Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Chapter 4. Configuring Red Hat OpenStack Platform for Service Telemetry Framework
To collect metrics, events, or both, and to send them to the Service Telemetry Framework (STF) storage domain, you must configure the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) overcloud to enable data collection and transport.
STF can support both single and multiple clouds. The default configuration in RHOSP and STF set up for a single cloud installation.
- For a single RHOSP overcloud deployment with default configuration, see Section 4.1, “Deploying Red Hat OpenStack Platform overcloud for Service Telemetry Framework”.
- To plan your RHOSP installation and configuration STF for multiple clouds, see Section 4.4, “Configuring multiple clouds”.
As part of an RHOSP overcloud deployment, you might need to configure additional features in your environment:
- To deploy data collection and transport to STF on RHOSP cloud nodes that employ routed L3 domains, such as distributed compute node (DCN) or spine-leaf, see Section 4.2, “Deploying to non-standard network topologies”.
- If you synchronized container images to a local registry, you must create an environment file and include the paths to the container images. For more information, see Section 4.3, “Adding Red Hat OpenStack Platform container images to the undercloud”.
4.1. Deploying Red Hat OpenStack Platform overcloud for Service Telemetry Framework
To configure the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) overcloud, you must configure the data collectors and the data transport to Service Telemetry Framework (STF), and deploy the overcloud.
Procedure
4.1.1. Getting CA certificate from Service Telemetry Framework for overcloud configuration
To connect your Red Hat OpenStack Platform overcloud to Service Telemetry Framework (STF), retrieve the CA certificate of AMQ Interconnect that runs within Service Telemetry Framework and use the certificate in the Red Hat OpenStack Platform configuration.
Procedure
View a list of available certificates in Service Telemetry Framework:
oc get secrets
$ oc get secretsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Retrieve and note the content of the
default-interconnect-selfsignedSecret:oc get secret/default-interconnect-selfsigned -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}' | base64 -d$ oc get secret/default-interconnect-selfsigned -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}' | base64 -dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.1.2. Retrieving the AMQ Interconnect route address
When you configure the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) overcloud for Service Telemetry Framework (STF), you must provide the AMQ Interconnect route address in the STF connection file.
Procedure
- Log in to your Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform environment.
In the
service-telemetryproject, retrieve the AMQ Interconnect route address:oc get routes -ogo-template='{{ range .items }}{{printf "%s\n" .spec.host }}{{ end }}' | grep "\-5671"$ oc get routes -ogo-template='{{ range .items }}{{printf "%s\n" .spec.host }}{{ end }}' | grep "\-5671" default-interconnect-5671-service-telemetry.apps.infra.watchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.1.3. Creating the base configuration for STF
To configure the base parameters to provide a compatible data collection and transport for Service Telemetry Framework (STF), you must create a file that defines the default data collection values.
Procedure
-
Log in to the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) undercloud as the
stackuser. Create a configuration file called
enable-stf.yamlin the/home/stackdirectory.ImportantSetting
EventPipelinePublishersandPipelinePublishersto empty lists results in no event or metric data passing to RHOSP legacy telemetry components, such as Gnocchi or Panko. If you need to send data to additional pipelines, the Ceilometer polling interval of 30 seconds, as specified inExtraConfig, might overwhelm the legacy components, and you must increase the interval to a larger value, such as300. Increasing the value to a longer polling interval results in less telemetry resolution in STF.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.1.4. Configuring the STF connection for the overcloud
To configure the Service Telemetry Framework (STF) connection, you must create a file that contains the connection configuration of the AMQ Interconnect for the overcloud to the STF deployment. Enable the collection of events and storage of the events in STF and deploy the overcloud. The default configuration is for a single cloud instance with the default message bus topics. For configuration of multiple cloud deployments, see Section 4.4, “Configuring multiple clouds”.
Prerequisites
- Retrieve the CA certificate from the AMQ Interconnect deployed by STF. For more information, see Section 4.1.1, “Getting CA certificate from Service Telemetry Framework for overcloud configuration”.
- Retrieve the AMQ Interconnect route address. For more information, see Section 4.1.2, “Retrieving the AMQ Interconnect route address”.
Procedure
-
Log in to the RHOSP undercloud as the
stackuser. -
Create a configuration file called
stf-connectors.yamlin the/home/stackdirectory. In the
stf-connectors.yamlfile, configure theMetricsQdrConnectorsaddress to connect the AMQ Interconnect on the overcloud to the STF deployment.-
Replace the
hostparameter with the value ofHOST/PORTthat you retrieved in Section 4.1.2, “Retrieving the AMQ Interconnect route address”. Replace the
caCertFileContentparameter with the contents retrieved in Section 4.1.1, “Getting CA certificate from Service Telemetry Framework for overcloud configuration”.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Replace the
4.1.5. Deploying the overcloud
Deploy or update the overcloud with the required environment files so that data is collected and transmitted to Service Telemetry Framework (STF).
Procedure
-
Log in to the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) undercloud as the
stackuser. Source the authentication file:
source stackrc
[stack@undercloud-0 ~]$ source stackrc (undercloud) [stack@undercloud-0 ~]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the following files to your RHOSP director deployment to configure data collection and AMQ Interconnect:
-
The
collectd-write-qdr.yamlfile to ensure that collectd telemetry and events are sent to STF -
The
ceilometer-write-qdr.yamlfile to ensure that Ceilometer telemetry and events are sent to STF -
The
qdr-edge-only.yamlfile to ensure that the message bus is enabled and connected to STF message bus routers -
The
enable-stf.yamlenvironment file to ensure defaults are configured correctly The
stf-connectors.yamlenvironment file to define the connection to STFCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
The
- Deploy the overcloud.
4.1.6. Validating client-side installation
To validate data collection from the Service Telemetry Framework (STF) storage domain, query the data sources for delivered data. To validate individual nodes in the Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) deployment, use SSH to connect to the console.
Some telemetry data is available only when RHOSP has active workloads.
Procedure
- Log in to an overcloud node, for example, controller-0.
Ensure that the
metrics_qdrcontainer is running on the node:sudo docker container inspect --format '{{.State.Status}}' metrics_qdr$ sudo docker container inspect --format '{{.State.Status}}' metrics_qdr runningCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Return the internal network address on which AMQ Interconnect is running, for example,
172.17.1.44listening on port5666:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Return a list of connections to the local AMQ Interconnect:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow There are four connections:
- Outbound connection to STF
- Inbound connection from ceilometer
- Inbound connection from collectd
Inbound connection from our
qdstatclientThe outbound STF connection is provided to the
MetricsQdrConnectorshost parameter and is the route for the STF storage domain. The other hosts are internal network addresses of the client connections to this AMQ Interconnect.
To ensure that messages are delivered, list the links, and view the
_edgeaddress in thedelivcolumn for delivery of messages:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To list the addresses from RHOSP nodes to STF, connect to Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform to retrieve the AMQ Interconnect pod name and list the connections. List the available AMQ Interconnect pods:
oc get pods -l application=default-interconnect
$ oc get pods -l application=default-interconnect NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE default-interconnect-7458fd4d69-bgzfb 1/1 Running 0 6d21hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Connect to the pod and list the known connections. In this example, there are three
edgeconnections from the RHOSP nodes with connectionid22, 23, and 24:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the number of messages delivered by the network, use each address with the
oc execcommand:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.2. Deploying to non-standard network topologies
If your nodes are on a separate network from the default InternalApi network, you must make configuration adjustments so that AMQ Interconnect can transport data to the Service Telemetry Framework (STF) server instance. This scenario is typical in a spine-leaf or a DCN topology. For more information about DCN configuration, see the Spine Leaf Networking guide.
