Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 12. Login Modules
12.1. Using Modules
12.1.1. LdapLoginModule
LdapLoginModule is a LoginModule implementation that authenticates against a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server. Use the LdapLoginModule if your user name and credentials are stored in an LDAP server that is accessible using a Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) LDAP provider.
Note
- Distinguished Name (DN)
- In Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), the distinguished name uniquely identifies an object in a directory. Each distinguished name must have a unique name and location from all other objects, which is achieved using a number of attribute-value pairs (AVPs). The AVPs define information such as common names, organization unit, among others. The combination of these values results in a unique string required by the LDAP.
Note
- java.naming.factory.initial
InitialContextFactoryimplementation class name. This defaults to the Sun LDAP provider implementationcom.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory.- java.naming.provider.url
- LDAP URL for the LDAP server.
- java.naming.security.authentication
- Security protocol level to use. The available values include
none,simple, andstrong. If the property is undefined, the behavior is determined by the service provider. - java.naming.security.protocol
- Transport protocol to use for secure access. Set this configuration option to the type of service provider (for example, SSL). If the property is undefined, the behavior is determined by the service provider.
- java.naming.security.principal
- Specifies the identity of the Principal for authenticating the caller to the service. This is built from other properties as described below.
- java.naming.security.credentials
- Specifies the credentials of the Principal for authenticating the caller to the service. Credentials can take the form of a hashed password, a clear-text password, a key, or a certificate. If the property is undefined, the behavior is determined by the service provider.
- principalDNPrefix
- Prefix added to the user name to form the user distinguished name . See
principalDNSuffixfor more info. - principalDNSuffix
- Suffix added to the user name when forming the user distinguished name. This is useful if you prompt a user for a user name and you do not want the user to have to enter the fully distinguished name. Using this property and
principalDNSuffixtheuserDNwill be formed asprincipalDNPrefix + username + principalDNSuffix - rolesCtxDN
- Fixed, distinguished name to the context for searching user roles.
- userRolesCtxDNAttributeName
- Name of an attribute in the user object that contains the distinguished name to the context to search for user roles. This differs from
rolesCtxDNin that the context to search for a user's roles can be unique for each user. - roleAttributeID
- Name of the attribute containing the user roles. If not specified, this defaults to
roles. - roleAttributeIsDN
- Flag indicating whether the roleAttributeID contains the fully distinguished name of a role object, or the role name. The role name is taken from the value of the roleNameAttributeId attribute of the context name by the distinguished name.If true, the role attribute represents the distinguished name of a role object. If false, the role name is taken from the value of
roleAttributeID. The default isfalse.Note
In certain directory schemas (e.g., MS ActiveDirectory), role attributes in the user object are stored as DNs to role objects instead of simple names. For implementations that use this schema type, roleAttributeIsDN must be set totrue. - roleNameAttributeID
- Name of the attribute of the context pointed to by the roleCtxDN distinguished name value which contains the role name. If the roleAttributeIsDN property is set to
true, this property is used to find the role object'snameattribute. The default isgroup. - uidAttributeID
- Name of the attribute in the object containing the user roles that corresponds to the user ID. This is used to locate the user roles. If not specified this defaults to
uid. - matchOnUserDN
- Flag that specifies whether the search for user roles should match on the user's fully distinguished name. If
true, the fulluserDNis used as the match value. Iffalse, only the user name is used as the match value against the uidAttributeName attribute. The default value isfalse. - unauthenticatedIdentity
- Principal name to assign to requests containing no authentication information. This behavior is inherited from the
UsernamePasswordLoginModulesuperclass. - allowEmptyPasswords
- A flag indicating if empty (length 0) passwords should be passed to the LDAP server. An empty password is treated as an anonymous log in by some LDAP servers, and this may not be a desirable feature. To reject empty passwords, set this to
false. If set totrue, the LDAP server will validate the empty password. The default istrue. - searchTimeLimit
- The timeout in milliseconds for the user/role searches. Defaults to 10000 (10 seconds).
- searchScope
- Sets the search scope to one of the strings. The default is SUBTREE_SCOPE. Other supported values include:
- OBJECT_SCOPE : only search the named roles context.
