Este conteúdo não está disponível no idioma selecionado.
Chapter 10. Tuning eventing configuration
10.1. Overriding Knative Eventing system deployment configurations
You can override the default configurations for some specific deployments by modifying the workloads spec in the KnativeEventing custom resource (CR). Currently, overriding default configuration settings is supported for the eventing-controller, eventing-webhook, and imc-controller fields, as well as for the readiness and liveness fields for probes.
The replicas spec cannot override the number of replicas for deployments that use the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), and does not work for the eventing-webhook deployment.
You can only override probes that are defined in the deployment by default.
All Knative Serving deployments define a readiness and a liveness probe by default, with these exceptions:
-
net-kourier-controllerand3scale-kourier-gatewayonly define a readiness probe. -
net-istio-controllerandnet-istio-webhookdefine no probes.
10.1.1. Overriding deployment configurations
Currently, overriding default configuration settings is supported for the eventing-controller, eventing-webhook, and imc-controller fields, as well as for the readiness and liveness fields for probes.
The replicas spec cannot override the number of replicas for deployments that use the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), and does not work for the eventing-webhook deployment.
In the following example, a KnativeEventing CR overrides the eventing-controller deployment so that:
-
The
readinessprobe timeouteventing-controlleris set to be 10 seconds. - The deployment has specified CPU and memory resource limits.
- The deployment has 3 replicas.
-
The
example-label: labellabel is added. -
The
example-annotation: annotationannotation is added. -
The
nodeSelectorfield is set to select nodes with thedisktype: hddlabel.
KnativeEventing CR example
- 1
- You can use the
readinessandlivenessprobe overrides to override all fields of a probe in a container of a deployment as specified in the Kubernetes API except for the fields related to the probe handler:exec,grpc,httpGet, andtcpSocket.
The KnativeEventing CR label and annotation settings override the deployment’s labels and annotations for both the deployment itself and the resulting pods.
10.1.2. Modifying consumer group IDs and topic names
You can change templates for generating consumer group IDs and topic names used by your triggers, brokers, and channels.
Prerequisites
- You have cluster or dedicated administrator permissions on OpenShift Container Platform.
-
The OpenShift Serverless Operator, Knative Eventing, and the
KnativeKafkacustom resource (CR) are installed on your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. - You have created a project or have access to a project that has the appropriate roles and permissions to create applications and other workloads in OpenShift Container Platform.
-
You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc).
Procedure
To change templates for generating consumer group IDs and topic names used by your triggers, brokers, and channels, modify the
KnativeKafkaresource:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The template for generating the consumer group ID used by your triggers. Use a valid Go
text/templatevalue. Defaults to{% raw %}"knative-trigger-{{ .Namespace }}-{{ .Name }}"{% endraw %}. - 2
- The template for generating Kafka topic names used by your brokers. Use a valid Go
text/templatevalue. Defaults to{% raw %}"knative-broker-{{ .Namespace }}-{{ .Name }}"{% endraw %}. - 3
- The template for generating Kafka topic names used by your channels. Use a valid Go
text/templatevalue. Defaults to{% raw %}"messaging-kafka.{{ .Namespace }}.{{ .Name }}"{% endraw %}.
Example template configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Apply the
KnativeKafkaYAML file:$ oc apply -f <knative_kafka_filename>
$ oc apply -f <knative_kafka_filename>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2. High availability
High availability (HA) is a standard feature of Kubernetes APIs that helps to ensure that APIs stay operational if a disruption occurs. In an HA deployment, if an active controller crashes or is deleted, another controller is readily available. This controller takes over processing of the APIs that were being serviced by the controller that is now unavailable.
HA in OpenShift Serverless is available through leader election, which is enabled by default after the Knative Serving or Eventing control plane is installed. When using a leader election HA pattern, instances of controllers are already scheduled and running inside the cluster before they are required. These controller instances compete to use a shared resource, known as the leader election lock. The instance of the controller that has access to the leader election lock resource at any given time is called the leader.
HA in OpenShift Serverless is available through leader election, which is enabled by default after the Knative Serving or Eventing control plane is installed. When using a leader election HA pattern, instances of controllers are already scheduled and running inside the cluster before they are required. These controller instances compete to use a shared resource, known as the leader election lock. The instance of the controller that has access to the leader election lock resource at any given time is called the leader.
10.2.1. Configuring high availability replicas for Knative Eventing
High availability (HA) is available by default for the Knative Eventing eventing-controller, eventing-webhook, imc-controller, imc-dispatcher, and mt-broker-controller components, which are configured to have two replicas each by default. You can change the number of replicas for these components by modifying the spec.high-availability.replicas value in the KnativeEventing custom resource (CR).
For Knative Eventing, the mt-broker-filter and mt-broker-ingress deployments are not scaled by HA. If multiple deployments are needed, scale these components manually.
Prerequisites
- You have cluster administrator permissions on OpenShift Container Platform, or you have cluster or dedicated administrator permissions on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS or OpenShift Dedicated.
- The OpenShift Serverless Operator and Knative Eventing are installed on your cluster.
Procedure
-
In the OpenShift Container Platform web console Administrator perspective, navigate to OperatorHub
Installed Operators. -
Select the
knative-eventingnamespace. - Click Knative Eventing in the list of Provided APIs for the OpenShift Serverless Operator to go to the Knative Eventing tab.
Click knative-eventing, then go to the YAML tab in the knative-eventing page.
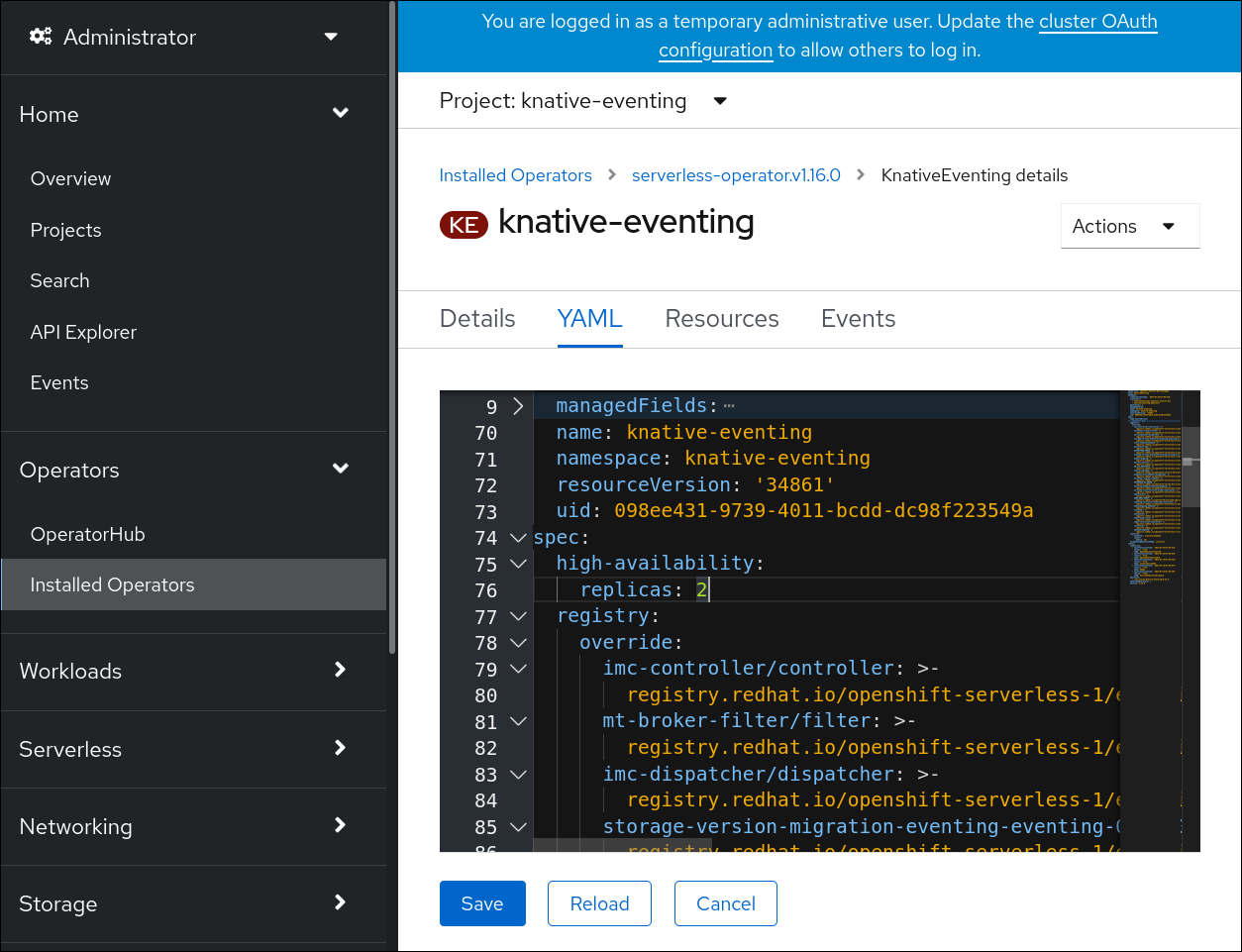
Modify the number of replicas in the
KnativeEventingCR:Example YAML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also specify the number of replicas for a specific workload.
