このコンテンツは選択した言語では利用できません。
Chapter 4. Running a Route
This tutorial walks you through the process of running a route to verify that the route correctly transfers messages from the source endpoint to the sink endpoint.
Goals
In this tutorial you complete the following tasks:
- Run a route as a local Camel context (without tests since you have not set up a test yet)
- Send messages through the route
- Examine the messages received by the sink endpoint
Prerequisites
To start this tutorial, you need the ZooOrderApp project resulting from:
- Completing the Chapter 2, Setting up your environment tutorial.
One of the following:
Completing the Chapter 3, Defining a Route tutorial.
or
-
Replacing your project’s
blueprint.xmlfile with the providedblueprintContexts/blueprint1.xmlfile, as described in the section called “About the resource files”.
Running the route
To run the route:
-
Open the
ZooOrderAppproject. In Project Explorer, select
ZooOrderApp/Camel Contexts/blueprint.xml: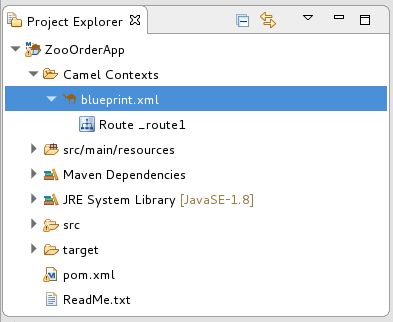
Right-click it to open the context menu, then select Run As
Local Camel Context (without tests). NoteIf you select Local Camel Context instead, the tooling automatically tries to run the routing context against a supplied JUnit test. Because a JUnit test does not exist, the tooling reverts to running the routing context without tests. In the Chapter 9, Testing a route with JUnit tutorial, you create a JUnit test case and modify it specifically for testing the ZooOrderApp project.
The Console panel opens to display log messages that reflect the progress of the project’s execution. At the beginning, Maven downloads the resources necessary to update the local Maven repository, which may take a few minutes.
Messages similar to the following at the end of the output indicate that the route executed successfully:
... [Blueprint Extender: 3] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Route: _route1 started and consuming from:Endpoint[file://src/data?noop=true] [Blueprint Extender: 3] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Total 1 routes, of which 1 are started. [Blueprint Extender: 1] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Apache Camel 2.18.1.redhat-00002 (CamelContext: ...) started in 0.163 seconds [Blueprint Extender: 3] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Apache Camel 2.18.1.redhat-00002 (CamelContext: ...) started in 0.918 seconds
... [Blueprint Extender: 3] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Route: _route1 started and consuming from:Endpoint[file://src/data?noop=true] [Blueprint Extender: 3] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Total 1 routes, of which 1 are started. [Blueprint Extender: 1] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Apache Camel 2.18.1.redhat-00002 (CamelContext: ...) started in 0.163 seconds [Blueprint Extender: 3] BlueprintCamelContext INFO Apache Camel 2.18.1.redhat-00002 (CamelContext: ...) started in 0.918 secondsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To shutdown the route, click
 located at the top of the Console view.
located at the top of the Console view.
Verifying the route
To verify that the route executed properly, you check to see whether the message XML files were copied from the source folder (src/data) to the target folder ('target/messages/received').
-
In Project Explorer, select
ZooOrderApp. - Right-click it to open the context menu, then select Refresh.
In Project Explorer, locate the folder
target/messages/and expand it: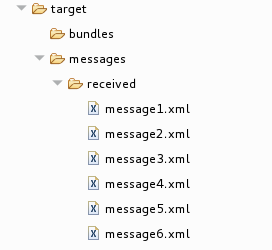
-
Verify that the
target/messages/receivedfolder contains the six message files,message1.xmlthroughmessage6.xml. Double-click
message1.xmlto open it in the route editor’s Design tab, then select the Source tab to see the XML code.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Next steps
In the Chapter 5, Adding a Content-Based Router tutorial you add a Content-Based Router that uses the content of a message to determine its destination.
Further reading
To learn more about:
- Configuring runtime profiles, see the Editing a routing context in the route editor section in "Tooling User Guide".
- Deploying Apache Camel applications, see Developing and Deploying Applications.