- ONELEVEL_SCOPE : search directly under the named roles context.
- SUBTREE_SCOPE : If the roles context is not a DirContext, search only the object. If the roles context is a DirContext, search the subtree rooted at the named object, including the named object itself.
- jaasSecurityDomain
- The JMX ObjectName of the JaasSecurityDomain used to decrypt the java.naming.security.principal. The encrypted form of the password is that returned by the JaasSecurityDomainencrypt64(byte[]) method. The org.jboss.security.plugins.PBEUtils can also be used to generate the encrypted form.
InitialLdapContext with an environment composed of the LDAP JNDI properties described previously in this section.
InitialLdapContext instance is created), the user's roles are queried by performing a search on the rolesCtxDN location with search attributes set to the roleAttributeName and uidAttributeName option values. The roles names are obtaining by invoking the toString method on the role attributes in the search result set.
Example 12.1. LDAP Login Module Authentication Policy
java.naming.factory.initial, java.naming.factory.url and java.naming.security options in the testLDAP <login-module> configuration indicate the following conditions:
- The Sun LDAP JNDI provider implementation will be used
- The LDAP server is located on host
ldaphost.jboss.orgon port 1389 - The LDAP simple authentication method will be use to connect to the LDAP server.
jsmith would map to uid=jsmith,ou=People,dc=jboss,dc=org.
Note
userPassword attribute of the user's entry (theduke in this example). Most LDAP servers operate in this manner, however if your LDAP server handles authentication differently you must ensure LDAP is configured according to your production environment requirements.
rolesCtxDN for entries whose uidAttributeID match the user. If matchOnUserDN is true, the search will be based on the full DN of the user. Otherwise the search will be based on the actual user name entered. In this example, the search is under ou=Roles,dc=jboss,dc=org for any entries that have a member attribute equal to uid=jduke,ou=People,dc=jboss,dc=org. The search would locate cn=JBossAdmin under the roles entry.
cn. The value returned would be JBossAdmin, so the jsmith user is assigned to the JBossAdmin role.
- LDAP Data Interchange Format (LDIF)
- Plain text data interchange format used to represent LDAP directory content and update requests. Directory content is represented as one record for each object or update request. Content consists of add, modify, delete, and rename requests.
Example 12.2. LDIF File Example
12.1.2. LdapExtLoginModule
- Distinguished Name (DN)
- In Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), the distinguished name uniquely identifies an object in a directory. Each distinguished name must have a unique name and location from all other objects, which is achieved using a number of attribute-value pairs (AVPs). The AVPs define information such as common names, organization unit, among others. The combination of these values results in a unique string required by the LDAP.
org.jboss.security.auth.spi.LdapExtLoginModule searches for the user to bind, as well as the associated roles, for authentication. The roles query recursively follows DNs to navigate a hierarchical role structure.
- Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY = "java.naming.factory.initial"
- Context.SECURITY_PROTOCOL = "java.naming.security.protocol"
- Context.PROVIDER_URL = "java.naming.provider.url"
- Context.SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION = "java.naming.security.authentication"
- Context.REFERRAL = "java.naming.referral"
- The initial LDAP server bind is authenticated using the bindDN and bindCredential properties. The bindDN is a user with permissions to search both the baseCtxDN and rolesCtxDN trees for the user and roles. The user DN to authenticate against is queried using the filter specified by the baseFilter property.
- The resulting userDN is authenticated by binding to the LDAP server using the userDN as the InitialLdapContext environment Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL. The Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS property is either set to the String password obtained by the callback handler.
- If this is successful, the associated user roles are queried using the rolesCtxDN, roleAttributeID, roleAttributeIsDN, roleNameAttributeID, and roleFilter options.
LdapExtLoginModule Properties
- baseCtxDN
- Specifies the fixed DN of the context to start the user search from.
- bindDN
- Specifies the DN used to bind against the LDAP server for the user and role queries. Set bindDN to a DN with read/search permissions on the baseCtxDN and rolesCtxDn properties.
- bindCredential
- The password for the bindDN. bindCredential can be encrypted if jaasSecurityDomain is specified. This property allows an external command to read the password. For example
{EXT}cat file_with_password. - jaasSecurityDomain
- The JMX ObjectName of the JaasSecurityDomain used to decrypt the
java.naming.security.principal. The encrypted form of the password is that returned by theJaasSecurityDomainencrypt64(byte[])method. The org.jboss.security.plugins.PBEUtils can also be used to generate the encrypted form. - baseFilter
- A search filter used to locate the context of the user to authenticate. The input username/userDN as obtained from the login module callback is substituted into the filter anywhere a
{0}expression exists. This substitution behavior originates from the standardDirContext.search(Name, String, Object[], SearchControls cons)method. An common example search filter is(uid={0}). - rolesCtxDN
- The fixed DN of the context to search for user roles. This is not the DN of where the actual roles are; this is the DN of where the objects containing the user roles are. For example, in active directory, this is the DN where the user account is.
- roleFilter
- Search filter used to locate the roles associated with the authenticated user. The input username/userDN as obtained from the login module callback is substituted into the filter anywhere a
{0}expression exists. The authenticated userDN is substituted into the filter anywhere a{1}is seen. An example search filter that matches on the input username is(member={0}). An alternative that matches on the authenticated userDN is(member={1}). - roleAttributeIsDN
- Flag indicating whether the roleAttributeID contains the full DN of a role object, or the role name. The role name is derived from the value of the roleNameAttributeId attribute of the context name by the distinguished name.If set to
true, the role attribute represents the distinguished name of a role object. If set tofalse, the role name is taken from the value ofroleAttributeID. The default isfalse.Note
In certain directory schemas (e.g., MS ActiveDirectory), role attributes in the user object are stored as DNs to role objects instead of simple names. For implementations that use this schema type, roleAttributeIsDN must be set totrue. - roleAttributeID
- Name of the attribute containing the user roles. If roleAttributeIsDN is set to
true, this property is the DN of the context to query for the roleNameAttributeID attribute. If the roleAttributeIsDN property is set tofalse, this property is the attribute name of the role name. - roleNameAttributeID
- Name of the attribute of the context pointed to by the roleCtxDN distinguished name value which contains the role name. If the roleAttributeIsDN property is set to
true, this property is used to find the role object'snameattribute. The default isgroup. - roleRecursion
- Specifies how many levels the role search traverses a given matching context. The default is
0(deactivated). - searchTimeLimit
- The timeout in milliseconds for the user/role searches. Defaults to 10000 (10 seconds).
- searchScope
- Sets the search scope to one of the strings. The default is SUBTREE_SCOPE. Other supported values include:
- OBJECT_SCOPE : only search the named roles context.
- ONELEVEL_SCOPE : search directly under the named roles context.
- SUBTREE_SCOPE : If the roles context is not a DirContext, search only the object. If the roles context is a DirContext, search the subtree rooted at the named object, including the named object itself.
- allowEmptyPasswords
- A flag indicating if
empty(length==0)passwords should be passed to the LDAP server.An empty password is treated as an anonymous log in by some LDAP servers. If set tofalse, empty passwords are rejected. If set totrue, the LDAP server validates the empty password. The default istrue. - defaultRole
- A role included for all authenticated users.
- parseRoleNameFromDN
- A flag indicating if the DN returned by a query contains the roleNameAttributeID. If set to
true, the DN is checked for the roleNameAttributeID. If set tofalse, the DN is not checked for the roleNameAttributeID. This flag can improve the performance of LDAP queries. - parseUsername
- A flag indicating if the DN is to be parsed for the username. If set to
true, the DN is parsed for the username. If set tofalsethe DN is not parsed for the username. This option is used together with usernameBeginString and usernameEndString. - usernameBeginString
- Defines the string which is to be removed from the start of the DN to reveal the username. This option is used together with usernameEndString.
- usernameEndString
- Defines the string which is to be removed from the end of the DN to reveal the username. This option is used together with usernameBeginString.
- distinguishedNameAttribute
- Defines a distinguished name to provide a unique 'path' to any object in the LDAP database.