NoteWorkload-specific configuration overrides the global setting for Knative Eventing.
Example YAML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the high availability limits are respected:
Example command
oc get hpa -n knative-eventing
$ oc get hpa -n knative-eventingCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE broker-filter-hpa Deployment/mt-broker-filter 1%/70% 3 12 3 112s broker-ingress-hpa Deployment/mt-broker-ingress 1%/70% 3 12 3 112s eventing-webhook Deployment/eventing-webhook 4%/100% 3 7 3 115s
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE broker-filter-hpa Deployment/mt-broker-filter 1%/70% 3 12 3 112s broker-ingress-hpa Deployment/mt-broker-ingress 1%/70% 3 12 3 112s eventing-webhook Deployment/eventing-webhook 4%/100% 3 7 3 115sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2.2. Configuring high availability replicas for the Knative broker implementation for Apache Kafka
High availability (HA) is available by default for the Knative broker implementation for Apache Kafka components kafka-controller and kafka-webhook-eventing, which are configured to have two each replicas by default. You can change the number of replicas for these components by modifying the spec.high-availability.replicas value in the KnativeKafka custom resource (CR).
Prerequisites
- You have cluster administrator permissions on OpenShift Container Platform, or you have cluster or dedicated administrator permissions on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS or OpenShift Dedicated.
- The OpenShift Serverless Operator and Knative broker for Apache Kafka are installed on your cluster.
Procedure
-
In the OpenShift Container Platform web console Administrator perspective, navigate to OperatorHub
Installed Operators. -
Select the
knative-eventingnamespace. - Click Knative Kafka in the list of Provided APIs for the OpenShift Serverless Operator to go to the Knative Kafka tab.
Click knative-kafka, then go to the YAML tab in the knative-kafka page.
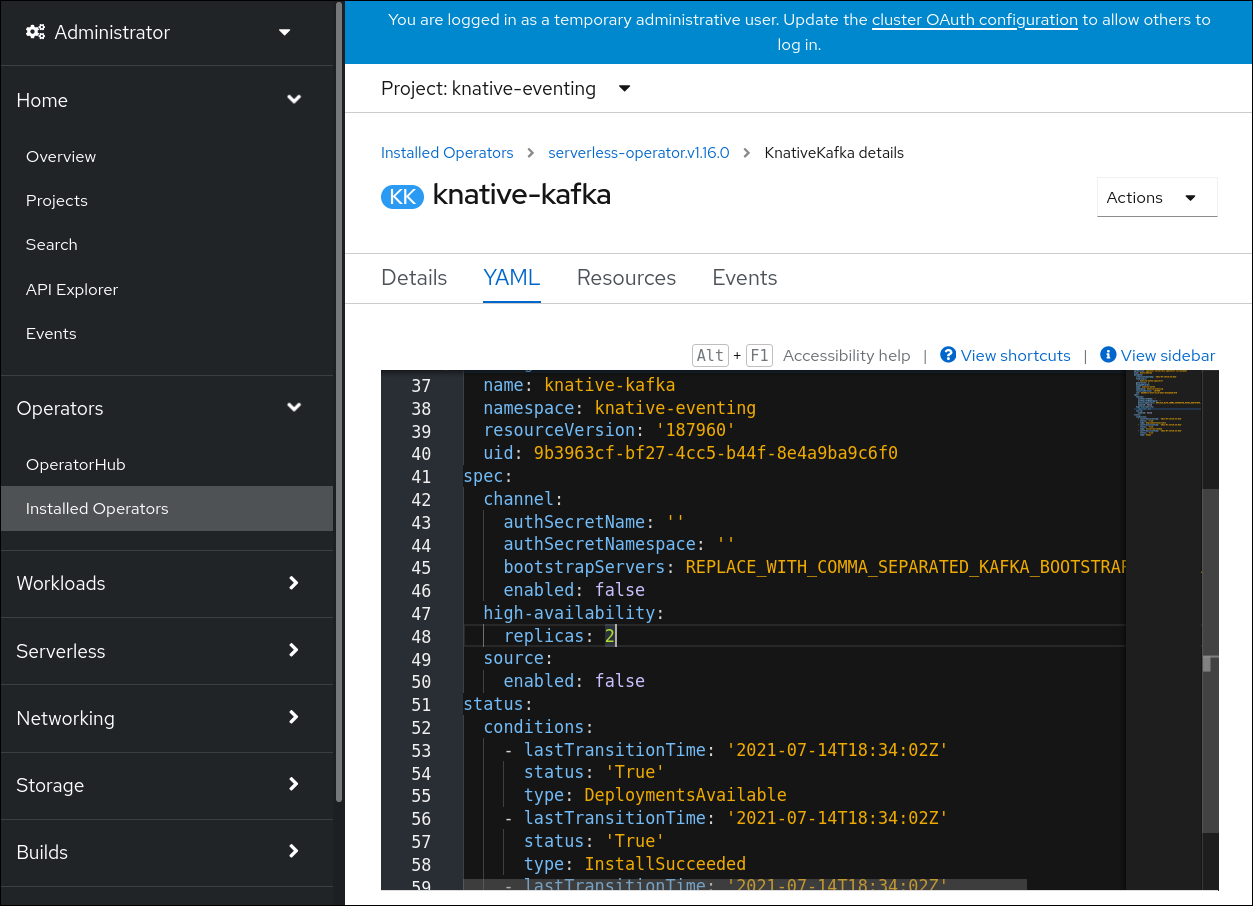
Modify the number of replicas in the
KnativeKafkaCR:Example YAML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.2.3. Overriding disruption budgets
A Pod Disruption Budget (PDB) is a standard feature of Kubernetes APIs that helps limit the disruption to an application when its pods need to be rescheduled for maintenance reasons.
Procedure
-
Override the default PDB for a specific resource by modifying the
minAvailableconfiguration value in theKnativeEventingcustom resource (CR).
Example PDB with a minAvailable seting of 70%
If you disable high-availability, for example, by changing the high-availability.replicas value to 1, make sure you also update the corresponding PDB minAvailable value to 0. Otherwise, the pod disruption budget prevents automatic cluster or Operator updates.