Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 7. Route advertisements
7.1. About route advertisements
To simplify network management and improve failover visibility, you can use route advertisements to share pod and egress IP routes between your cluster and the provider network. This feature requires the OVN-Kubernetes plugin and a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) provider.
For more information, see About BGP routing.
7.1.1. Advertise cluster network routes with Border Gateway Protocol
To simplify routing and improve failover visibility without manual route management, you can enable route advertisements. Route advertisements allow you to advertise default and user-defined network routes, including EgressIPs, between your cluster and the provider network.
With route advertisements enabled, you can advertise network routes for the default pod network and user-defined networks to the provider network, including EgressIPs, and importing routes from the provider network to the default pod network and CUDNs. This simplifies routing while improving failover visibility, and eliminates manual route management.
From the provider network, IP addresses advertised from the default pod network and user defined networks can be reached directly and vice versa.
For example, you can import routes to the default pod network so you no longer need to manually configure routes on each node. Previously, you might have been setting the routingViaHost parameter to true and manually configuring routes on each node to approximate a similar configuration. With route advertisements you can accomplish this task seamlessly with routingViaHost parameter set to false.
You could also set the routingViaHost parameter to true in the Network custom resource CR for your cluster, but you must then manually configure routes on each node to simulate a similar configuration. When you enable route advertisements, you can set routingViaHost=false in the Network CR without having to then manually configure routes one each node.
Route reflectors on the provider network are supported and can reduce the number of BGP connections required to advertise routes on large networks.
If you use EgressIPs with route advertisements enabled, the layer 3 provider network is aware of EgressIP failovers. This means that you can locate cluster nodes that host EgressIPs on different layer 2 segments whereas before only the layer 2 provider network was aware so that required all the egress nodes to be on the same layer 2 segment.
7.1.1.1. Supported platforms
Advertising routes with border gateway protocol (BGP) is supported on the bare-metal infrastructure type.
7.1.1.2. Infrastructure requirements
To use route advertisements, you must have configured BGP for your network infrastructure. Outages or misconfigurations of your network infrastructure might cause disruptions to your cluster network.
7.1.1.3. Compatibility with other networking features
Route advertisements support the following OpenShift Container Platform Networking features:
- Multiple external gateways (MEG)
- MEG is not supported with this feature.
- EgressIPs
Supports the use and advertisement of EgressIPs. The node where an egress IP address resides advertises the EgressIP. An egress IP address must be on the same layer 2 network subnet as the egress node. The following limitations apply:
- Advertising EgressIPs from a user-defined network (CUDN) operating in layer 2 mode are not supported.
- Advertising EgressIPs for a network that has both egress IP addresses assigned to the primary network interface and egress IP addresses assigned to additional network interfaces is impractical. All EgressIPs are advertised on all of the BGP sessions of the selected FRRConfiguration instances, regardless of whether these sessions are established over the same interface that the EgressIP is assigned to or not, potentially leading to unwanted advertisements.
- Services
- Works with the MetalLB Operator to advertise services to the provider network.
- Egress service
- Full support.
- Egress firewall
- Full support.
- Egress QoS
- Full support.
- Network policies
- Full support.
- Direct pod ingress
- Full support for the default cluster network and cluster user-defined (CUDN) networks.
7.1.1.4. Considerations for use with the MetalLB Operator
The MetalLB Operator is installed as an add-on to the cluster. Deployment of the MetalLB Operator automatically enables FRR-K8s as an additional routing capability provider. This feature and the MetalLB Operator use the same FRR-K8s deployment.
7.1.1.5. Considerations for naming cluster user-defined networks (CUDNs)
When referencing a VRF device in a FRRConfiguration CR, the VRF name is the same as the CUDN name for VRF names that are less than or equal to 15 characters. It is recommended to use a VRF name no longer than 15 characters so that the VRF name can be inferred from the CUDN name.
7.1.1.6. BGP routing custom resources
The following custom resources (CRs) are used to configure route advertisements with BGP:
RouteAdvertisements-
This CR defines the advertisements for the BGP routing. From this CR, the OVN-Kubernetes controller generates a
FRRConfigurationobject that configures the FRR daemon to advertise cluster network routes. This CR is cluster scoped. FRRConfiguration-
This CR is used to define BGP peers and to configure route imports from the provider network into the cluster network. Before applying
RouteAdvertisementsobjects, at least one FRRConfiguration object must be initially defined to configure the BGP peers. This CR is namespaced.
7.1.1.7. OVN-Kubernetes controller generation of FRRConfiguration objects
An FRRConfiguration object is generated for each network and node selected by a RouteAdvertisements CR with the appropriate advertised prefixes that apply to each node. The OVN-Kubernetes controller checks whether the RouteAdvertisements-CR-selected nodes are a subset of the nodes that are selected by the RouteAdvertisements-CR-selected FRR configurations.
Any filtering or selection of prefixes to receive are not considered in FRRConfiguration objects that are generated from the RouteAdvertisement CRs. Configure any prefixes to receive on other FRRConfiguration objects. OVN-Kubernetes imports routes from the VRF into the appropriate network.
7.1.1.8. Cluster Network Operator configuration
The Cluster Network Operator (CNO) API exposes several fields to configure route advertisements:
-
spec.additionalRoutingCapabilities.providers: Specifies an additional routing provider, which is required to advertise routes. The only supported value isFRR, which enables deployment of the FRR-K8S daemon for the cluster. When enabled, the FRR-K8S daemon is deployed on all nodes. -
spec.defaultNetwork.ovnKubernetesConfig.routeAdvertisements: Enables route advertisements for the default cluster network and CUDN networks. Thespec.additionalRoutingCapabilitiesfield must be set toFRRto enable this feature.
7.1.2. RouteAdvertisements object configuration
To control how cluster networks and egress IP addresses are advertised to external routers, configure the cluster-scoped RouteAdvertisements object to specify networks and select the appropriate nodes and routing targets for your environment.
You can define an RouteAdvertisements object, which is cluster scoped, with the following properties.
The fields for the RouteAdvertisements custom resource (CR) are described in the following table:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Specifies the name of the |
|
|
|
Specifies an array that can contain a list of different types of networks to advertise. Supports only the |
|
|
|
Determines which |
|
|
| Specifies which networks to advertise among default cluster network and cluster user defined networks (CUDNs). |
|
|
|
Limits the advertisements to selected nodes. When |
|
|
|
Determines which router to advertise the routes in. Routes are advertised on the routers associated with this virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) target, as specified on the selected |
7.1.3. Examples advertising pod IP addresses with BGP
To implement Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for your cluster, you can use these examples to configure route advertisements for pod IP addresses and egress IP addresses. Examples include configurations for default cluster networks, user-defined networks, and VRF-lite designs.
The following examples describe several configurations for advertising pod IP addresses and EgressIPs with Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). The external network border router has the 172.18.0.5 IP address. These configures assume that you have configured an external route reflector that can relay routes to all nodes on the cluster network.
7.1.3.1. Advertising the default cluster network
In this scenario, the default cluster network is exposed to the external network so that pod IP addresses and EgressIPs are advertised to the provider network.
This scenario relies upon the following FRRConfiguration object:
FRRConfiguration CR
When the OVN-Kubernetes controller sees this RouteAdvertisements CR, it generates further FRRConfiguration objects based on the selected ones that configure the FRR daemon to advertise the routes for the default cluster network.
An example of a FRRConfiguration CR generated by OVN-Kubernetes
In the example generated FRRConfiguration object, <default_network_host_subnet> is the subnet of the default cluster network that is advertised to the provider network.
7.1.3.2. Advertising pod IPs from a cluster user-defined network over BGP
In this scenario, the blue cluster user-defined network (CUDN) is exposed to the external network so that the network’s pod IP addresses and EgressIPs are advertised to the provider network.
This scenario relies upon the following FRRConfiguration object:
FRRConfiguration CR
With this FRRConfiguration object, routes will be imported from neighbor 172.18.0.5 into the default VRF and are available to the default cluster network.
The CUDNs are advertised over the default VRF as illustrated in the following diagram:

- Red CUDN
-
A VRF named
redassociated with a CUDN namedred -
A subnet of
10.0.0.0/24
-
A VRF named
- Blue CUDN
-
A VRF named
blueassociated with a CUDN namedblue -
A subnet of
10.0.1.0/24
-
A VRF named
In this configuration, two separate CUDNs are defined. The red network covers the 10.0.0.0/24 subnet and the blue network covers the 10.0.1.0/24 subnet. The red and blue networks are labeled as export: true.
The following RouteAdvertisements CR describes the configuration for the red and blue tenants:
RouteAdvertisements CR for the red and blue tenants
When the OVN-Kubernetes controller sees this RouteAdvertisements CR, it generates further FRRConfiguration objects based on the selected ones that configure the FRR daemon to advertise the routes. The following example is of one such configuration object, with the number of FRRConfiguration objects created depending on the node and networks selected.
An example of a FRRConfiguration CR generated by OVN-Kubernetes
The generated FRRConfiguration object configures the subnet 10.0.1.0/24, which belongs to network blue, to be imported into the default VRF and advertised to the 172.18.0.5 neighbor. An FRRConfiguration object is generated for each network and nodes selected by a RouteAdvertisements CR with the appropriate prefixes that apply to each node.
When the targetVRF field is omitted, the routes are leaked and advertised over the default VRF. Additionally, routes that were imported to the default VRF after the definition of the initial FRRConfiguration object are also imported into the blue VRF.
7.1.3.3. Advertising pod IPs from a cluster user-defined network over BGP with VPN
In this scenario, a VLAN interface is attached to the VRF device associated with the blue network. This setup provides a VRF lite design, where FRR-K8S is used to advertise the blue network only over the corresponding BGP session on the blue network VRF/VLAN link to the next hop Provide Edge (PE) router. The red tenant uses the same configuration. The blue and red networks are labeled as export: true.
This scenario does not support the use of EgressIPs.
The following diagram illustrates this configuration:
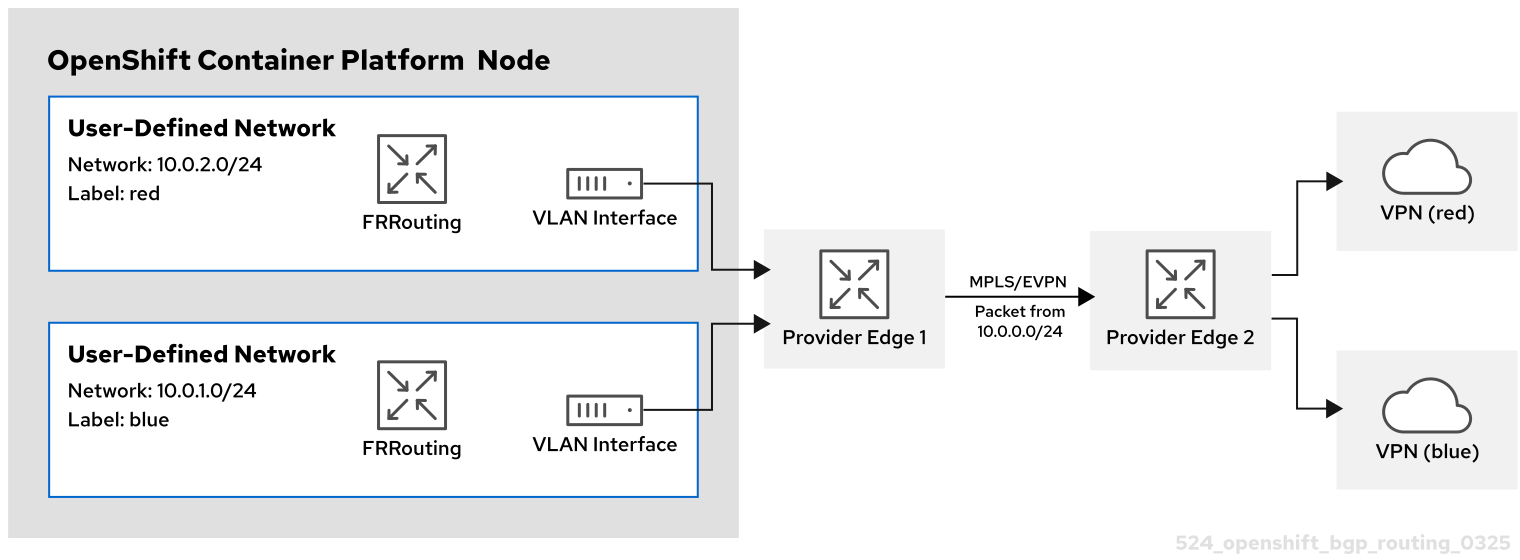
- Red CUDN
-
A VRF named
redassociated with a CUDN namedred - A VLAN interface attached to the VRF device and connected to the external PE router
-
An assigned subnet of
10.0.2.0/24
-
A VRF named
- Blue CUDN
-
A VRF named
blueassociated with a CUDN namedblue - A VLAN interface attached to the VRF device and connected to the external PE router
-
An assigned subnet of
10.0.1.0/24
-
A VRF named
This approach is available only when you set routingViaHost=true in the ovnKubernetesConfig.gatewayConfig specification of the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
In the following configuration, an additional FRRConfiguration CR configures peering with the PE router on the blue and red VLANs:
FRRConfiguration CR manually configured for BGP VPN setup
The following RouteAdvertisements CR describes the configuration for the blue and red tenants:
RouteAdvertisements CR for the blue and red tenants
In the RouteAdvertisements CR, the targetVRF is set to auto so that advertisements occur within the VRF device that corresponds to the individual networks that are selected. In this scenario, the pod subnet for blue is advertised over the blue VRF device, and the pod subnet for red is advertised over the red VRF device. Additionally, each BGP session imports routes to only the corresponding CUDN VRF as defined by the initial FRRConfiguration object.