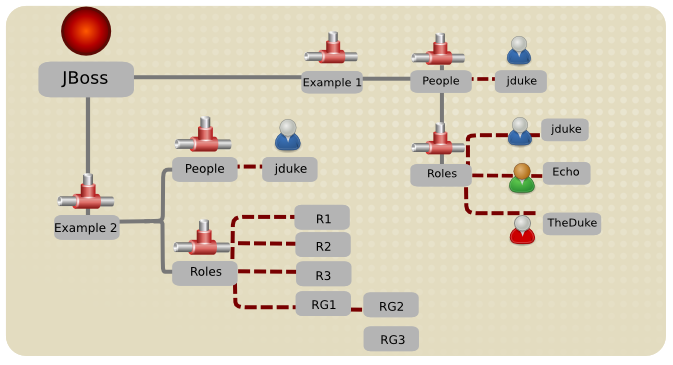
Figure 12.1. LDAP Structure Example
Example 12.3. Example 2 LDAP Configuration
Example 12.4. Example 3 LDAP Configuration
Example 12.5. Example 4 LDAP Configuration
Example 12.6. Default ActiveDirectory Configuration
Example 12.7. Recursive Roles ActiveDirectory Configuration
12.1.3. Password Stacking
password-stacking attribute to useFirstPass. If a previous module configured for password stacking has authenticated the user, all the other stacking modules will consider the user authenticated and only attempt to provide a set of roles for the authorization step.
password-stacking option is set to useFirstPass, this module first looks for a shared user name and password under the property names javax.security.auth.login.name and javax.security.auth.login.password respectively in the login module shared state map.
Note
Example 12.8. Password Stacking Sample
12.1.4. Password Hashing
Example 12.9. Password Hashing
nobody and contains based64-encoded, MD5 hashes of the passwords in a usersb64.properties file. The usersb64.properties file can be part of the deployment classpath, or be saved in the /conf directory.
- hashAlgorithm
- Name of the
java.security.MessageDigestalgorithm to use to hash the password. There is no default so this option must be specified to enable hashing. Typical values areMD5andSHA. - hashEncoding
- String that specifies one of three encoding types:
base64,hexorrfc2617. The default isbase64. - hashCharset
- Encoding character set used to convert the clear text password to a byte array. The platform default encoding is the default.
- hashUserPassword
- Specifies the hashing algorithm must be applied to the password the user submits. The hashed user password is compared against the value in the login module, which is expected to be a hash of the password. The default is
true. - hashStorePassword
- Specifies the hashing algorithm must be applied to the password stored on the server side. This is used for digest authentication, where the user submits a hash of the user password along with a request-specific tokens from the server to be compare. The hash algorithm (for digest, this would be
rfc2617) is utilized to compute a server-side hash, which should match the hashed value sent from the client.
org.jboss.security.Util class provides a static helper method that will hash a password using the specified encoding. The following example produces a base64-encoded, MD5 hashed password.
String hashedPassword = Util.createPasswordHash("MD5",
Util.BASE64_ENCODING, null, null, "password");
String hashedPassword = Util.createPasswordHash("MD5",
Util.BASE64_ENCODING, null, null, "password");
password - is piped into the OpenSSL digest function then piped into another OpenSSL function to convert into base64-encoded format.
echo -n password | openssl dgst -md5 -binary | openssl base64
echo -n password | openssl dgst -md5 -binary | openssl base64X03MO1qnZdYdgyfeuILPmQ==. This value must be stored in the users properties file specified in the application policy - usersb64.properties - in the example above.
12.1.5. Unauthenticated Identity
unauthenticatedIdentity is a login module configuration option that assigns a specific identity (guest, for example) to requests that are made with no associated authentication information. This can be used to allow unprotected servlets to invoke methods on EJBs that do not require a specific role. Such a principal has no associated roles and so can only access either unsecured EJBs or EJB methods that are associated with the unchecked permission constraint.
- unauthenticatedIdentity: This defines the principal name that should be assigned to requests that contain no authentication information.
12.1.6. UsersRolesLoginModule
UsersRolesLoginModule is a simple login module that supports multiple users and user roles loaded from Java properties files. The user name-to-password mapping file is called users.properties and the user name-to-roles mapping file is called roles.properties.
- usersProperties
- Name of the properties resource (file) containing the user name to password mappings. This defaults to
<file_prefix>-users.properties. - rolesProperties
- Name of the properties resource (file) containing the user name to roles mappings. This defaults to
<file_prefix>-roles.properties.
Example 12.10. UserRolesLoginModule
ejb3-sampleapp-users.properties file uses a username=password format with each user entry on a separate line:
username1=password1 username2=password2 ...
username1=password1
username2=password2
...
ejb3-sampleapp-roles.properties file referenced in Example 12.10, “UserRolesLoginModule” uses the pattern username=role1,role2, with an optional group name value. For example:
username1=role1,role2,... username1.RoleGroup1=role3,role4,... username2=role1,role3,...
username1=role1,role2,...
username1.RoleGroup1=role3,role4,...
username2=role1,role3,...
ejb3-sampleapp-roles.properties is used to assign the user name roles to a particular named group of roles where the XXX portion of the property name is the group name. The user name=... form is an abbreviation for user name.Roles=..., where the Roles group name is the standard name the JaasSecurityManager expects to contain the roles which define the users permissions.
jduke user name:
jduke=TheDuke,AnimatedCharacter jduke.Roles=TheDuke,AnimatedCharacter
jduke=TheDuke,AnimatedCharacter
jduke.Roles=TheDuke,AnimatedCharacter
12.1.7. DatabaseServerLoginModule
DatabaseServerLoginModule is a Java Database Connectivity-based (JDBC) login module that supports authentication and role mapping. Use this login module if you have your user name, password and role information stored in a relational database.
Note
DatabaseServerLoginModule is based on two logical tables:
Table Principals(PrincipalID text, Password text) Table Roles(PrincipalID text, Role text, RoleGroup text)
Table Principals(PrincipalID text, Password text)
Table Roles(PrincipalID text, Role text, RoleGroup text)
Principals table associates the user PrincipalID with the valid password and the Roles table associates the user PrincipalID with its role sets. The roles used for user permissions must be contained in rows with a RoleGroup column value of Roles.
java.sql.ResultSet has the same logical structure as the Principals and Roles tables described previously. The actual names of the tables and columns are not relevant as the results are accessed based on the column index.
Principals and Roles, as already declared. The following statements populate the tables with the following data:
PrincipalIDjavawith aPasswordofechomanin thePrincipalstablePrincipalIDjavawith a role namedEchoin theRolesRoleGroupin theRolestablePrincipalIDjavawith a role namedcaller_javain theCallerPrincipalRoleGroupin theRolestable
INSERT INTO Principals VALUES('java', 'echoman')
INSERT INTO Roles VALUES('java', 'Echo', 'Roles')
INSERT INTO Roles VALUES('java', 'caller_java', 'CallerPrincipal')
INSERT INTO Principals VALUES('java', 'echoman')
INSERT INTO Roles VALUES('java', 'Echo', 'Roles')
INSERT INTO Roles VALUES('java', 'caller_java', 'CallerPrincipal')
- dsJndiName
- The JNDI name for the
DataSourceof the database containing the logicalPrincipalsandRolestables. If not specified this defaults tojava:/DefaultDS. - principalsQuery
- The prepared statement query equivalent to:
select Password from Principals where PrincipalID=?. If not specified this is the exact prepared statement that will be used. - rolesQuery
- The prepared statement query equivalent to:
select Role, RoleGroup from Roles where PrincipalID=?. If not specified this is the exact prepared statement that will be used. - ignorePasswordCase
- A boolean flag indicating if the password comparison should ignore case. This can be useful for hashed password encoding where the case of the hashed password is not significant.
- principalClass
- An option that specifies a
Principalimplementation class. This must support a constructor taking a string argument for the principal name. - transactionManagerJndiName
- The JNDI name of the transaction manager used by the login module. If no value is provided, the default
java:/TransactionManageris used. - suspendResume
- A boolean flag indicating whether an active transaction associated with the current thread should be suspended during a database operation and resumed after the operation is completed. The default value is
true.
DatabaseServerLoginModule configuration could be constructed as follows:
CREATE TABLE Users(username VARCHAR(64) PRIMARY KEY, passwd VARCHAR(64)) CREATE TABLE UserRoles(username VARCHAR(64), userRoles VARCHAR(32))
CREATE TABLE Users(username VARCHAR(64) PRIMARY KEY, passwd VARCHAR(64))
CREATE TABLE UserRoles(username VARCHAR(64), userRoles VARCHAR(32))
login-config.xml entry would be:
12.1.8. BaseCertLoginModule
BaseCertLoginModule authenticates users based on X509 certificates. A typical use case for this login module is CLIENT-CERT authentication in the web tier.
CertRolesLoginModule and DatabaseCertLoginModule extend the behavior to obtain the authorization roles from either a properties file or database.
BaseCertLoginModule needs a KeyStore to perform user validation. This is obtained through a org.jboss.security.SecurityDomain implementation. Typically, the SecurityDomain implementation is configured using the org.jboss.security.plugins.JaasSecurityDomain MBean as shown in this jboss-service.xml configuration fragment:
jmx-console, with a SecurityDomain implementation available through JNDI under the name java:/jaas/jmx-console. The security domain follows the JBossSX security domain naming pattern.
Procedure 12.1. Secure Web Applications with Certificates and Role-based Authorization
jmx-console.war, using client certificates and role-based authorization.
Declare Resources and Roles
Modifyweb.xmlto declare the resources to be secured along with the allowed roles and security domain to be used for authentication and authorization.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the JBoss Security Domain
In thejboss-web.xmlfile, specify the required security domain.<jboss-web> <security-domain>jmx-console</security-domain> </jboss-web>
<jboss-web> <security-domain>jmx-console</security-domain> </jboss-web>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify Login Module Configuration
Define the login module configuration for the jmx-console security domain you just specified. This is done in theconf/login-config.xmlfile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
BaseCertLoginModule is used for authentication of the client cert, and the UsersRolesLoginModule is only used for authorization due to the password-stacking=useFirstPass option. Both the localhost.keystore and the jmx-console-roles.properties require an entry that maps to the principal associated with the client cert.
Example 12.11. Certificate Example
localhost.keystore would need the certificate in Example 12.11, “Certificate Example” stored with an alias of CN=unit-tests-client, OU=JBoss Inc., O=JBoss Inc., ST=Washington, C=US. The jmx-console-roles.properties would also need an entry for the same entry. Since the DN contains characters that are normally treated as delimiters, you must escape the problem characters using a backslash ('\') as illustrated below.
# A sample roles.properties file for use with the UsersRolesLoginModule CN\=unit-tests-client,\ OU\=JBoss\ Inc.,\ O\=JBoss\ Inc.,\ ST\=Washington,\ C\=US=JBossAdmin admin=JBossAdmin
# A sample roles.properties file for use with the UsersRolesLoginModule
CN\=unit-tests-client,\ OU\=JBoss\ Inc.,\ O\=JBoss\ Inc.,\ ST\=Washington,\ C\=US=JBossAdmin
admin=JBossAdmin12.1.9. IdentityLoginModule
IdentityLoginModule is a simple login module that associates a hard-coded user name to any subject authenticated against the module. It creates a SimplePrincipal instance using the name specified by the principal option.
Note
- principal
- This is the name to use for the
SimplePrincipalall users are authenticated as. The principal name defaults toguestif no principal option is specified. - roles
- This is a comma-delimited list of roles that will be assigned to the user.
jduke and assign role names of TheDuke, and AnimatedCharacter:.
12.1.10. RunAsLoginModule
RunAsLoginModule (org.jboss.security.auth.spi.RunAsLoginModule) is a helper module that pushes a run as role onto the stack for the duration of the log in phase of authentication, and pops the run as role in either the commit or abort phase.
RunAsLoginModule must be configured ahead of the login modules that require a run as role established.
- roleName
- Name of the role to use as the run as role during log in phase. If not specified a default of
nobodyis used.
12.1.11. RunAsIdentity Creation
javax.security.auth.Subject instance or an org.jboss.security.RunAsIdentity instance. Both these classes store one or more principals that represent the identity and a list of roles that the identity possesses. In the case of the javax.security.auth.Subject a list of credentials is also stored.
ejb-jar.xml deployment descriptor, you specify one or more roles that a user must have to access the various EJB methods. A comparison of these lists reveals whether the user has one of the roles necessary to access the EJB method.
