此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
10.2.7. Web Content Security Constraints
In a web application, security is defined by the roles that are allowed access to content by a URL pattern that identifies the protected content. This set of information is declared by using the
web.xml security-constraint element.
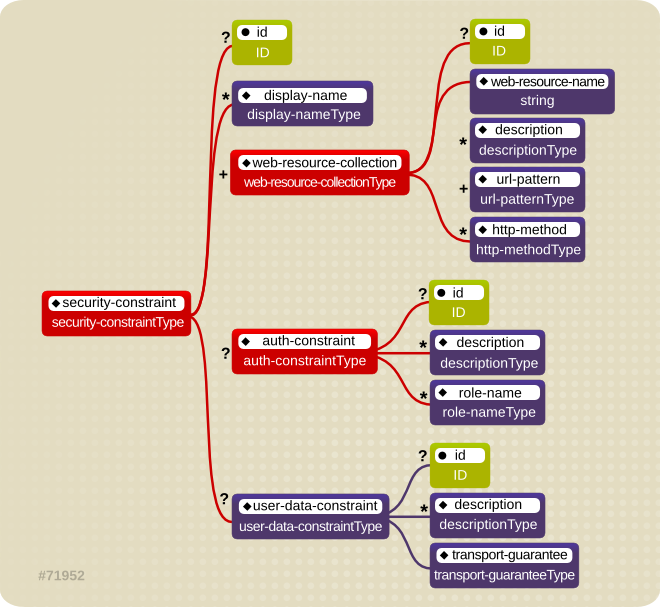
Figure 10.5. Web Content Security Constraints
The content to be secured is declared using one or more <web-resource-collection> elements. Each <web-resource-collection> element contains an optional series of <url-pattern> elements followed by an optional series of <http-method> elements. The <url-pattern> element value specifies a URL pattern against which a request URL must match for the request to correspond to an attempt to access secured content. The <http-method> element value specifies a type of HTTP request to allow.
The optional <user-data-constraint> element specifies the requirements for the transport layer of the client to server connection. The requirement may be for content integrity (preventing data tampering in the communication process) or for confidentiality (preventing reading while in transit). The <transport-guarantee> element value specifies the degree to which communication between the client and server should be protected. Its values are
NONE, INTEGRAL, and CONFIDENTIAL. A value of NONE means that the application does not require any transport guarantees. A value of INTEGRAL means that the application requires the data sent between the client and server to be sent in such a way that it can not be changed in transit. A value of CONFIDENTIAL means that the application requires the data to be transmitted in a fashion that prevents other entities from observing the contents of the transmission. In most cases, the presence of the INTEGRAL or CONFIDENTIAL flag indicates that the use of SSL is required.
The optional <login-config> element is used to configure the authentication method that should be used, the realm name that should be used for the application, and the attributes that are needed by the form login mechanism.
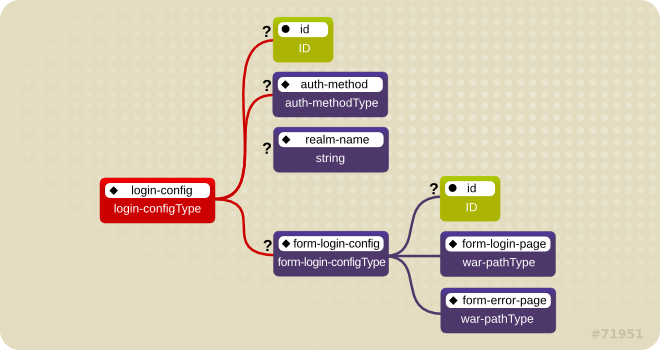
Figure 10.6. Web Login Configuration
The <auth-method> child element specifies the authentication mechanism for the web application. As a prerequisite to gaining access to any web resources that are protected by an authorization constraint, a user must have authenticated using the configured mechanism. Legal <auth-method> values are
BASIC, DIGEST, FORM, SPNEGO, and CLIENT-CERT. The <realm-name> child element specifies the realm name to use in HTTP basic and digest authorization. The <form-login-config> child element specifies the log in as well as error pages that should be used in form-based log in. If the <auth-method> value is not FORM, then form-login-config and its child elements are ignored.
The following configuration example indicates that any URL lying under the web application's
/restricted path requires an AuthorizedUser role. There is no required transport guarantee and the authentication method used for obtaining the user identity is BASIC HTTP authentication.
Example 10.6. web.xml Descriptor Fragment