When the OVN-Kubernetes controller sees this RouteAdvertisements CR, it generates further FRRConfiguration objects based on the selected ones that configure the FRR daemon to advertise the routes for the blue and red tenants.
FRRConfiguration CR generated by OVN-Kubernetes for blue and red tenants
In this scenario, any filtering or selection of routes to receive must be done in the FRRConfiguration CR that defines peering relationships.
7.2. Enabling route advertisements
To improve network reachability and failover visibility for your cluster, you can enable route advertisements for pod and egress IP addresses. This configuration requires the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin and allows your cluster to share routes with an external provider network.
As a cluster administrator, you can configure additional route advertisements for your cluster. You must use the OVN-Kubernetes network plugin.
7.2.1. Enabling route advertisements
To improve network reachability and failover visibility, you can enable additional routing support for your cluster. You can enable route advertisements to manage network traffic within your environment.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - The cluster is installed on compatible infrastructure.
Procedure
To enable a routing provider and additional route advertisements, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3. Disabling route advertisements
To stop the broadcast of cluster network routes and egress IP addresses to your provider network, you can disable route advertisements. Disabling this feature removes the automatically generated routing configurations while maintaining your existing network infrastructure.
7.3.1. Disabling route advertisements
To prevent your cluster from advertising additional routes to the network, you must disable the route advertisements feature in the network operator configuration. You can disable route advertisements to manage network traffic and maintain security within your environment.
Prerequisites
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole. - The cluster is installed on compatible infrastructure.
Procedure
To disable additional routing support, enter the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4. Example route advertisements setup
To learn how to implement a route reflection setup on bare-metal infrastructure, you can follow this sample configuration. This example demonstrates how to enable the necessary feature gates and configure objects to advertise pod and egress IP routes.
As a cluster administrator, you can configure the following example route advertisements setup for your cluster. This configuration is intended as a sample that demonstrates how to configure route advertisements.
7.4.1. Sample route advertisements setup
You can implement Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing by using a sample configuration to set up route advertisements for your cluster. This configuration demonstrates how to configure route reflection on bare-metal infrastructure to share pod and egress IP routes.
As a cluster administrator, you can enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing support for your cluster. The configuration uses route reflection rather than a full mesh setup.
BGP routing is supported only on bare-metal infrastructure.
Prerequisites
-
You installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). -
You are logged in to the cluster as a user with
cluster-adminprivileges. - The cluster is installed on bare-metal infrastructure.
- You have a bare-metal system with access to the cluster where you plan to run the FRR daemon container.
Procedure
Confirm that the
RouteAdvertisementsfeature gate is enabled by running the following command:oc get featuregate -oyaml | grep -i routeadvertisement
$ oc get featuregate -oyaml | grep -i routeadvertisementCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
- name: RouteAdvertisements
- name: RouteAdvertisementsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the Cluster Network Operator (CNO) by running the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow It might take a few minutes for the CNO to restart all nodes.
