이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
Chapter 9. Examples
Use the following examples to understand how to launch a compute instance post-deployment with various network configurations.
9.1. Example 1: Launching a Compute node with one NIC on the tenant and provider networks
Use this example to understand how to launch a Compute node with the private tenant network and the provider network after you deploy the all-in-one Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment. This example is based on a single NIC configuration and requires at least three IP addresses.
Prerequisites
To complete this example successfully, you must have the following IP addresses available in your environment:
- One IP address for the OpenStack services.
- One IP address for the virtual router to provide connectivity to the tenant network. This IP address is assigned automatically in this example.
- At least one IP address for floating IPs on the provider network.
Procedure
Create configuration helper variables:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a basic flavor:
openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tiny
$ openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tinyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download CirrOS and create an OpenStack image:
wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img
$ wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img $ openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.imgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure SSH:
ssh-keygen openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub default
$ ssh-keygen $ openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a simple network security group:
openstack security group create basic
$ openstack security group create basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the new network security group:
Enable SSH:
openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
$ openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable ping:
openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable DNS:
openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create Neutron networks:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a virtual router:
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. openstack router create vrouter openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public openstack router add subnet vrouter private-net
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. $ openstack router create vrouter $ openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public $ openstack router add subnet vrouter private-netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a floating IP:
openstack floating ip create public
$ openstack floating ip create publicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the instance:
openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserver
$ openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Assign the floating IP:
openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>
$ openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.Test SSH:
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.
Network Architecture
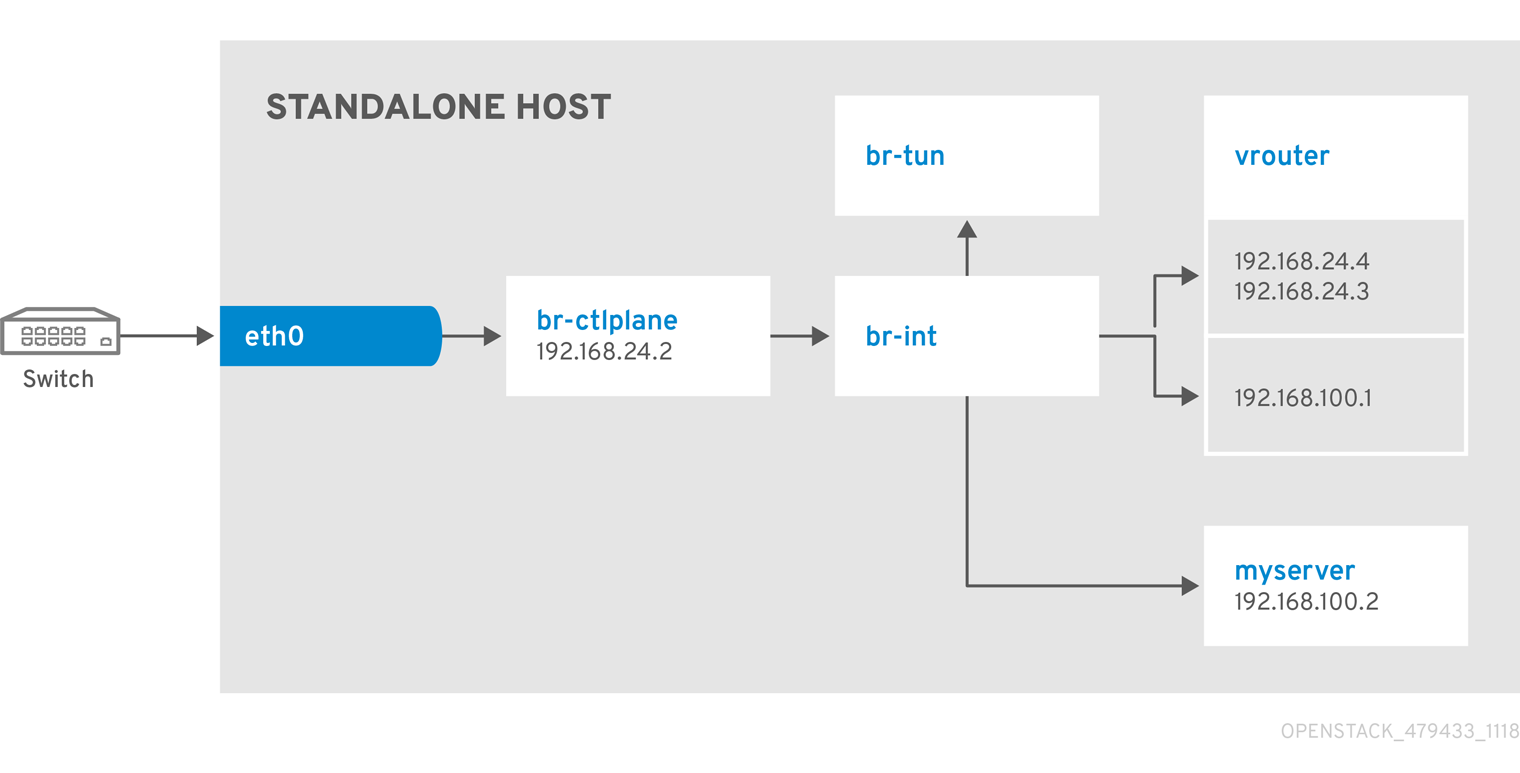
9.2. Example 2: Launching a Compute node with one NIC on the provider network
Use this example to understand how to launch a Compute node with the provider network after you deploy the all-in-one Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment. This example is based on a single NIC configuration and requires at least four IP addresses.
Prerequisites
To complete this example successfully, you must have the following IP addresses available in your environment:
- One IP address for the OpenStack services.
- One IP address for the virtual router to provide connectivity to the tenant network. This IP address is assigned automatically in this example.
- One IP address for DHCP on the provider network.
- At least one IP address for floating IPs on the provider network.
Procedure
Create configuration helper variables:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a basic flavor:
openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tiny
$ openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tinyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download CirrOS and create an OpenStack image:
wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img
$ wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img $ openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.imgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure SSH:
ssh-keygen openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub default
$ ssh-keygen $ openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a simple network security group:
openstack security group create basic
$ openstack security group create basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the new network security group:
Enable SSH:
openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
$ openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable ping:
openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable DNS:
openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create Neutron networks:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a virtual router:
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. openstack router create vrouter openstack port create --network public --fixed-ip subnet=public-net,ip-address=$VROUTER_IP vrouter-port openstack router add port vrouter vrouter-port
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. $ openstack router create vrouter $ openstack port create --network public --fixed-ip subnet=public-net,ip-address=$VROUTER_IP vrouter-port $ openstack router add port vrouter vrouter-portCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the instance:
openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network public --security-group basic myserver
$ openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network public --security-group basic myserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Test SSH:
ssh cirros@<VM_IP>
ssh cirros@<VM_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
VM_IPwith the address of the virtual machine that you create in the previous step.
Network Architecture
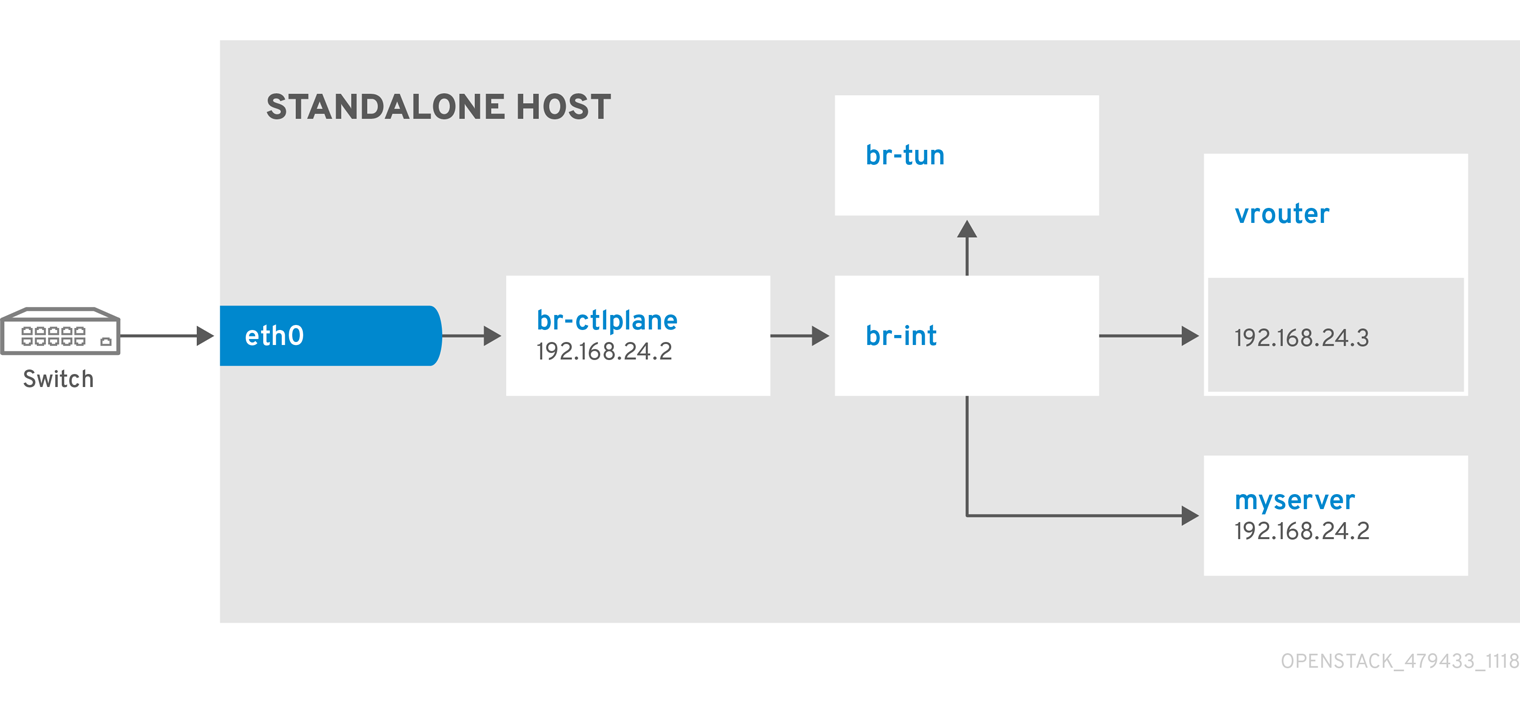
9.3. Example 3: Launching a Compute node with two NICs on the tenant and provider networks
Use this example to understand how to launch a Compute node with the private tenant network and the provider network after you deploy the all-in-one Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment. This example is based on a dual NIC configuration and requires at least three IP addresses on the provider network.
Prerequisites
- One IP address for a gateway on the provider network.
- One IP address for OpenStack endpoints.
- One IP address for the virtual router to provide connectivity to the tenant network. This IP address is assigned automatically in this example.
- At least one IP address for floating IPs on the provider network.
Procedure
Create configuration helper variables:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a basic flavor:
openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tiny
$ openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tinyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download CirrOS and create an OpenStack image:
wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img
$ wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img $ openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.imgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure SSH:
ssh-keygen openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub default
$ ssh-keygen $ openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a simple network security group:
openstack security group create basic
$ openstack security group create basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the new network security group:
Enable SSH:
openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
$ openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable ping:
openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable DNS:
openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create Neutron networks:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a virtual router:
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. openstack router create vrouter openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public openstack router add subnet vrouter private-net
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. $ openstack router create vrouter $ openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public $ openstack router add subnet vrouter private-netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a floating IP:
openstack floating ip create public
$ openstack floating ip create publicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the instance:
openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserver
$ openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Assign the floating IP:
openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>
$ openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.Test SSH:
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.
Network Architecture
