Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 1. Overview of available storage options
Explore local, remote, and cluster-based storage options available on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Covers directly attached storage devices and remote storage accessed over LAN, internet, or Fibre Channel networks to understand storage architecture.
Local storage implies that the storage devices are either installed on the system or directly attached to the system.
With remote storage, devices are accessed over LAN, the internet, or using a Fibre Channel network. The following high level Red Hat Enterprise Linux storage diagram describes the different storage options.
Figure 1.1. High level Red Hat Enterprise Linux storage diagram
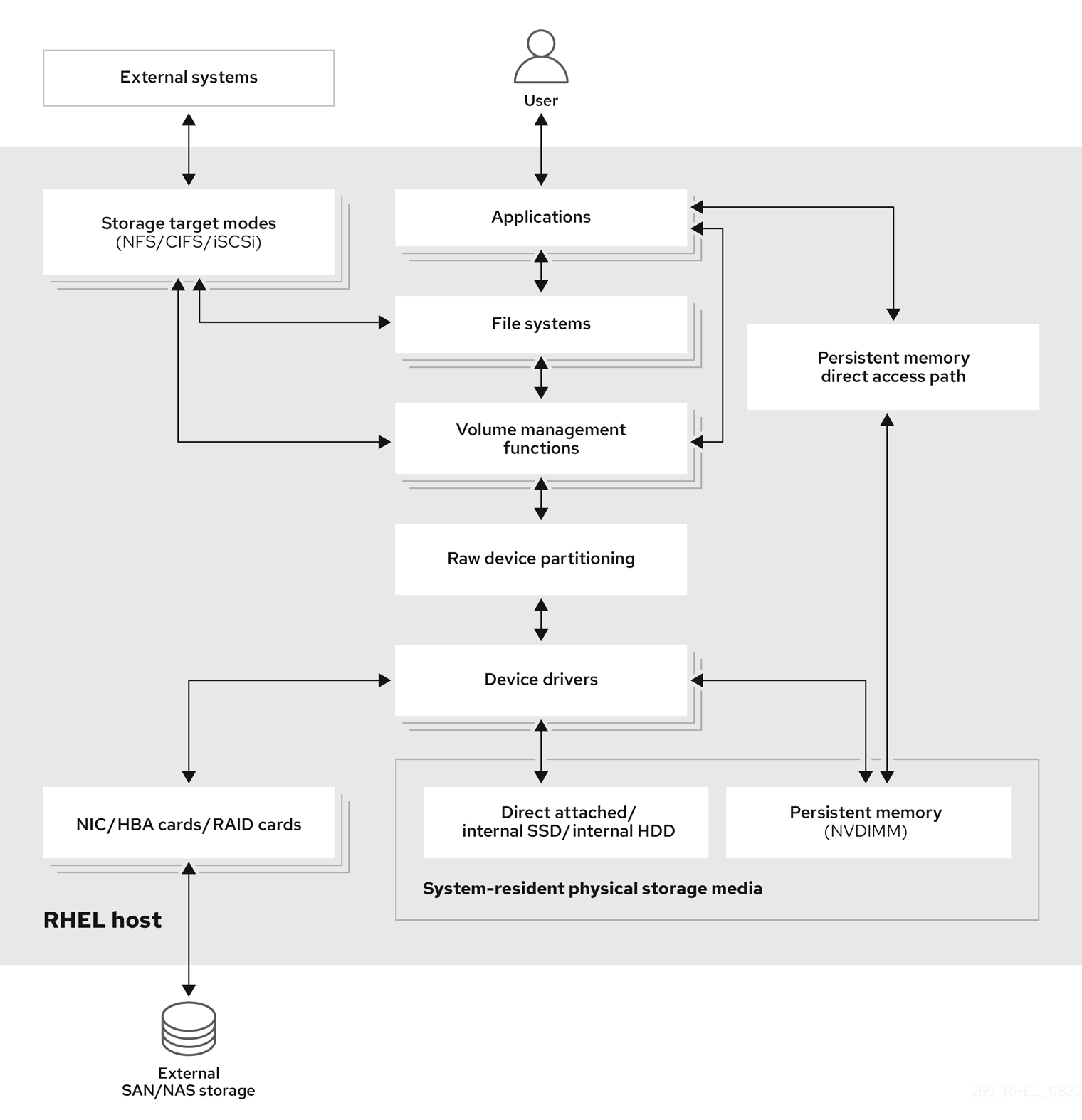
1.1. Local storage overview
Local storage refers to storage devices that are installed on or directly attached to your system. This includes disk partitions, logical volumes, and file systems that you can manage without network connectivity.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 10 offers several local storage options.
- Basic disk administration
By using
partedandfdisk, you can create, modify, delete, and view disk partitions. The following are the partitioning layout standards:- GUID Partition Table (GPT)
- It uses a globally unique identifier (GUID) and provides a unique disk and partition GUID.
- Master Boot Record (MBR)
- It is used with BIOS-based computers. You can create primary, extended, and logical partitions.
- Storage consumption options
- Non-Volatile Dual In-line Memory Modules (NVDIMM) Management
- It is a combination of memory and storage. You can enable and manage various types of storage on NVDIMM devices connected to your system.
- Block Storage Management
- Data is stored in the form of blocks where each block has a unique identifier.
- File Storage
- Data is stored at file level on the local system. These data can be accessed locally by using XFS (default) or ext4, and over a network by using NFS and SMB.
- Logical volumes
- Logical Volume Manager (LVM)
- It creates logical devices from physical devices. Logical volume (LV) is a combination of the physical volumes (PV) and volume groups (VG).
- Virtual Data Optimizer (VDO)
It is used for data reduction by using deduplication, compression, and thin provisioning. Using LV below VDO helps in:
- Extending of VDO volume
- Spanning VDO volume over multiple devices
- Local file systems
- XFS
- The default RHEL file system.
- Ext4
- A legacy file system.
- Stratis
- Stratis is a hybrid user-and-kernel local storage management system that supports advanced storage features.
1.2. Remote storage overview
Remote storage provides access to storage devices over a network connection such as LAN, internet, or Fibre Channel. This allows you to centralize storage resources and share them across multiple systems.
The following are the remote storage options available in RHEL 10:
- Storage connectivity options
- iSCSI
- RHEL 10 uses the targetcli tool to add, remove, view, and monitor iSCSI storage interconnects.
- Fibre Channel (FC)
RHEL 10 provides the following native Fibre Channel drivers:
-
lpfc -
qla2xxx -
zfcp
-
- Non-volatile Memory Express (NVMe)
An interface that allows a host software utility to communicate with solid state drives. Use the following types of fabric transport to configure NVMe over fabrics:
- NVMe over fabrics using Remote Direct Memory Access (NVMe/RDMA)
- NVMe over fabrics using Fibre Channel (NVMe/FC)
- NVMe over fabrics using TCP (NVMe/TCP)
- Device Mapper multipathing (DM Multipath)
- Allows you to configure multiple I/O paths between server nodes and storage arrays into a single device. These I/O paths are physical SAN connections that can include separate cables, switches, and controllers.
- Network file system
- NFS
- SMB