Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
7.7. Routing Slip
Overview
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
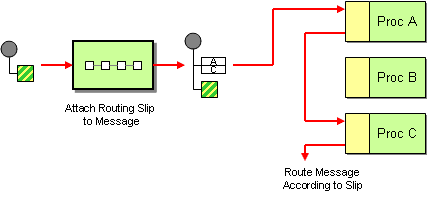
The routing slip pattern, shown in Figure 7.9, “Routing Slip Pattern”, enables you to route a message consecutively through a series of processing steps, where the sequence of steps is not known at design time and can vary for each message. The list of endpoints through which the message should pass is stored in a header field (the slip), which Apache Camel reads at run time to construct a pipeline on the fly.
Figure 7.9. Routing Slip Pattern
The slip header
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The routing slip appears in a user-defined header, where the header value is a comma-separated list of endpoint URIs. For example, a routing slip that specifies a sequence of security tasks—decrypting, authenticating, and de-duplicating a message—might look like the following:
cxf:bean:decrypt,cxf:bean:authenticate,cxf:bean:dedup
cxf:bean:decrypt,cxf:bean:authenticate,cxf:bean:dedupThe current endpoint property
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
From Camel 2.5 the Routing Slip will set a property (
Exchange.SLIP_ENDPOINT) on the exchange which contains the current endpoint as it advanced though the slip. This enables you to find out how far the exchange has progressed through the slip.
The Routing Slip will compute the slip beforehand which means, the slip is only computed once. If you need to compute the slip on-the-fly then use the Dynamic Router pattern instead.
Java DSL example
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The following route takes messages from the
direct:a endpoint and reads a routing slip from the aRoutingSlipHeader header:
from("direct:b").routingSlip("aRoutingSlipHeader");
from("direct:b").routingSlip("aRoutingSlipHeader");
You can specify the header name either as a string literal or as an expression.
You can also customize the URI delimiter using the two-argument form of
routingSlip(). The following example defines a route that uses the aRoutingSlipHeader header key for the routing slip and uses the # character as the URI delimiter:
from("direct:c").routingSlip("aRoutingSlipHeader", "#");
from("direct:c").routingSlip("aRoutingSlipHeader", "#");XML configuration example
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The following example shows how to configure the same route in XML:
Ignore invalid endpoints
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The Routing Slip now supports
ignoreInvalidEndpoints, which the Recipient List pattern also supports. You can use it to skip endpoints that are invalid. For example:
from("direct:a").routingSlip("myHeader").ignoreInvalidEndpoints();
from("direct:a").routingSlip("myHeader").ignoreInvalidEndpoints();
In Spring XML, this feature is enabled by setting the
ignoreInvalidEndpoints attribute on the <routingSlip> tag:
Consider the case where
myHeader contains the two endpoints, direct:foo,xxx:bar. The first endpoint is valid and works. The second is invalid and, therefore, ignored. Apache Camel logs at INFO level whenever an invalid endpoint is encountered.
Options
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The
routingSlip DSL command supports the following options:
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
uriDelimiter
|
,
|
Delimiter used if the Expression returned multiple endpoints. |
ignoreInvalidEndpoints
|
false
|
If an endpoint uri could not be resolved, should it be ignored. Otherwise Camel will thrown an exception stating the endpoint uri is not valid. |