Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Virtualized and Non-Virtualized Environments
In a non-virtualized environment, hosts are separated from each other physically and each host has a self-contained environment, consisting of services such as a web server, or a DNS server. These services communicate directly to their own user space, host kernel and physical host, offering their services directly to the network. The following image represents a non-virtualized environment:
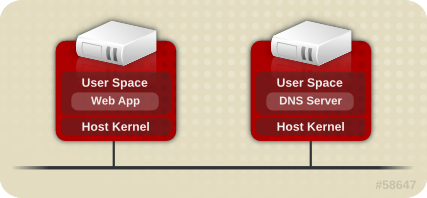
Figure 1.1. Non-Virtualized Environment
In a virtualized environment, several operating systems can be housed (as "guests") within a single host kernel and physical host. The following image represents a virtualized environment:
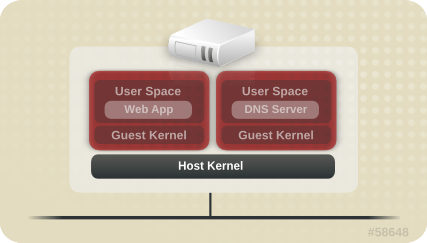
Figure 1.2. Virtualized Environment