Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
8.2. Message Filter
Overview
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
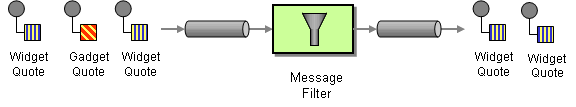
A message filter is a processor that eliminates undesired messages based on specific criteria. In Apache Camel, the message filter pattern, shown in Figure 8.2, “Message Filter Pattern”, is implemented by the
filter() Java DSL command. The filter() command takes a single predicate argument, which controls the filter. When the predicate is true, the incoming message is allowed to proceed, and when the predicate is false, the incoming message is blocked.
Figure 8.2. Message Filter Pattern
Java DSL example
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The following example shows how to create a route from endpoint,
seda:a, to endpoint, seda:b, that blocks all messages except for those messages whose foo header have the value, bar:
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("seda:a").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("seda:b");
}
};
RouteBuilder builder = new RouteBuilder() {
public void configure() {
from("seda:a").filter(header("foo").isEqualTo("bar")).to("seda:b");
}
};
To evaluate more complex filter predicates, you can invoke one of the supported scripting languages, such as XPath, XQuery, or SQL (see Expression and Predicate Languages). The following example defines a route that blocks all messages except for those containing a
person element whose name attribute is equal to James:
from("direct:start").
filter().xpath("/person[@name='James']").
to("mock:result");
from("direct:start").
filter().xpath("/person[@name='James']").
to("mock:result");XML configuration example
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The following example shows how to configure the route with an XPath predicate in XML (see Expression and Predicate Languages):
Filtered endpoint required inside </filter> tag
Make sure you put the endpoint you want to filter (for example,
<to uri="seda:b"/>) before the closing </filter> tag or the filter will not be applied (in 2.8+, omitting this will result in an error).
Filtering with beans
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Here is an example of using a bean to define the filter behavior:
Using stop()
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Available as of Camel 2.0
Stop is a special type of filter that filters out all messages. Stop is convenient to use in a Content-Based Router when you need to stop further processing in one of the predicates.
In the following example, we do not want messages with the word
Bye in the message body to propagate any further in the route. We prevent this in the when() predicate using .stop().
Knowing if Exchange was filtered or not
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Available as of Camel 2.5
The Message Filter EIP will add a property on the Exchange which states if it was filtered or not.
The property has the key
Exchannge.FILTER_MATCHED which has the String value of CamelFilterMatched. Its value is a boolean indicating true or false. If the value is true then the Exchange was routed in the filter block.