Example 12.12. org.jboss.security.RunAsIdentity Creation
ejb-jar.xml file, you specify a <security-identity> element with a <run-as> role defined as a child of the <session> element.
<run-as-principal> element in the jboss-web.xml file.
<security-identity> element in both the ejb-jar.xml and jboss-web.xml files are parsed at deployment time. The <run-as> role name and the <run-as-principal> name are then stored in the org.jboss.metadata.SecurityIdentityMetaData class.
Example 12.13. Assigning multiple roles to a RunAsIdentity
jboss-web.xml deployment descriptor <assembly-descriptor> element group.
<run-as-principal> of "Mark" was created. The configuration in this example extends the "Admin" role, by adding the "Support" role. The new role contains extra principals, including the originally defined principal "John".
<security-role> element in both the ejb-jar.xml and jboss.xml files are parsed at deployment time. The <role-name> and the <principal-name> data is stored in the org.jboss.metadata.SecurityIdentityMetaData class.
12.1.12. ClientLoginModule
ClientLoginModule (org.jboss.security.ClientLoginModule) is an implementation of LoginModule for use by JBoss clients for establishing caller identity and credentials. This simply sets the org.jboss.security.SecurityAssociation.principal to the value of the NameCallback filled in by the callbackhandler, and the org.jboss.security.SecurityAssociation.credential to the value of the PasswordCallback filled in by the callbackhandler.
ClientLoginModule is the only supported mechanism for a client to establish the current thread's caller. Both stand-alone client applications, and server environments (acting as JBoss EJB clients where the security environment has not been configured to use JBossSX transparently) must use ClientLoginModule.
ClientLoginModule.
- multi-threaded
- Value that specifies the way login threads connect to principal and credential storage sources. When set to true, each login thread has its own principal and credential storage and each separate thread must perform its own log in. This is useful in client environments where multiple user identities are active in separate threads. When set to false the login identity and credentials are global variables that apply to all threads in the VM. The default setting is
false. - password-stacking
- Activates client-side authentication of clients using other login modules such as the
LdapLoginModule. Whenpassword-stackingoption is set touseFirstPass, the module first looks for a shared user name and password usingjavax.security.auth.login.nameandjavax.security.auth.login.passwordrespectively in the login module shared state map. This allows a module configured prior to this one to establish a valid JBoss user name and password. - restore-login-identity
- Value that specifies whether the
SecurityAssociationprincipal and credential seen on entry to thelogin()method are saved and restored on either abort or logout. This is necessary if you must change identities and then restore the original caller identity. If set totrue, the principal and credential information is saved and restored on abort or logout. If set tofalse, abort and logout clear theSecurityAssociation. The default value isfalse.
12.1.13. SPNEGOLoginModule
SPNEGOLoginModule (org.jboss.security.negotiation.spnego.SPNEGOLoginModule) is an implementation of LoginModule that establishes caller identity and credentials with a KDC. The module implements SPNEGO (Simple and Protected GSSAPI Negotiation mechanism) and is a part of the JBoss Negotiation project. This authentication can be used in the chained configuration with the AdvancedLDAPLoginModule to allow cooperation with an LDAP server. For further information on JBoss Negotiation refer to the Negotiation User Guide.
12.1.14. RoleMappingLoginModule
RoleMappingLoginModule is a login module that supports mapping roles that are the end result of the authentication process to one or more declarative roles; for example, if the authentication process has determined that the user "A" has the roles "ldapAdmin" and "testAdmin", and the declarative role defined in the web.xml or ejb-jar.xml file for access is "admin", then this login module maps the "admin" roles to the user "A".
- rolesProperties
- Name of the properties file that defines the addition/substitution rules; the value defines the file in the form as located using Classloader or with its absolute location given by the java.net.url pattern (for example,
file:/rolesMap.properties) - replaceRole
- Flag determining if the key role is replaced with the mapped roles or the mapped roles are added to the key role (set to
trueto have the key role replaced with the mapped roles)
RoleMappingLoginModule must be defined as an optional module to a login module configuration as it alters mapping of the previously mapped roles.
Example 12.14. Properties File used by a RoleMappingLoginModule
ldapAdmin=admin, testAdmin
ldapAdmin=admin, testAdmin