Get the IP addresses of the nodes by running the following command:
oc get node -owide
$ oc get node -owideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the default pod network of each node by running the following command:
oc get node <node_name> -o=jsonpath={.metadata.annotations.k8s\\.ovn\\.org/node-subnets}$ oc get node <node_name> -o=jsonpath={.metadata.annotations.k8s\\.ovn\\.org/node-subnets}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
{"default":["10.129.0.0/23"],"ns1.udn-network-primary-layer3":["10.150.6.0/24"]}{"default":["10.129.0.0/23"],"ns1.udn-network-primary-layer3":["10.150.6.0/24"]}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On the bare-metal hypervisor, get the IP address for the external FRR container to use by running the following command:
ip -j -d route get <a cluster node's IP> | jq -r '.[] | .dev' | xargs ip -d -j address show | jq -r '.[] | .addr_info[0].local'
$ ip -j -d route get <a cluster node's IP> | jq -r '.[] | .dev' | xargs ip -d -j address show | jq -r '.[] | .addr_info[0].local'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
frr.conffile for FRR that includes each node’s IP address, as shown in the following example:Example
frr.confconfiguration fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a file named
daemonsthat includes the following content:Example
daemonsconfiguration fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Save both the
frr.confanddaemonsfiles in the same directory, such as/tmp/frr. Create an external FRR container by running the following command:
sudo podman run -d --privileged --network host --rm --ulimit core=-1 --name frr --volume /tmp/frr:/etc/frr quay.io/frrouting/frr:9.1.0
$ sudo podman run -d --privileged --network host --rm --ulimit core=-1 --name frr --volume /tmp/frr:/etc/frr quay.io/frrouting/frr:9.1.0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the following
FRRConfigurationandRouteAdvertisementsconfigurations:Create a
receive_all.yamlfile that includes the following content:Example
receive_all.yamlconfiguration fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a
ra.yamlfile that includes the following content:Example
ra.yamlconfiguration fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Apply the
receive_all.yamlandra.yamlfiles by running the following command:for f in receive_all.yaml ra.yaml; do oc apply -f $f; done
$ for f in receive_all.yaml ra.yaml; do oc apply -f $f; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that the configurations were applied:
Verify that the
FRRConfigurationconfigurations were created by running the following command:oc get frrconfiguration -A
$ oc get frrconfiguration -ACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
RouteAdvertisementsconfigurations were created by running the following command:oc get ra -A
$ oc get ra -ACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME STATUS default Accepted
NAME STATUS default AcceptedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Get the external FRR container ID by running the following command:
sudo podman ps | grep frr
$ sudo podman ps | grep frrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
22cfc713890e quay.io/frrouting/frr:9.1.0 /usr/lib/frr/dock... 5 hours ago Up 5 hours ago frr
22cfc713890e quay.io/frrouting/frr:9.1.0 /usr/lib/frr/dock... 5 hours ago Up 5 hours ago frrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the container ID that you obtained in the previous step to check the BGP neighbor and routes in the external FRR container’s
vtyshsession. Run the following command:sudo podman exec -it <container_id> vtysh -c "show ip bgp"
$ sudo podman exec -it <container_id> vtysh -c "show ip bgp"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the
frr-k8spod for each cluster node by running the following command:oc -n openshift-frr-k8s get pod -owide
$ oc -n openshift-frr-k8s get pod -owideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, check BGP routes on the cluster node’s
frr-k8spod in the FRR container by running the following command:oc -n openshift-frr-k8s -c frr rsh frr-k8s-86wmq
$ oc -n openshift-frr-k8s -c frr rsh frr-k8s-86wmqCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the IP routes from the cluster node by running the following command:
vtysh
sh-5.1# vtyshCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Hello, this is FRRouting (version 8.5.3). Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al.
Hello, this is FRRouting (version 8.5.3). Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the IP routes by running the following command:
worker-2# show ip bgp
worker-2# show ip bgpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, debug the node by running the following command:
oc debug node/<node_name>
$ oc debug node/<node_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Temporary namespace openshift-debug-lbtgh is created for debugging node... Starting pod/worker-2-debug-zrg4v ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` Pod IP: 192.168.111.25 If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.
Temporary namespace openshift-debug-lbtgh is created for debugging node... Starting pod/worker-2-debug-zrg4v ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` Pod IP: 192.168.111.25 If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the BGP routes are being advertised by running the following command:
ip route show | grep bgp
sh-5.1# ip route show | grep bgpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow