Ce contenu n'est pas disponible dans la langue sélectionnée.
2.2. Data Centers
2.2.1. Introduction to Data Centers
A data center is a logical entity that defines the set of resources used in a specific environment. A data center is considered a container resource, in that it is comprised of logical resources, in the form of clusters and hosts; network resources, in the form of logical networks and physical NICs; and storage resources, in the form of storage domains.
A data center can contain multiple clusters, which can contain multiple hosts; it can have multiple storage domains associated to it; and it can support multiple virtual machines on each of its hosts. A Red Hat Virtualization environment can contain multiple data centers; the data center infrastructure allows you to keep these centers separate.
All data centers are managed from the single Administration Portal.
Figure 2.1. Data Centers
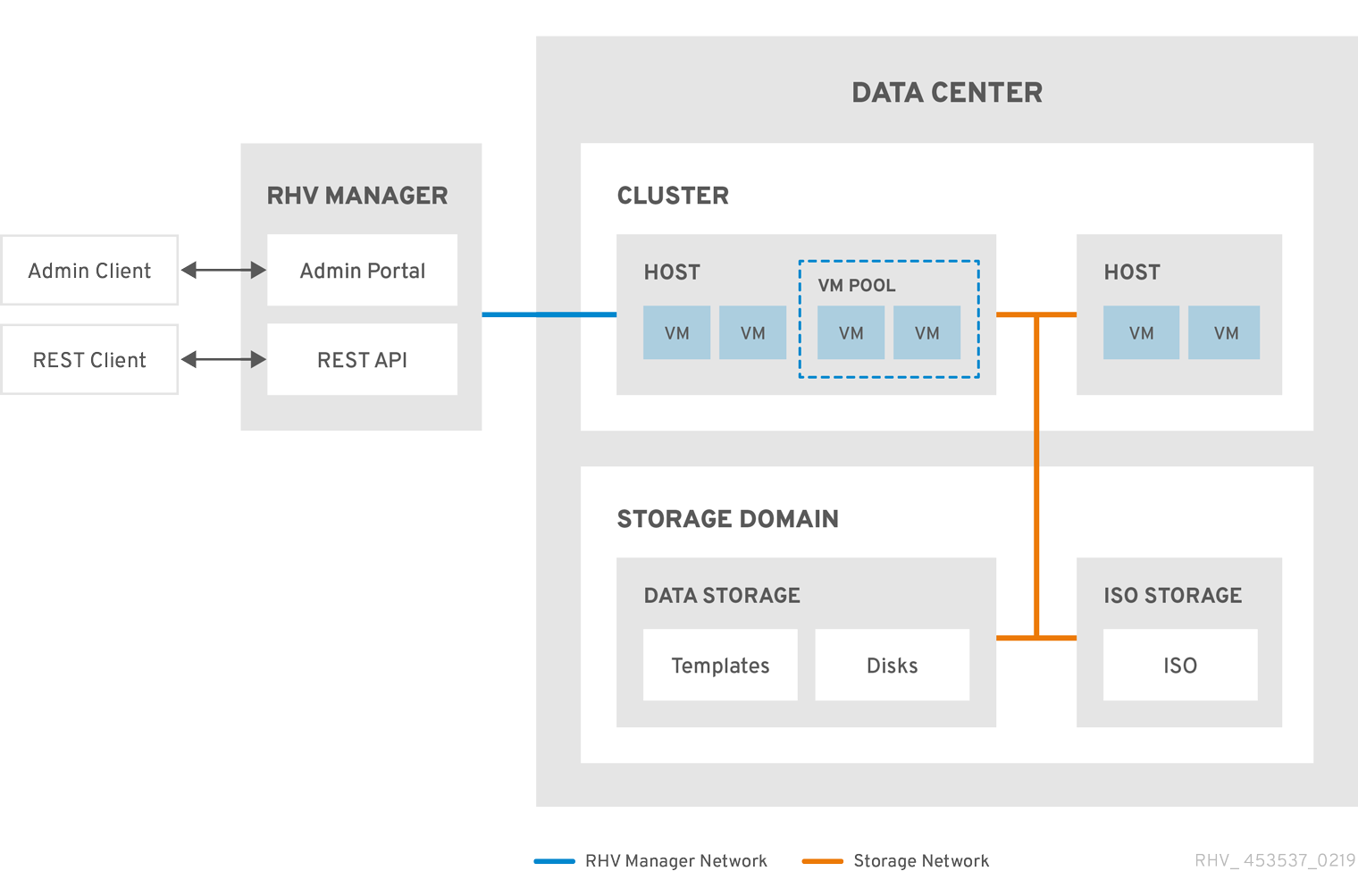
Red Hat Virtualization creates a default data center during installation. You can configure the default data center, or set up new appropriately named data centers.
