Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
4.3. Message Endpoint
Overview
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
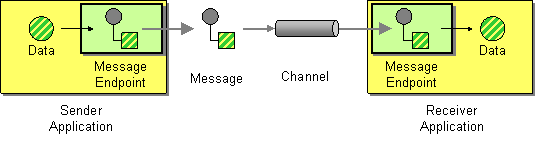
A message endpoint is the interface between an application and a messaging system. As shown in Figure 4.3, “Message Endpoint Pattern”, you can have a sender endpoint, sometimes called a proxy or a service consumer, which is responsible for sending In messages, and a receiver endpoint, sometimes called an endpoint or a service, which is responsible for receiving In messages.
Figure 4.3. Message Endpoint Pattern
Types of endpoint
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Apache Camel defines two basic types of endpoint:
- Consumer endpoint — Appears at the start of a Apache Camel route and reads In messages from an incoming channel (equivalent to a receiver endpoint).
- Producer endpoint — Appears at the end of a Apache Camel route and writes In messages to an outgoing channel (equivalent to a sender endpoint). It is possible to define a route with multiple producer endpoints.
Endpoint URIs
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
In Apache Camel, an endpoint is represented by an endpoint URI, which typically encapsulates the following kinds of data:
- Endpoint URI for a consumer endpoint — Advertises a specific location (for example, to expose a service to which senders can connect). Alternatively, the URI can specify a message source, such as a message queue. The endpoint URI can include settings to configure the endpoint.
- Endpoint URI for a producer endpoint — Contains details of where to send messages and includes the settings to configure the endpoint. In some cases, the URI specifies the location of a remote receiver endpoint; in other cases, the destination can have an abstract form, such as a queue name.
An endpoint URI in Apache Camel has the following general form:
ComponentPrefix:ComponentSpecificURI
ComponentPrefix:ComponentSpecificURI
Where ComponentPrefix is a URI prefix that identifies a particular Apache Camel component (see "EIP Component Reference" for details of all the supported components). The remaining part of the URI, ComponentSpecificURI, has a syntax defined by the particular component. For example, to connect to the JMS queue,
Foo.Bar, you can define an endpoint URI like the following:
jms:Foo.Bar
jms:Foo.Bar
To define a route that connects the consumer endpoint,
file://local/router/messages/foo, directly to the producer endpoint, jms:Foo.Bar, you can use the following Java DSL fragment:
from("file://local/router/messages/foo").to("jms:Foo.Bar");
from("file://local/router/messages/foo").to("jms:Foo.Bar");
Alternatively, you can define the same route in XML, as follows: