此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
9.4. JNDI over HTTP
In addition to the legacy RMI/JRMP with a socket bootstrap protocol, JBoss provides support for accessing its JNDI naming service over HTTP.
9.4.1. Accessing JNDI over HTTP
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This capability is provided by
http-invoker.sar. The structure of the http-invoker.sar is:
The
jboss-service.xml descriptor defines the HttpInvoker and HttpInvokerHA MBeans. These services handle the routing of methods invocations that are sent via HTTP to the appropriate target MBean on the JMX bus.
The
http-invoker.war web application contains servlets that handle the details of the HTTP transport. The NamingFactoryServlet handles creation requests for the JBoss JNDI naming service javax.naming.Context implementation. The InvokerServlet handles invocations made by RMI/HTTP clients. The ReadOnlyAccessFilter allows one to secure the JNDI naming service while making a single JNDI context available for read-only access by unauthenticated clients.
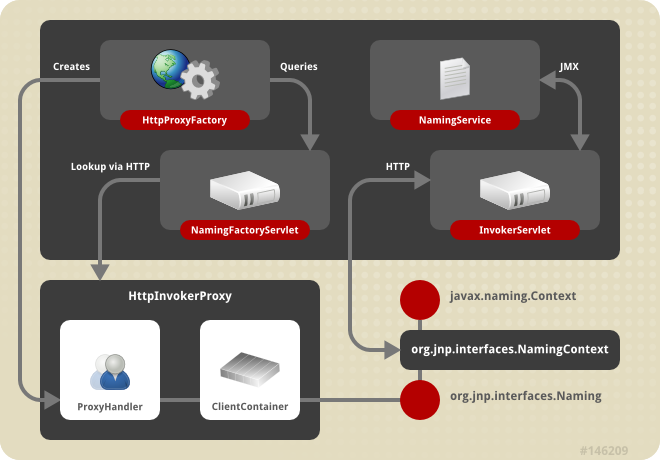
Figure 9.2. The HTTP invoker proxy/server structure for a JNDI Context
Before looking at the configurations let us look at the operation of the
http-invoker services. Figure 9.2, “The HTTP invoker proxy/server structure for a JNDI Context” shows a logical view of the structure of a JBoss JNDI proxy and its relationship to the server side components of the http-invoker. The proxy is obtained from the NamingFactoryServlet using an InitialContext with the Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY property set to org.jboss.naming.HttpNamingContextFactory, and the Context.PROVIDER_URL property set to the HTTP URL of the NamingFactoryServlet. The resulting proxy is embedded in an org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContext instance that provides the Context interface implementation.
The proxy is an instance of
org.jboss.invocation.http.interfaces.HttpInvokerProxy, and implements the org.jnp.interfaces.Naming interface. Internally the HttpInvokerProxy contains an invoker that marshals the Naming interface method invocations to the InvokerServlet via HTTP posts. The InvokerServlet translates these posts into JMX invocations to the NamingService, and returns the invocation response back to the proxy in the HTTP post response.
There are several configuration values that need to be set to tie all of these components together and Figure 9.3, “The relationship between configuration files and JNDI/HTTP component” illustrates the relationship between configuration files and the corresponding components.
Figure 9.3. The relationship between configuration files and JNDI/HTTP component
The
http-invoker.sar/META-INF/jboss-service.xml descriptor defines the HttpProxyFactory that creates the HttpInvokerProxy for the NamingService. The attributes that need to be configured for the HttpProxyFactory include:
- InvokerName: The JMX
ObjectNameof theNamingServicedefined in theconf/jboss-service.xmldescriptor. The standard setting used in the JBoss distributions isjboss:service=Naming. - InvokerURL or InvokerURLPrefix + InvokerURLSuffix + UseHostName. You can specify the full HTTP URL to the
InvokerServletusing theInvokerURLattribute, or you can specify the hostname independent parts of the URL and have theHttpProxyFactoryfill them in. An exampleInvokerURLvalue would behttp://jbosshost1.dot.com:8080/invoker/JMXInvokerServlet. This can be broken down into:- InvokerURLPrefix: the URL prefix prior to the hostname. Typically this will be
http://orhttps://if SSL is to be used. - InvokerURLSuffix: the URL suffix after the hostname. This will include the port number of the web server as well as the deployed path to the
InvokerServlet. For the exampleInvokerURLvalue theInvokerURLSuffixwould be:8080/invoker/JMXInvokerServletwithout the quotes. The port number is determined by the web container service settings. The path to theInvokerServletis specified in thehttp-invoker.sar/invoker.war/WEB-INF/web.xmldescriptor. - UseHostName: a flag indicating if the hostname should be used in place of the host IP address when building the hostname portion of the full
InvokerURL. If true,InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostNamemethod will be used. Otherwise, theInetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress()method is used.
- ExportedInterface: The
org.jnp.interfaces.Naminginterface the proxy will expose to clients. The actual client of this proxy is the JBoss JNDI implementationNamingContextclass, which JNDI client obtain fromInitialContextlookups when using the JBoss JNDI provider. - JndiName: The name in JNDI under which the proxy is bound. This needs to be set to a blank/empty string to indicate the interface should not be bound into JNDI. We can not use the JNDI to bootstrap itself. This is the role of the
NamingFactoryServlet.
The
http-invoker.sar/invoker.war/WEB-INF/web.xml descriptor defines the mappings of the NamingFactoryServlet and InvokerServlet along with their initialization parameters. The configuration of the NamingFactoryServlet relevant to JNDI/HTTP is the JNDIFactory entry which defines:
- A
namingProxyMBeaninitialization parameter that maps to theHttpProxyFactoryMBean name. This is used by theNamingFactoryServletto obtain theNamingproxy which it will return in response to HTTP posts. For the defaulthttp-invoker.sar/META-INF/jboss-service.xmlsettings the namejboss:service=invoker,type=http,target=Naming. - A proxy initialization parameter that defines the name of the
namingProxyMBeanattribute to query for the Naming proxy value. This defaults to an attribute name ofProxy. - The servlet mapping for the
JNDIFactoryconfiguration. The default setting for the unsecured mapping is/JNDIFactory/*. This is relative to the context root of thehttp-invoker.sar/invoker.war, which by default is the WAR name minus the.warsuffix.
The configuration of the
InvokerServlet relevant to JNDI/HTTP is the JMXInvokerServlet which defines:
- The servlet mapping of the
InvokerServlet. The default setting for the unsecured mapping is/JMXInvokerServlet/*. This is relative to the context root of thehttp-invoker.sar/invoker.war, which by default is the WAR name minus the.warsuffix.