If you use STF with Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) 13 and plan to monitor your Ceph, Block, or Object Storage nodes, you must make configuration changes that are similar to the configuration changes that you make to the spine-leaf and DCN network configuration. To monitor Ceph nodes, use the CephStorageExtraConfig parameter to define which network interface to load into the AMQ Interconnect and collectd configuration files.
CephStorageExtraConfig:
tripleo::profile::base::metrics::collectd::amqp_host: "%{hiera('storage')}"
tripleo::profile::base::metrics::qdr::listener_addr: "%{hiera('storage')}"
tripleo::profile::base::ceilometer::agent::notification::notifier_host_addr: "%{hiera('storage')}"
CephStorageExtraConfig:
tripleo::profile::base::metrics::collectd::amqp_host: "%{hiera('storage')}"
tripleo::profile::base::metrics::qdr::listener_addr: "%{hiera('storage')}"
tripleo::profile::base::ceilometer::agent::notification::notifier_host_addr: "%{hiera('storage')}"
Similarly, you must specify BlockStorageExtraConfig and ObjectStorageExtraConfig parameters if your environment uses Block and Object Storage roles.
To deploy a spine-leaf topology, you must create roles and networks, then assign those networks to the available roles. When you configure data collection and transport for STF for an RHOSP deployment, the default network for roles is InternalApi. For Ceph, Block and Object storage roles, the default network is Storage. Because a spine-leaf configuration can result in different networks being assigned to different Leaf groupings and those names are typically unique, additional configuration is required in the parameter_defaults section of the RHOSP environment files.
Procedure
- Document which networks are available for each of the Leaf roles. For examples of network name definitions, see Creating a network data file in the Spine Leaf Networking guide. For more information about the creation of the Leaf groupings (roles) and assignment of the networks to those groupings, see Creating a roles data file in the Spine Leaf Networking guide.
Add the following configuration example to the
ExtraConfigsection for each of the leaf roles. In this example,internal_api0is the value defined in thename_lowerparameter of your network definition , and is the network to which theCompute0leaf role is connected. In this case, the network identification of 0 corresponds to the Compute role for leaf 0, and represents a value that is different from the default internal API network name.For the
Compute0leaf role, specify extra configuration to perform a hiera lookup to determine which network interface for a particular network to assign to the collectd AMQP host parameter. Perform the same configuration for the AMQ Interconnect listener address parameter.Compute0ExtraConfig: tripleo::profile::base::metrics::collectd::amqp_host: "%{hiera('internal_api0')}" tripleo::profile::base::metrics::qdr::listener_addr: "%{hiera('internal_api0')}"Compute0ExtraConfig: tripleo::profile::base::metrics::collectd::amqp_host: "%{hiera('internal_api0')}" tripleo::profile::base::metrics::qdr::listener_addr: "%{hiera('internal_api0')}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example configuration is on a CephStorage leaf role:
CephStorage0ExtraConfig: tripleo::profile::base::metrics::collectd::amqp_host: "%{hiera('storage0')}" tripleo::profile::base::metrics::qdr::listener_addr: "%{hiera('storage0')}"CephStorage0ExtraConfig: tripleo::profile::base::metrics::collectd::amqp_host: "%{hiera('storage0')}" tripleo::profile::base::metrics::qdr::listener_addr: "%{hiera('storage0')}"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.3. Adding Red Hat OpenStack Platform container images to the undercloud
If you synchronized container images to a local registry, you must create an environment file and include the paths to the container images.
Procedure
Create a new environment file, for example,
container-images.yaml, and insert the following container images and paths:parameter_defaults: DockerCollectdConfigImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-collectd:latest DockerCollectdImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-collectd:latest DockerMetricsQdrConfigImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-qdrouterd:latest DockerMetricsQdrImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-qdrouterd:latestparameter_defaults: DockerCollectdConfigImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-collectd:latest DockerCollectdImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-collectd:latest DockerMetricsQdrConfigImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-qdrouterd:latest DockerMetricsQdrImage: <image-registry-path>/rhosp{vernum}/openstack-qdrouterd:latestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
<image-registry-path>with the path to the image registry.To deploy collectd and AMQ Interconnect to your overcloud, include the
/usr/share/local-container-images/container-images.yamlenvironment file so Red Hat OpenStack Platform director can prepare the images. The following snippet is an example of how to include this environment file:openstack overcloud container image prepare \ ...
$ openstack overcloud container image prepare \ ... -e /usr/share/local-container-images/container-images.yaml \ ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
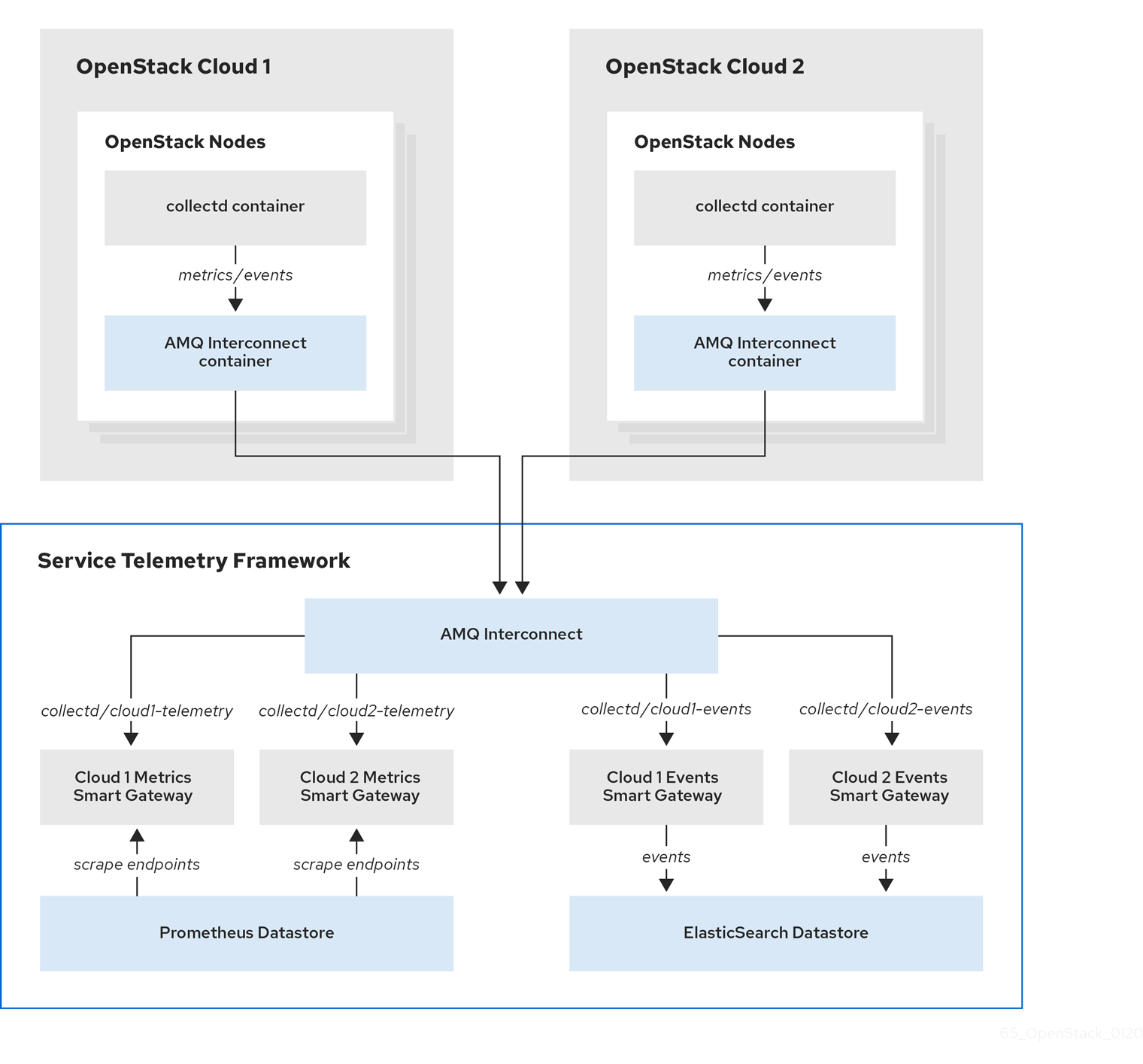
4.4. Configuring multiple clouds
You can configure multiple Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) clouds to target a single instance of Service Telemetry Framework (STF). When you configure multiple clouds, every cloud must send metrics and events on their own unique message bus topic. In the STF deployment, Smart Gateway instances listen on these topics to save information to the common data store. Data that is stored by the Smart Gateway in the data storage domain is filtered by using the metadata that each of Smart Gateways creates.
Figure 4.1. Two RHOSP clouds connect to STF
To configure the RHOSP overcloud for a multiple cloud scenario, complete the following tasks:
- Plan the AMQP address prefixes that you want to use for each cloud. For more information, see Section 4.4.1, “Planning AMQP address prefixes”.
- Deploy metrics and events consumer Smart Gateways for each cloud to listen on the corresponding address prefixes. For more information, see Section 4.4.2, “Deploying Smart Gateways”.
- Configure each cloud with a unique domain name. For more information, see Section 4.4.4, “Setting a unique cloud domain”.
- Create the base configuration for STF. For more information, see Section 4.1.3, “Creating the base configuration for STF”.
- Configure each cloud to send its metrics and events to STF on the correct address. For more information, see Section 4.4.5, “Creating the Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment file for multiple clouds”.
4.4.1. Planning AMQP address prefixes
By default, Red Hat OpenStack Platform nodes receive data through two data collectors; collectd and Ceilometer. These components send telemetry data or notifications to the respective AMQP addresses, for example, collectd/telemetry. STF Smart Gateways listen on the AMQP addresses for monitoring data. To support multiple clouds and to identify which cloud generated the monitoring data, configure each cloud to send data to a unique address. Add a cloud identifier prefix to the second part of the address. The following list shows some example addresses and identifiers:
-
collectd/cloud1-telemetry -
collectd/cloud1-notify -
anycast/ceilometer/cloud1-metering.sample -
anycast/ceilometer/cloud1-event.sample -
collectd/cloud2-telemetry -
collectd/cloud2-notify -
anycast/ceilometer/cloud2-metering.sample -
anycast/ceilometer/cloud2-event.sample -
collectd/us-east-1-telemetry -
collectd/us-west-3-telemetry
4.4.2. Deploying Smart Gateways
You must deploy a Smart Gateway for each of the data collection types for each cloud; one for collectd metrics, one for collectd events, one for Ceilometer metrics, and one for Ceilometer events. Configure each of the Smart Gateways to listen on the AMQP address that you define for the corresponding cloud. To define Smart Gateways, configure the clouds parameter in the ServiceTelemetry manifest.
When you deploy STF for the first time, Smart Gateway manifests are created that define the initial Smart Gateways for a single cloud. When you deploy Smart Gateways for multiple cloud support, you deploy multiple Smart Gateways for each of the data collection types that handle the metrics and the events data for each cloud. The initial Smart Gateways are defined in cloud1 with the following subscription addresses:
| collector | type | default subscription address |
| collectd | metrics | collectd/telemetry |
| collectd | events | collectd/notify |
| Ceilometer | metrics | anycast/ceilometer/metering.sample |
| Ceilometer | events | anycast/ceilometer/event.sample |
Prerequisites
- You have determined your cloud naming scheme. For more information about determining your naming scheme, see Section 4.4.1, “Planning AMQP address prefixes”.
-
You have created your list of clouds objects. For more information about creating the content for the
cloudsparameter, see the section called “The clouds parameter”.
Procedure
- Log in to Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
Change to the
service-telemetrynamespace:oc project service-telemetry
$ oc project service-telemetryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
defaultServiceTelemetry object and add acloudsparameter with your configuration:WarningLong cloud names might exceed the maximum pod name of 63 characters. Ensure that the combination of the
ServiceTelemetrynamedefaultand theclouds.namedoes not exceed 19 characters. Cloud names cannot contain any special characters, such as-. Limit cloud names to alphanumeric (a-z, 0-9).Topic addresses have no character limitation and can be different from the
clouds.namevalue.oc edit stf default
$ oc edit stf defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the ServiceTelemetry object.
Verify that each Smart Gateway is running. This can take several minutes depending on the number of Smart Gateways:
oc get po -l app=smart-gateway
$ oc get po -l app=smart-gatewayCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE default-cloud1-ceil-event-smartgateway-6cfb65478c-g5q82 2/2 Running 0 13h default-cloud1-ceil-meter-smartgateway-58f885c76d-xmxwn 2/2 Running 0 13h default-cloud1-coll-event-smartgateway-58fbbd4485-rl9bd 2/2 Running 0 13h default-cloud1-coll-meter-smartgateway-7c6fc495c4-jn728 2/2 Running 0 13h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE default-cloud1-ceil-event-smartgateway-6cfb65478c-g5q82 2/2 Running 0 13h default-cloud1-ceil-meter-smartgateway-58f885c76d-xmxwn 2/2 Running 0 13h default-cloud1-coll-event-smartgateway-58fbbd4485-rl9bd 2/2 Running 0 13h default-cloud1-coll-meter-smartgateway-7c6fc495c4-jn728 2/2 Running 0 13hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.4.3. Deleting the default Smart Gateways
After you configure Service Telemetry Framework (STF) for multiple clouds, you can delete the default Smart Gateways if they are no longer in use. The Service Telemetry Operator can remove SmartGateway objects that were created but are no longer listed in the ServiceTelemetry clouds list of objects. To enable the removal of SmartGateway objects that are not defined by the clouds parameter, you must set the cloudsRemoveOnMissing parameter to true in the ServiceTelemetry manifest.
If you do not want to deploy any Smart Gateways, define an empty clouds list by using the clouds: [] parameter.
The cloudsRemoveOnMissing parameter is disabled by default. If you enable the cloudsRemoveOnMissing parameter, you remove any manually created SmartGateway objects in the current namespace without any possibility to restore.
Procedure
-
Define your
cloudsparameter with the list of cloud objects that you want the Service Telemetry Operator to manage. For more information, see the section called “The clouds parameter”. Edit the ServiceTelemetry object and add the
cloudsRemoveOnMissingparameter:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the modifications.
Verify that the Operator deleted the Smart Gateways. This can take several minutes while the Operators reconcile the changes:
oc get smartgateways
$ oc get smartgatewaysCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.4.4. Setting a unique cloud domain
To ensure that AMQ Interconnect router connections from Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) to Service Telemetry Framework (STF) are unique and do not conflict, configure the CloudDomain parameter.
Procedure
-
Create a new environment file, for example,
hostnames.yaml. Set the
CloudDomainparameter in the environment file, as shown in the following example:parameter_defaults: CloudDomain: newyork-west-04 CephStorageHostnameFormat: 'ceph-%index%' ObjectStorageHostnameFormat: 'swift-%index%' ComputeHostnameFormat: 'compute-%index%'parameter_defaults: CloudDomain: newyork-west-04 CephStorageHostnameFormat: 'ceph-%index%' ObjectStorageHostnameFormat: 'swift-%index%' ComputeHostnameFormat: 'compute-%index%'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the new environment file to your deployment. For more information, see Section 4.4.5, “Creating the Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment file for multiple clouds” and Core overcloud parameters in the Overcloud Parameters guide.
4.4.5. Creating the Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment file for multiple clouds
To label traffic according to the cloud of origin, you must create a configuration with cloud-specific instance names. Create an stf-connectors.yaml file and adjust the values of CeilometerQdrEventsConfig, CeilometerQdrMetricsConfig and CollectdAmqpInstances to match the AMQP address prefix scheme.
Prerequisites
- You have retrieved the CA certificate from the AMQ Interconnect deployed by STF. For more information, see Section 4.1.1, “Getting CA certificate from Service Telemetry Framework for overcloud configuration”.
- You have created your list of clouds objects. For more information about creating the content for the clouds parameter, see the clouds configuration parameter.
- You have retrieved the AMQ Interconnect route address. For more information, see Section 4.1.2, “Retrieving the AMQ Interconnect route address”.
- You have created the base configuration for STF. For more information, see Section 4.1.3, “Creating the base configuration for STF”.
- You have created a unique domain name environment file. For more information, see Section 4.4.4, “Setting a unique cloud domain”.
Procedure
-
Log in to the Red Hat OpenStack Platform undercloud as the
stackuser. -
Create a configuration file called
stf-connectors.yamlin the/home/stackdirectory. In the
stf-connectors.yamlfile, configure theMetricsQdrConnectorsaddress to connect to the AMQ Interconnect on the overcloud deployment. Configure theCeilometerQdrEventsConfig,CeilometerQdrMetricsConfig, andCollectdAmqpInstancestopic values to match the AMQP address that you want for this cloud deployment.Replace the
caCertFileContentparameter with the contents retrieved in Section 4.1.1, “Getting CA certificate from Service Telemetry Framework for overcloud configuration”.stf-connectors.yaml
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Directly load the collectd service because you are not including the
collectd-write-qdr.yamlenvironment file for multiple cloud deployments. - 2
- Replace the
hostparameter with the value ofHOST/PORTthat you retrieved in Section 4.1.2, “Retrieving the AMQ Interconnect route address”. - 3
- Define the topic for Ceilometer events. This value is the address format of
anycast/ceilometer/cloud1-event.sample. - 4
- Define the topic for Ceilometer metrics. This value is the address format of
anycast/ceilometer/cloud1-metering.sample. - 5
- Define the topic for collectd events. This value is the format of
collectd/cloud1-notify. - 6
- Define the topic for collectd metrics. This value is the format of
collectd/cloud1-telemetry.
-
Ensure that the naming convention in the
stf-connectors.yamlfile aligns with thespec.bridge.amqpUrlfield in the Smart Gateway configuration. For example, configure theCeilometerQdrEventsConfig.topicfield to a value ofcloud1-event. Source the authentication file:
source stackrc
[stack@undercloud-0 ~]$ source stackrc (undercloud) [stack@undercloud-0 ~]$Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Include the
stf-connectors.yamlfile and unique domain name environment filehostnames.yamlin theopenstack overcloud deploymentcommand, with any other environment files relevant to your environment:WarningIf you use the
collectd-write-qdr.yamlfile with a customCollectdAmqpInstancesparameter, data publishes to the custom and default topics. In a multiple cloud environment, the configuration of theresource_registryparameter in thestf-connectors.yamlfile loads the collectd service.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Deploy the Red Hat OpenStack Platform overcloud.
Additional resources
- For information about how to validate the deployment, see Section 4.1.6, “Validating client-side installation”.
4.4.6. Querying metrics data from multiple clouds
Data stored in Prometheus has a service label according to the Smart Gateway it was scraped from. You can use this label to query data from a specific cloud.
To query data from a specific cloud, use a Prometheus promql query that matches the associated service label; for example: collectd_uptime{service="default-cloud1-coll-meter"}.