Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 156. Apache Spark
Apache Spark component
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
This documentation page covers the Apache Spark component for Apache Camel. The main purpose of the Spark integration with Camel is to provide a bridge between Camel connectors and Spark tasks. In particular Camel connector provides a way to route message from various transports, dynamically choose a task to execute, use incoming message as input data for that task and finally deliver the results of the execution back to the Camel pipeline.
Note
Apache Spark is not supported on Apache Karaf.
Supported architectural styles
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
Spark component can be used as a driver application deployed into an application server (or executed as a fat jar).
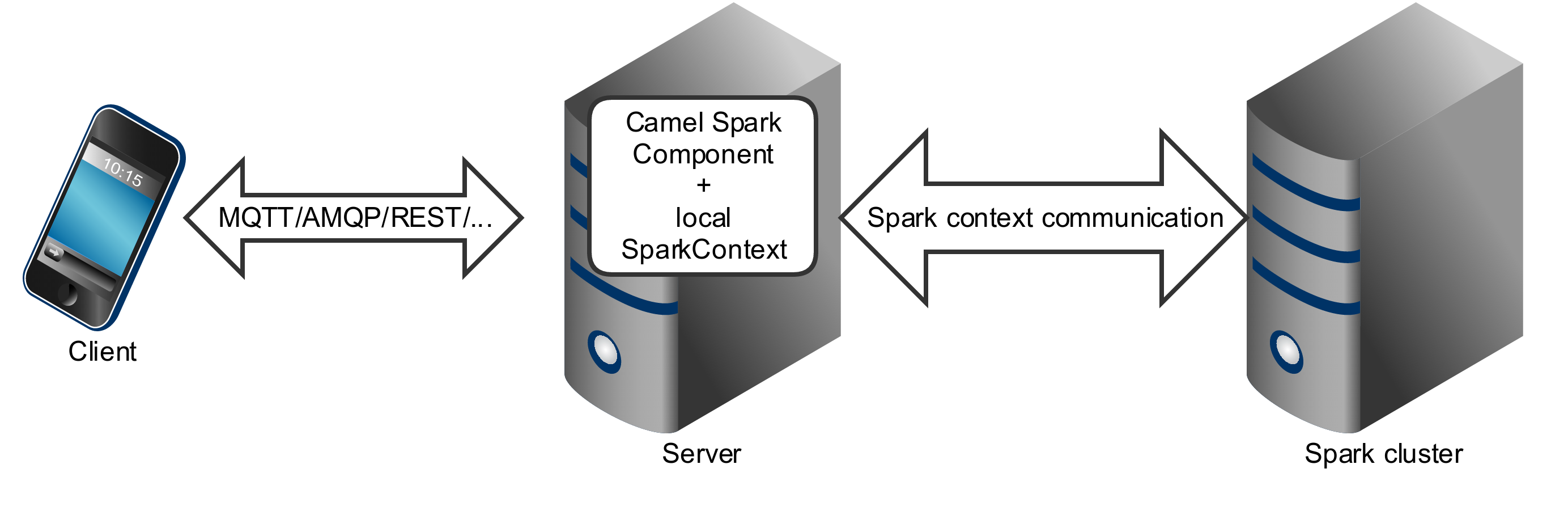
Spark component can also be submitted as a job directly into the Spark cluster.
