following details:
- VM IP Address - The IP address must belong to the same subnet as the host. For example, if the host is in 10.1.1.0/24, the Hosted Engine virtual machine’s IP must be in the same subnet range (10.1.1.1-254/24).
- Gateway Address
- DNS Servers
- Bridge Interface
- Select the Bridge Interface from the drop-down list.
- Root password
- The root password to be used for the Hosted Engine virtual machine.
- Root SSH Access
- Specify whether to allow Root SSH Access.The default value of Root SSH Access is set to Yes.
- Number of Virtual CPUs
- Enter the Number of Virtual CPUs for the virtual machine.
- Memory Size (MiB)
Enter the Memory Size (MiB). The available memory is displayed next to the input field.
NoteRed Hat recommends to retain the values of Root SSH Access, Number of Virtual CPUs and Memory Size to default values.
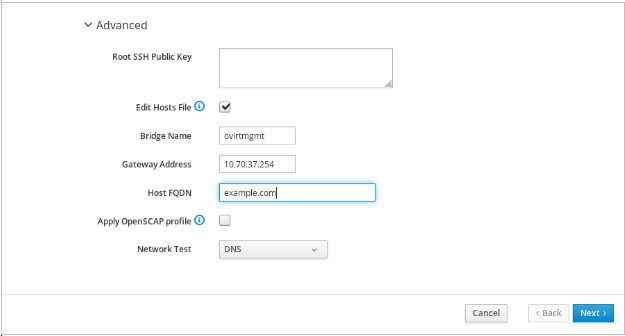
Optionally expand the Advanced fields.
- Root SSH Public Key
- Enter a Root SSH Public Key to use for root access to the Hosted Engine virtual machine.
- Edit Hosts File
- Select or clear the Edit Hosts File check box to specify whether to add entries for the Hosted Engine virtual machine and the base host to the virtual machine’s /etc/hosts file. You must ensure that the host names are resolvable.
- Bridge Name
- Change the management Bridge Name, or accept the default ovirtmgmt.
- Gateway Address
- Enter the Gateway Address for the management bridge.
- Host FQDN
- Enter the Host FQDN of the first host to add to the Manager. This is the front-end FQDN of the base host you are running the deployment on.
- Network Test
-
If you have a static network configuration or are using an isolated environment with addresses defined in
/etc/hosts, set Network Test to Ping.
- Click Next. Your FQDNs are validated before the next screen appears.
Specify virtualization management details
Enter the password to be used by the
adminaccount in the Administration Portal. You can also specify an email address for notifications, the notifications can also be configured post deployment; see Chapter 10, Post-deployment configuration suggestions.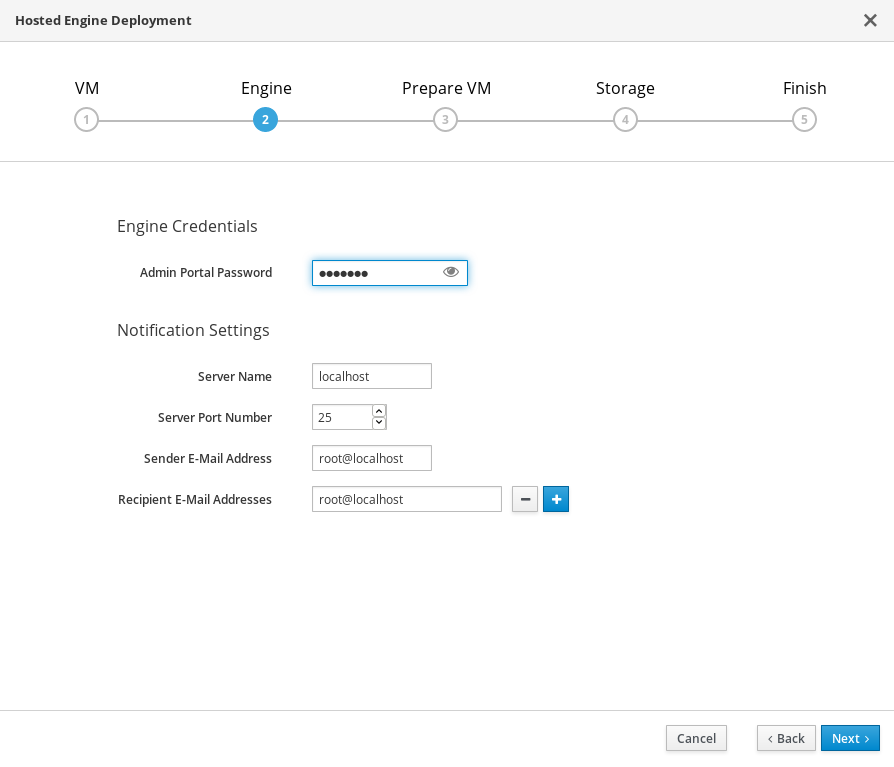
- Click Next.
Review virtual machine configuration
Ensure that the details listed on this tab are correct. Click Back to correct any incorrect information.
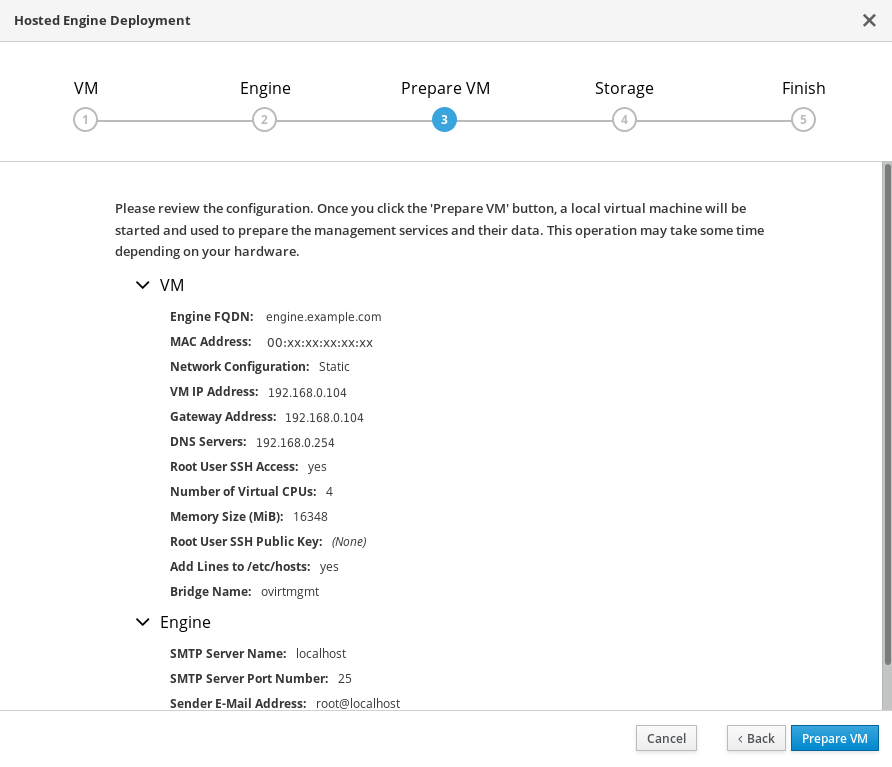
- Click Prepare VM.
Wait for virtual machine preparation to complete.
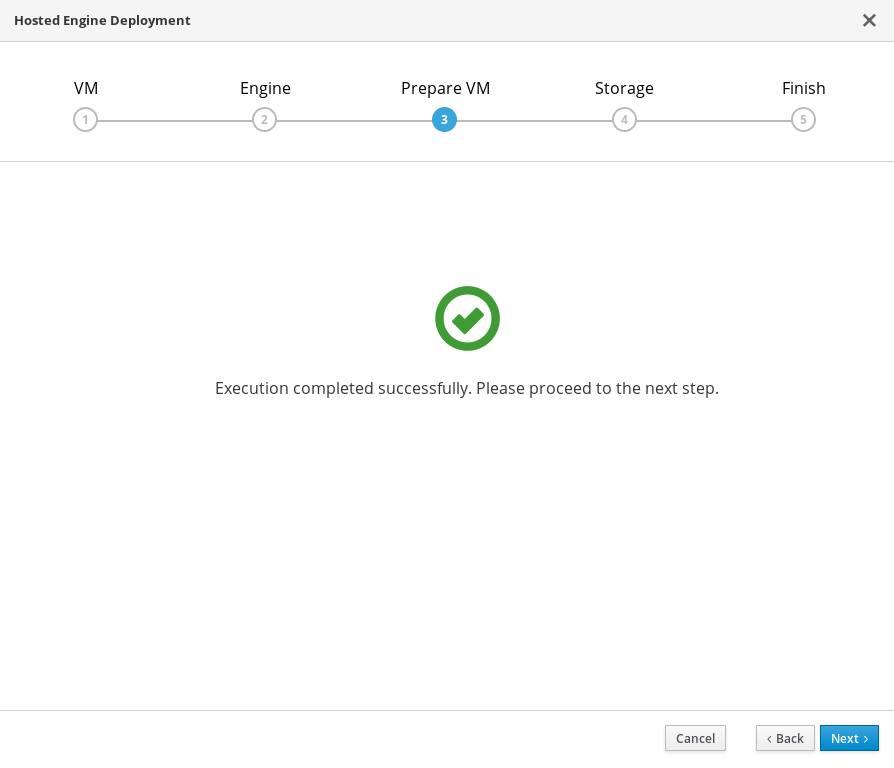
If preparation does not occur successfully, see Viewing Hosted Engine deployment errors.
- Click Next.
Specify storage for the Hosted Engine virtual machine
Specify the back-end address and location of the
enginevolume.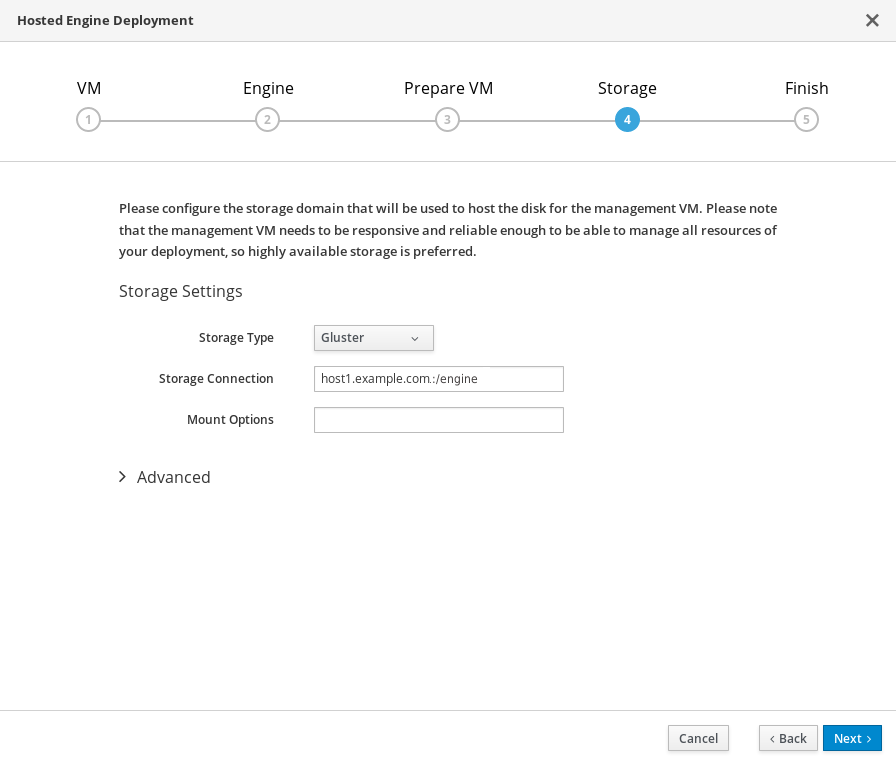
- Click Next.
Finalize Hosted Engine deployment
Review your deployment details and verify that they are correct.
NoteThe responses you provided during configuration are saved to an answer file to help you reinstall the hosted engine if necessary. The answer file is created at
/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine/answers.confby default. This file should not be modified manually without assistance from Red Hat Support.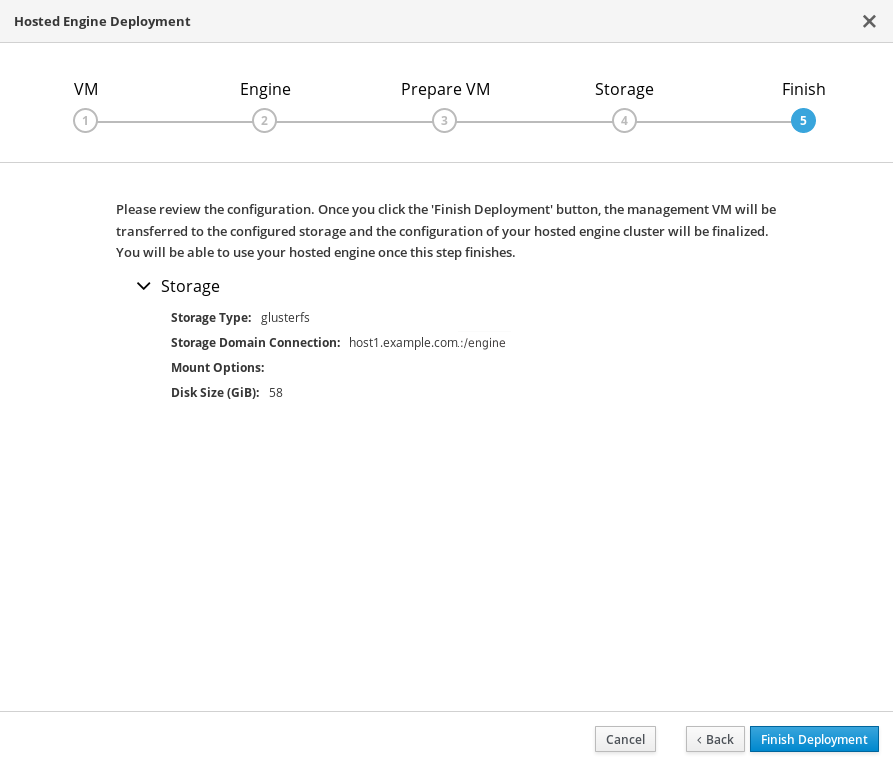
- Click Finish Deployment.
Wait for deployment to complete
This can take some time, depending on your configuration details.
The window displays the following when complete.
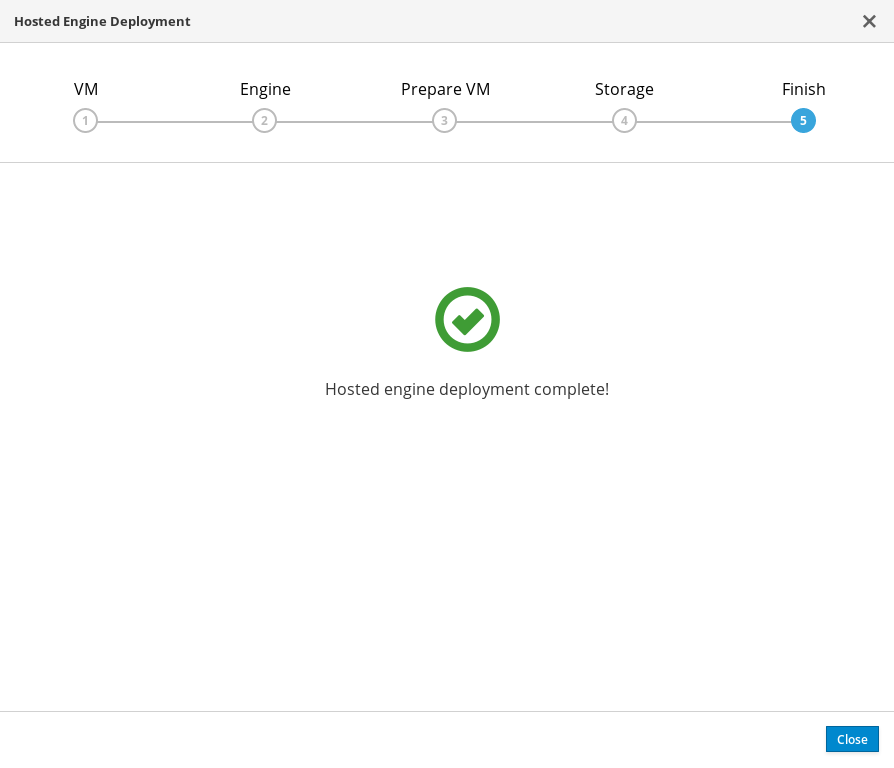 Important
ImportantIf deployment does not complete successfully, see Viewing Hosted Engine deployment errors.
Click Close.
Verify hosted engine deployment
Browse to the Administration Portal (for example, http://engine.example.com/ovirt-engine) and verify that you can log in using the administrative credentials you configured earlier. Click Dashboard and look for your hosts, storage domains, and virtual machines.