Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
Chapter 3. Using Kerberos
Maintaining system security and integrity within a network is critical, and it encompasses every user, application, service, and server within the network infrastructure. It requires an understanding of everything that is running on the network and the manner in which these services are used. At the core of maintaining this security is maintaining access to these applications and services and enforcing that access.
Kerberos provides a mechanism that allows both users and machines to identify themselves to network and receive defined, limited access to the areas and services that the administrator configured. Kerberos authenticates entities by verifying their identity, and Kerberos also secures this authenticating data so that it cannot be accessed and used or tampered with by an outsider.
3.1. About Kerberos
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol created by MIT, and uses symmetric-key cryptography[1] to authenticate users to network services, which means passwords are never actually sent over the network.
Consequently, when users authenticate to network services using Kerberos, unauthorized users attempting to gather passwords by monitoring network traffic are effectively thwarted.
3.1.1. How Kerberos Works
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Most conventional network services use password-based authentication schemes, where a user supplies a password to access a given network server. However, the transmission of authentication information for many services is unencrypted. For such a scheme to be secure, the network has to be inaccessible to outsiders, and all computers and users on the network must be trusted and trustworthy.
With simple, password-based authentication, a network that is connected to the Internet cannot be assumed to be secure. Any attacker who gains access to the network can use a simple packet analyzer, or packet sniffer, to intercept usernames and passwords, compromising user accounts and, therefore, the integrity of the entire security infrastructure.
Kerberos eliminates the transmission of unencrypted passwords across the network and removes the potential threat of an attacker sniffing the network.
Rather than authenticating each user to each network service separately as with simple password authentication, Kerberos uses symmetric encryption and a trusted third party (a key distribution center or KDC) to authenticate users to a suite of network services. The computers managed by that KDC and any secondary KDCs constitute a realm.
When a user authenticates to the KDC, the KDC sends a set of credentials (a ticket) specific to that session back to the user's machine, and any Kerberos-aware services look for the ticket on the user's machine rather than requiring the user to authenticate using a password.
As shown in Figure 3.1, “Kerberos Authentication, in Steps”, each user is identified to the KDC with a unique identity, called a principal. When a user on a Kerberos-aware network logs into his workstation, his principal is sent to the KDC as part of a request for a ticket-getting ticket (or TGT) from the authentication server. This request can be sent by the login program so that it is transparent to the user or can be sent manually by a user through the
kinit program after the user logs in.
The KDC then checks for the principal in its database. If the principal is found, the KDC creates a TGT, encrypts it using the user's key, and sends the TGT to that user.
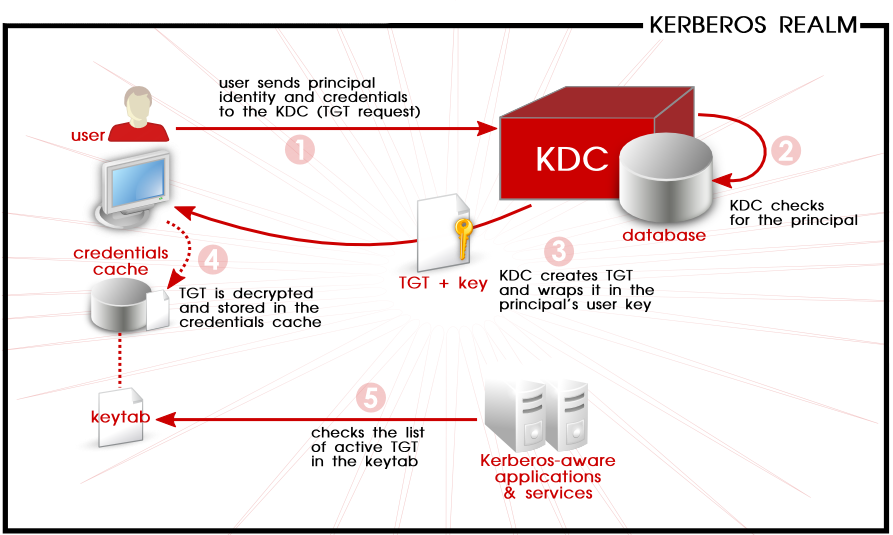
Figure 3.1. Kerberos Authentication, in Steps
The login or
kinit program on the client then decrypts the TGT using the user's key, which it computes from the user's password. The user's key is used only on the client machine and is not transmitted over the network. The ticket (or credentials) sent by the KDC are stored in a local file, the credentials cache, which can be checked by Kerberos-aware services.
After authentication, servers can check an unencrypted list of recognized principals and their keys rather than checking
kinit; this is kept in a keytab.
The TGT is set to expire after a certain period of time (usually ten to twenty-four hours) and is stored in the client machine's credentials cache. An expiration time is set so that a compromised TGT is of use to an attacker for only a short period of time. After the TGT has been issued, the user does not have to re-enter their password until the TGT expires or until they log out and log in again.
Whenever the user needs access to a network service, the client software uses the TGT to request a new ticket for that specific service from the ticket-granting server (TGS). The service ticket is then used to authenticate the user to that service transparently.