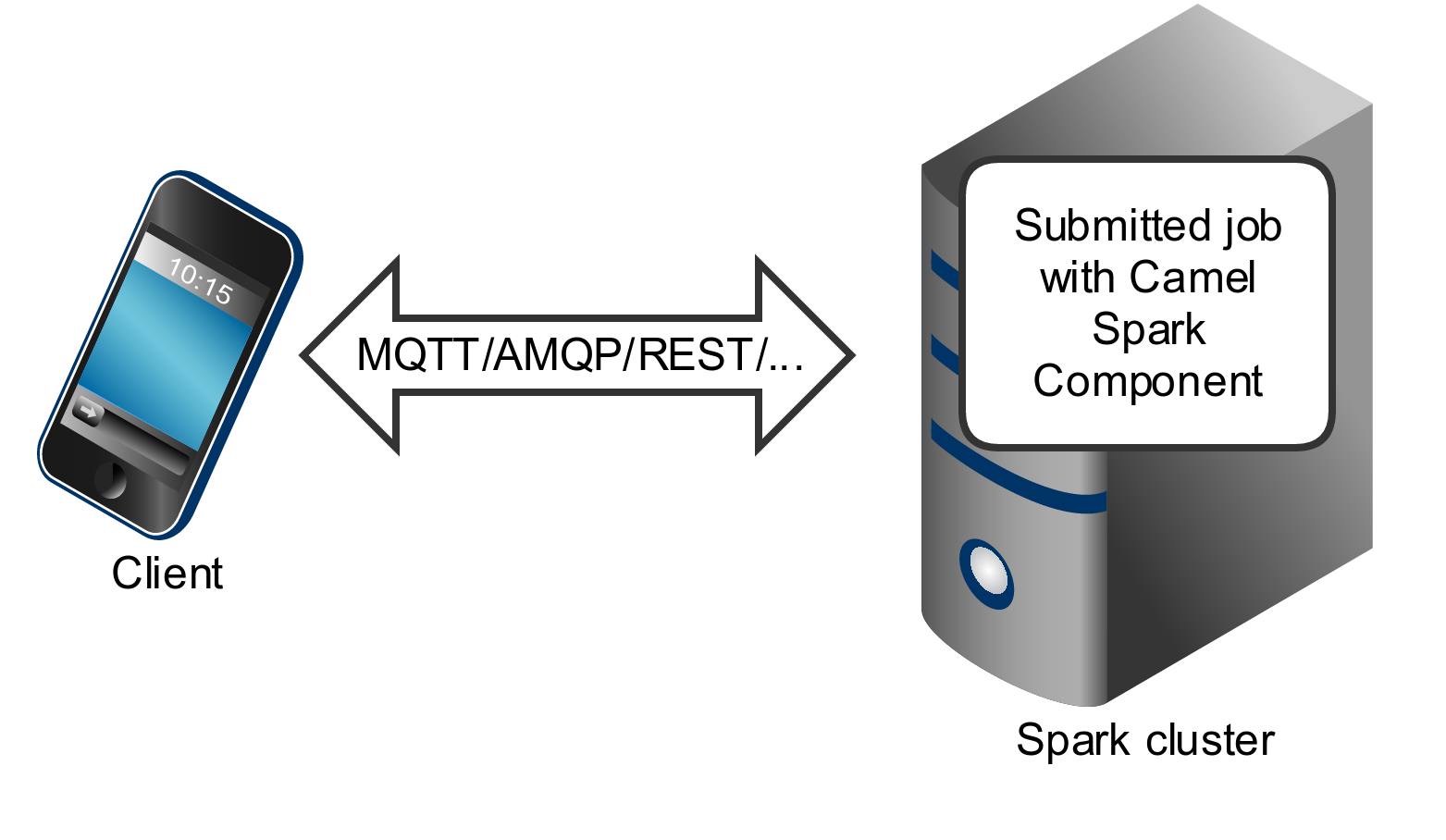
While Spark component is primary designed to work as a long running job serving as an bridge between Spark cluster and the other endpoints, you can also use it as a fire-once short job.
Running Spark in OSGi servers
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
Currently the Spark component doesn't support execution in the OSGi container. Spark has been designed to be executed as a fat jar, usually submitted as a job to a cluster. For those reasons running Spark in an OSGi server is at least challenging and is not support by Camel as well.
URI format
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
Currently the Spark component supports only producers - it it intended to invoke a Spark job and return results. You can call RDD, data frame or Hive SQL job.
spark:{rdd|dataframe|hive}
spark:{rdd|dataframe|hive}RDD jobs
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
To invoke an RDD job, use the following URI:
spark:rdd?rdd=#testFileRdd&rddCallback=#transformation
spark:rdd?rdd=#testFileRdd&rddCallback=#transformation
Where
rdd option refers to the name of an RDD instance (subclass of org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDDLike) from a Camel registry, while rddCallback refers to the implementation of org.apache.camel.component.spark.RddCallback interface (also from a registry). RDD callback provides a single method used to apply incoming messages against the given RDD. Results of callback computations are saved as a body to an exchange.
public interface RddCallback<T> {
T onRdd(JavaRDDLike rdd, Object... payloads);
}
public interface RddCallback<T> {
T onRdd(JavaRDDLike rdd, Object... payloads);
}
The following snippet demonstrates how to send message as an input to the job and return results:
String pattern = "job input";
long linesCount = producerTemplate.requestBody("spark:rdd?rdd=#myRdd&rddCallback=#countLinesContaining", pattern, long.class);
String pattern = "job input";
long linesCount = producerTemplate.requestBody("spark:rdd?rdd=#myRdd&rddCallback=#countLinesContaining", pattern, long.class);
The RDD callback for the snippet above registered as Spring bean could look as follows:
The RDD definition in Spring could looks as follows:
@Bean
JavaRDDLike myRdd(JavaSparkContext sparkContext) {
return sparkContext.textFile("testrdd.txt");
}
@Bean
JavaRDDLike myRdd(JavaSparkContext sparkContext) {
return sparkContext.textFile("testrdd.txt");
}RDD jobs options
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
| Option | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
rdd
|
RDD instance (subclass of org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDDLike).
|
null
|
rddCallback
|
Instance of org.apache.camel.component.spark.RddCallback interface.
|
null
|
Void RDD callbacks
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
If your RDD callback doesn't return any value back to a Camel pipeline, you can either return
null value or use VoidRddCallback base class:
Converting RDD callbacks
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
If you know what type of the input data will be sent to the RDD callback, you can use
ConvertingRddCallback and let Camel to automatically convert incoming messages before inserting those into the callback:
Annotated RDD callbacks
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
Probably the easiest way to work with the RDD callbacks is to provide class with method marked with
@RddCallback annotation:
If you will pass CamelContext to the annotated RDD callback factory method, the created callback will be able to convert incoming payloads to match the parameters of the annotated method:
DataFrame jobs
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
Instead of working with RDDs Spark component can work with DataFrames as well.
To invoke an DataFrame job, use the following URI:
spark:dataframe?dataFrame=#testDataFrame&dataFrameCallback=#transformation
spark:dataframe?dataFrame=#testDataFrame&dataFrameCallback=#transformation
Where
dataFrame option refers to the name of a DataFrame instance (instance of org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame) from a Camel registry, while dataFrameCallback refers to the implementation of org.apache.camel.component.spark.DataFrameCallback interface (also from a registry). DataFrame callback provides a single method used to apply incoming messages against the given DataFrame. Results of callback computations are saved as a body to an exchange.
public interface DataFrameCallback<T> {
T onDataFrame(DataFrame dataFrame, Object... payloads);
}
public interface DataFrameCallback<T> {
T onDataFrame(DataFrame dataFrame, Object... payloads);
}
The following snippet demonstrates how to send message as an input to a job and return results:
String model = "Micra";
long linesCount = producerTemplate.requestBody("spark:dataFrame?dataFrame=#cars&dataFrameCallback=#findCarWithModel", model, long.class);
String model = "Micra";
long linesCount = producerTemplate.requestBody("spark:dataFrame?dataFrame=#cars&dataFrameCallback=#findCarWithModel", model, long.class);
The DataFrame callback for the snippet above registered as Spring bean could look as follows:
The DataFrame definition in Spring could looks as follows:
DataFrame jobs options
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
| Option | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
dataFrame
|
DataFrame instance (subclass of org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame).
|
null
|
dataFrameCallback
|
Instance of org.apache.camel.component.spark.DataFrameCallback interface.
|
null
|
Hive jobs
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
Instead of working with RDDs or DataFrame Spark component can also receive Hive SQL queries as payloads. To send Hive query to Spark component, use the following URI:
spark:hive
spark:hive
The following snippet demonstrates how to send message as an input to a job and return results:
long carsCount = template.requestBody("spark:hive?collect=false", "SELECT * FROM cars", Long.class);
List<Row> cars = template.requestBody("spark:hive", "SELECT * FROM cars", List.class);
long carsCount = template.requestBody("spark:hive?collect=false", "SELECT * FROM cars", Long.class);
List<Row> cars = template.requestBody("spark:hive", "SELECT * FROM cars", List.class);
The table we want to execute query against should be registered in a HiveContext before we query it. For example in Spring such registration could look as follows:
Hive jobs options
Copia collegamentoCollegamento copiato negli appunti!
| Option | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
collect
|
Indicates if results should be collected (as a list of org.apache.spark.sql.Row instances) or if count() should be called against those.
|
true
|