このコンテンツは選択した言語では利用できません。
Chapter 19. Near Caching
Near caches are optional caches for Hot Rod Java client implementations that keep recently accessed data close to the user, providing faster access to data that is accessed frequently. This cache acts as a local Hot Rod client cache that is updated whenever a remote entry is retrieved via
get or getVersioned operations.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, near cache consistency is achieved by using remote events, which send notifications to clients when entries are modified or removed (refer to Section 7.7, “Remote Event Listeners (Hot Rod)”). With Near Caching, local cache remains consistent with remote cache. Local entry is updated or invalidated whenever remote entry on the server is updated or removed. At the client level, near caching is configurable as either Lazy or Eager modes, which is determined by the user when enabling near caching.
Note
Near caching is disabled for Hot Rod clients by default.
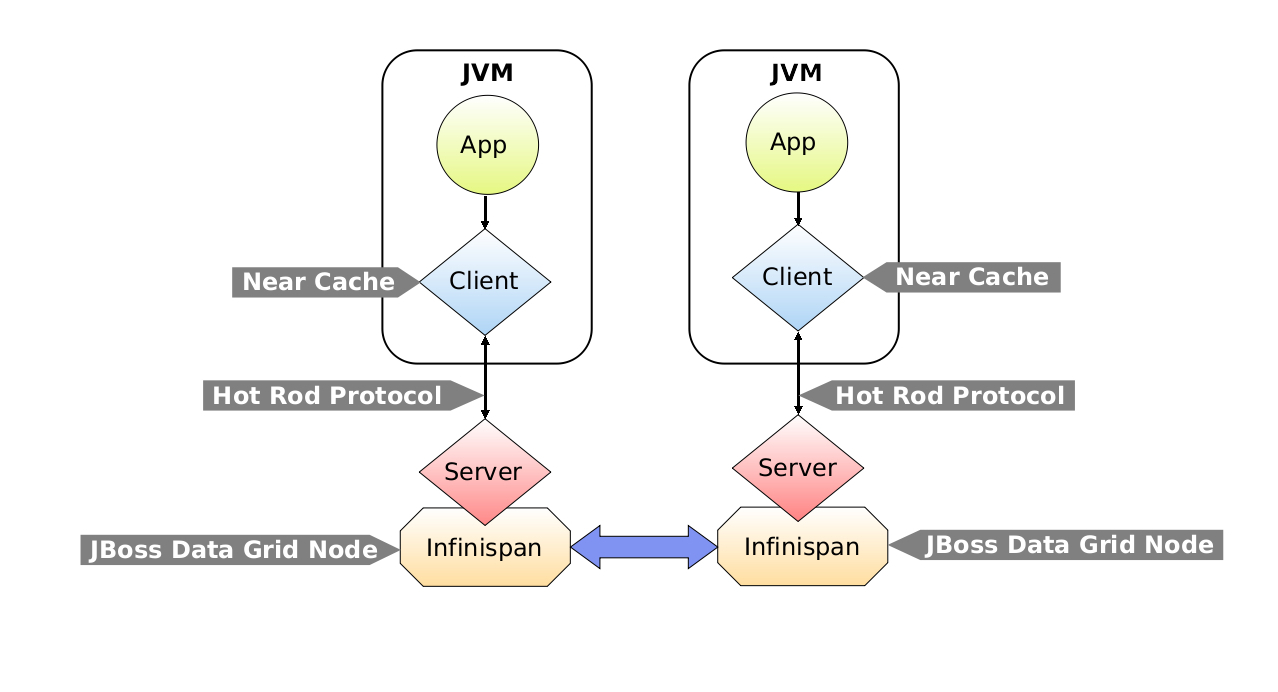
Figure 19.1. Near Caching Architecture
19.1. Lazy and Eager Near Caches
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
- Lazy Near Cache
- Entries are only added to lazy near caches when they are received remotely via
getorgetVersioned. If a cache entry is modified or removed on the server side, the Hot Rod client receives the events, which then invalidate the near cache entries by removing them from the near cache. This is an efficient way of maintaining near cache consistency as the events sent back to the client only contain key information. However, if a cache entry is retrieved after being modified the Hot Rod client must then retrieve it from the remote server. - Eager Near Cache
- Eager near caches are eagerly populated as entries are created on the server. When entries are modified, the latest value is sent along with the notification to the client, which stores it in the near cache. Eager caches are also populated when an entry is retrieved remotely, provided it is not already present. Eager near caches have the advantage of reducing the cost of accessing the server by having newly created entries present in the near cache before requests to retrieve them are received.Eager near caches also allow modified entries that are re-queried by the client to be fetched directly from the near cache. The drawback of using eager near caching is that events received from the server are larger in size due to shipping value information, and entries may be sent to the client that will not be queried.
Warning
Although the eager near caching setting is provided, it is not supported for production use, as with high number of events, value sizes, or clients, eager near caching can generate a large amount of network traffic and potentially overload clients. For production use, it is recommended to use lazy near caches instead.