Warning
The Kerberos system can be compromised if a user on the network authenticates against a non-Kerberos aware service by transmitting a password in plain text. The use of non-Kerberos aware services (including telnet and FTP) is highly discouraged. Other encrypted protocols, such as SSH or SSL-secured services, is preferred to unencrypted services, but this is still not ideal.
Kerberos relies on being able to resolve machine names and on accurate timestamps to issue and expire tickets. Thus, Kerberos requires both adequate clock synchronization and a working domain name service (DNS) to function correctly.
- Approximate clock synchronization between the machines on the network can be set up using a service such as
ntpd, which is documented in/usr/share/doc/ntp-version-number/html/index.html. - Both DNS entries and hosts on the network must be properly configured, which is covered in the Kerberos documentation in
/usr/share/doc/krb5-server-version-number.
3.1.2. Considerations for Deploying Kerberos
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Although Kerberos removes a common and severe security threat, it is difficult to implement for a variety of reasons:
- Migrating user passwords from a standard UNIX password database, such as
/etc/passwdor/etc/shadow, to a Kerberos password database can be tedious. There is no automated mechanism to perform this task. This is covered in question 2.23 in the online Kerberos FAQ for the US Navy. - Kerberos assumes that each user is trusted but is using an untrusted host on an untrusted network. Its primary goal is to prevent unencrypted passwords from being transmitted across that network. However, if anyone other than the proper user has access to the one host that issues tickets used for authentication — the KDC — the entire Kerberos authentication system are at risk.
- For an application to use Kerberos, its source must be modified to make the appropriate calls into the Kerberos libraries. Applications modified in this way are considered to be Kerberos-aware, or kerberized. For some applications, this can be quite problematic due to the size of the application or its design. For other incompatible applications, changes must be made to the way in which the server and client communicate. Again, this can require extensive programming. Closed-source applications that do not have Kerberos support by default are often the most problematic.
- Kerberos is an all-or-nothing solution. If Kerberos is used on the network, any unencrypted passwords transferred to a non-Kerberos aware service are at risk. Thus, the network gains no benefit from the use of Kerberos. To secure a network with Kerberos, one must either use Kerberos-aware versions of all client/server applications that transmit passwords unencrypted, or not use that client/server application at all.
3.1.3. Additional Resources for Kerberos
Copiar o linkLink copiado para a área de transferência!
Kerberos can be a complex service to implement, with a lot of flexibility in how it is deployed. Table 3.1, “External Kerberos Documentation” and Table 3.2, “Important Kerberos Manpages” list of a few of the most important or most useful sources for more information on using Kerberos.
| Documentation | Location |
|---|---|
| Kerberos V5 Installation Guide (in both PostScript and HTML) | /usr/share/doc/krb5-server-version-number |
| Kerberos V5 System Administrator's Guide (in both PostScript and HTML) | /usr/share/doc/krb5-server-version-number |
| Kerberos V5 UNIX User's Guide (in both PostScript and HTML) | /usr/share/doc/krb5-workstation-version-number |
| "Kerberos: The Network Authentication Protocol" webpage from MIT | http://web.mit.edu/kerberos/www/ |
| The Kerberos Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) | http://www.cmf.nrl.navy.mil/CCS/people/kenh/kerberos-faq.html |
| Designing an Authentication System: a Dialogue in Four Scenes, originally by Bill Bryant in 1988, modified by Theodore Ts'o in 1997. This document is a conversation between two developers who are thinking through the creation of a Kerberos-style authentication system. The conversational style of the discussion makes this a good starting place for people who are completely unfamiliar with Kerberos. | http://web.mit.edu/kerberos/www/dialogue.html |
| A how-to article for kerberizing a network. | http://www.ornl.gov/~jar/HowToKerb.html |
Any of the manpage files can be opened by running
man command_name.
| Manpage | Description |
|---|---|
| Client Applications | |
| kerberos | An introduction to the Kerberos system which describes how credentials work and provides recommendations for obtaining and destroying Kerberos tickets. The bottom of the man page references a number of related man pages. |
| kinit | Describes how to use this command to obtain and cache a ticket-granting ticket. |
| kdestroy | Describes how to use this command to destroy Kerberos credentials. |
| klist | Describes how to use this command to list cached Kerberos credentials. |
| Administrative Applications | |
| kadmin | Describes how to use this command to administer the Kerberos V5 database. |
| kdb5_util | Describes how to use this command to create and perform low-level administrative functions on the Kerberos V5 database. |
| Server Applications | |
| krb5kdc | Describes available command line options for the Kerberos V5 KDC. |
| kadmind | Describes available command line options for the Kerberos V5 administration server. |
| Configuration Files | |
| krb5.conf | Describes the format and options available within the configuration file for the Kerberos V5 library. |
| kdc.conf | Describes the format and options available within the configuration file for the Kerberos V5 AS and KDC. |
[1]
A system where both the client and the server share a common key that is used to encrypt and decrypt network communication.