2.2.2. The Storage Pool Manager
The Storage Pool Manager (SPM) is a role given to one of the hosts in the data center enabling it to manage the storage domains of the data center. The SPM entity can be run on any host in the data center; the Red Hat Virtualization Manager grants the role to one of the hosts. The SPM does not preclude the host from its standard operation; a host running as SPM can still host virtual resources.
The SPM entity controls access to storage by coordinating the metadata across the storage domains. This includes creating, deleting, and manipulating virtual disks (images), snapshots, and templates, and allocating storage for sparse block devices (on SAN). This is an exclusive responsibility: only one host can be the SPM in the data center at one time to ensure metadata integrity.
The Red Hat Virtualization Manager ensures that the SPM is always available. The Manager moves the SPM role to a different host if the SPM host encounters problems accessing the storage. When the SPM starts, it ensures that it is the only host granted the role; therefore it will acquire a storage-centric lease. This process can take some time.
2.2.3. SPM Priority
The SPM role uses some of a host’s available resources. The SPM priority setting of a host alters the likelihood of the host being assigned the SPM role: a host with high SPM priority will be assigned the SPM role before a host with low SPM priority. Critical virtual machines on hosts with low SPM priority will not have to contend with SPM operations for host resources.
You can change a host’s SPM priority in the SPM tab in the Edit Host window.
2.2.4. Data Center Tasks
2.2.4.1. Creating a New Data Center
This procedure creates a data center in your virtualization environment. The data center requires a functioning cluster, host, and storage domain to operate.
After you set the Compatibility Version, you cannot lower the version number. Version regression is not supported.
You can specify a MAC pool range for a cluster. Setting a MAC pool range is no longer supported.
Procedure
-
Click
. - Click New.
- Enter the Name and Description of the data center.
- Select the Storage Type, Compatibility Version, and Quota Mode of the data center from the drop-down menus.
- Click to create the data center and open the Data Center - Guide Me window.
-
The Guide Me window lists the entities that need to be configured for the data center. Configure these entities or postpone configuration by clicking the Configure Later button. Configuration can be resumed by selecting the data center and clicking More Actions (
 ), then clicking Guide Me.
), then clicking Guide Me.
The new data center will remain Uninitialized until a cluster, host, and storage domain are configured for it; use Guide Me to configure these entities.
2.2.4.2. Explanation of Settings in the New Data Center and Edit Data Center Windows
The table below describes the settings of a data center as displayed in the New Data Center and Edit Data Center windows. Invalid entries are outlined in orange when you click , prohibiting the changes being accepted. In addition, field prompts indicate the expected values or range of values.
| Field | Description/Action |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the data center. This text field has a 40-character limit and must be a unique name with any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores. |
| Description | The description of the data center. This field is recommended but not mandatory. |
| Storage Type | Choose Shared or Local storage type. Different types of storage domains (iSCSI, NFS, FC, POSIX, and Gluster) can be added to the same data center. Local and shared domains, however, cannot be mixed. You can change the storage type after the data center is initialized. See Changing the Data Center Storage Type. |
| Compatibility Version | The version of Red Hat Virtualization. After upgrading the Red Hat Virtualization Manager, the hosts, clusters and data centers may still be in the earlier version. Ensure that you have upgraded all the hosts, then the clusters, before you upgrade the Compatibility Level of the data center. |
| Quota Mode | Quota is a resource limitation tool provided with Red Hat Virtualization. Choose one of:
|
| Comment | Optionally add a plain text comment about the data center. |
2.2.4.3. Re-Initializing a Data Center: Recovery Procedure
This recovery procedure replaces the master data domain of your data center with a new master data domain. You must re-initialize your master data domain if its data is corrupted. Re-initializing a data center allows you to restore all other resources associated with the data center, including clusters, hosts, and non-problematic storage domains.
You can import any backup or exported virtual machines or templates into your new master data domain.
Procedure
-
Click
and select the data center. - Ensure that any storage domains attached to the data center are in maintenance mode.
-
Click More Actions (
 ), then click Re-Initialize Data Center.
), then click Re-Initialize Data Center.
- The Data Center Re-Initialize window lists all available (detached; in maintenance mode) storage domains. Click the radio button for the storage domain you are adding to the data center.
- Select the Approve operation check box.
- Click .
The storage domain is attached to the data center as the master data domain and activated. You can now import any backup or exported virtual machines or templates into your new master data domain.
2.2.4.4. Removing a Data Center
An active host is required to remove a data center. Removing a data center will not remove the associated resources.
Procedure
- Ensure the storage domains attached to the data center are in maintenance mode.
-
Click
and select the data center to remove. - Click Remove.
- Click .
2.2.4.5. Force Removing a Data Center
A data center becomes Non Responsive if the attached storage domain is corrupt or if the host becomes Non Responsive. You cannot Remove the data center under either circumstance.
Force Remove does not require an active host. It also permanently removes the attached storage domain.
It may be necessary to Destroy a corrupted storage domain before you can Force Remove the data center.
Procedure
-
Click
and select the data center to remove. -
Click More Actions (
 ), then click Force Remove.
), then click Force Remove.
- Select the Approve operation check box.
- Click
The data center and attached storage domain are permanently removed from the Red Hat Virtualization environment.
2.2.4.6. Changing the Data Center Storage Type
You can change the storage type of the data center after it has been initialized. This is useful for data domains that are used to move virtual machines or templates around.
Limitations
- Shared to Local - For a data center that does not contain more than one host and more than one cluster, since a local data center does not support it.
- Local to Shared - For a data center that does not contain a local storage domain.
Procedure
-
Click
and select the data center to change. - Click Edit.
- Change the Storage Type to the desired value.
- Click .
2.2.4.7. Changing the Data Center Compatibility Version
Red Hat Virtualization data centers have a compatibility version. The compatibility version indicates the version of Red Hat Virtualization with which the data center is intended to be compatible. All clusters in the data center must support the desired compatibility level.
Prerequisites
- To change the data center compatibility level, you must first update the compatibility version of all clusters and virtual machines in the data center.
Procedure
-
In the Administration Portal, click
. - Select the data center to change and click .
- Change the Compatibility Version to the desired value.
- Click . The Change Data Center Compatibility Version confirmation dialog opens.
- Click to confirm.
2.2.5. Data Centers and Storage Domains
2.2.5.1. Attaching an Existing Data Domain to a Data Center
Data domains that are Unattached can be attached to a data center. Shared storage domains of multiple types (iSCSI, NFS, FC, POSIX, and Gluster) can be added to the same data center.
Procedure
-
Click
. - Click a data center’s name. This opens the details view.
- Click the Storage tab to list the storage domains already attached to the data center.
- Click Attach Data.
- Select the check box for the data domain to attach to the data center. You can select multiple check boxes to attach multiple data domains.
- Click .
The data domain is attached to the data center and is automatically activated.
2.2.5.2. Attaching an Existing ISO domain to a Data Center
An ISO domain that is Unattached can be attached to a data center. The ISO domain must be of the same Storage Type as the data center.
Only one ISO domain can be attached to a data center.
Procedure
-
Click
. - Click a data center’s name. This opens the details view.
- Click the Storage tab to list the storage domains already attached to the data center.
- Click Attach ISO.
- Click the radio button for the appropriate ISO domain.
- Click .
The ISO domain is attached to the data center and is automatically activated.
2.2.5.3. Attaching an Existing Export Domain to a Data Center
The export storage domain is deprecated. Storage data domains can be unattached from a data center and imported to another data center in the same environment, or in a different environment. Virtual machines, floating virtual disks, and templates can then be uploaded from the imported storage domain to the attached data center. See Importing Existing Storage Domains for information on importing storage domains.
An export domain that is Unattached can be attached to a data center. Only one export domain can be attached to a data center.
Procedure
-
Click
. - Click a data center’s name. This opens the details view.
- Click the Storage tab to list the storage domains already attached to the data center.
- Click Attach Export.
- Click the radio button for the appropriate export domain.
- Click .
The export domain is attached to the data center and is automatically activated.
2.2.5.4. Detaching a Storage Domain from a Data Center
Detaching a storage domain from a data center stops the data center from associating with that storage domain. The storage domain is not removed from the Red Hat Virtualization environment; it can be attached to another data center.
Data, such as virtual machines and templates, remains attached to the storage domain.
Although it possible to detach the last master storage domain, this is not recommended.
If the master storage domain is detached, it must be reinitialized.
If the storage domain is reinitialized, all your data will be lost, and the storage domain might not find your disks again.
Procedure
-
Click
. - Click a data center’s name. This opens the details view.
- Click the Storage tab to list the storage domains attached to the data center.
-
Select the storage domain to detach. If the storage domain is
Active, click Maintenance. - Click to initiate maintenance mode.
- Click Detach.
- Click .
It can take up to several minutes for the storage domain to disappear from the details view.