이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
Chapter 39. Payload-Based Route
39.1. Processing Messages in PAYLOAD Format
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Overview
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
Select the PAYLOAD format, if you want to access the SOAP message body in XML format, encoded as a DOM object (that is, of
org.w3c.dom.Node type). One of the advantages of the PAYLOAD format is that no JAX-WS and JAXB stub code is required, which allows your application to be dynamic, potentially handling many different WSDL interfaces.
Having a message body in XML format enables you to parse the request using XML languages such as XPath and to generate responses using templating languages, such as Velocity.
Note
The DOM format is not the optimal type to use for large XML message bodies. For large messages, consider using the techniques described in Chapter 40, Provider-Based Route.
Demonstration location
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The code presented in this chapter is taken from the following demonstration:
cxf-webinars-jboss-fuse-6.3/customer-ws-camel-cxf-payload
cxf-webinars-jboss-fuse-6.3/customer-ws-camel-cxf-payload
For details of how to download and install the demonstration code, see Chapter 34, Demonstration Code for Camel/CXF
Camel CXF component
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The Camel CXF component is an Apache CXF component that integrates Web services with routes. You can use it either to instantiate consumer endpoints (at the start of a route), which behave like Web service instances, or to instantiate producer endpoints (at any other points in the route), which behave like WS clients.
Note
Came CXF endpoints—which are instantiated using the
cxf:cxfEndpoint XML element and are implemented by the Apache Camel project—are not to be confused with the Apache CXF JAX-WS endpoints—which are instantiated using the jaxws:endpoint XML element and are implemented by the Apache CXF project.
PAYLOAD data format
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
The PAYLOAD data format is selected by setting the
dataFormat=PAYLOAD option on a Camel CXF endpoint URI and it has the following characteristics:
- Enables you to access the message body as a DOM object (XML payload).
- No JAX-WS or JAXB stub code required.
- The SOAP body is marshalled as follows:
- The message body is effectively an XML payload of
org.w3c.dom.Nodetype (wrapped in aCxfPayloadobject). - The type of the message body is
org.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfPayload.
- The SOAP headers are converted into headers in the exchange's In message, of
org.apache.cxf.binding.soap.SoapHeadertype.
Implementing and building a PAYLOAD route
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
To implement and build the demonstration PAYLOAD-based route, starting from scratch, you would perform the following steps:
- Instantiate the Camel CXF endpoint in Spring, using the
cxf:cxfEndpointelement. - Implement the route in XML, where you can use the content-based router to sort requests by operation name.
- For each operation, define a processor bean to process the request.
- Define velocity templates for generating the reponse messages.
Sample PAYLOAD route
링크 복사링크가 클립보드에 복사되었습니다!
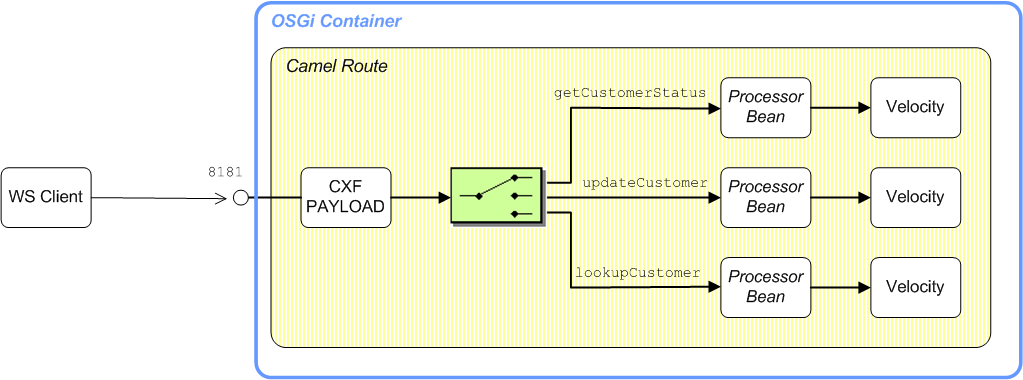
Figure 39.1, “Sample PAYLOAD Route” shows an outline of the route that is used to process the operations of the
CustomerService Web service using the PAYLOAD data format. After sorting the request messages by operation name, an operation-specific processor bean reads the incoming request parameters. Finally, the response messages are generated using Velocity templates.
Figure 39.1. Sample PAYLOAD Route