此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
30.4. State Transfer Between Sites
When an offline master site is back online, it is necessary to synchronize its state with the latest data from the backup site. State transfer allows state to be transferred from one site to another, meaning the master site is synchronized and made consistent with the backup site. Similarly, when a backup site becomes available, state transfer can be utilized to make it consistent with the master site.
A system administrator or an authorized entity initiates the state transfer manually using JMX. The system administrator invokes the
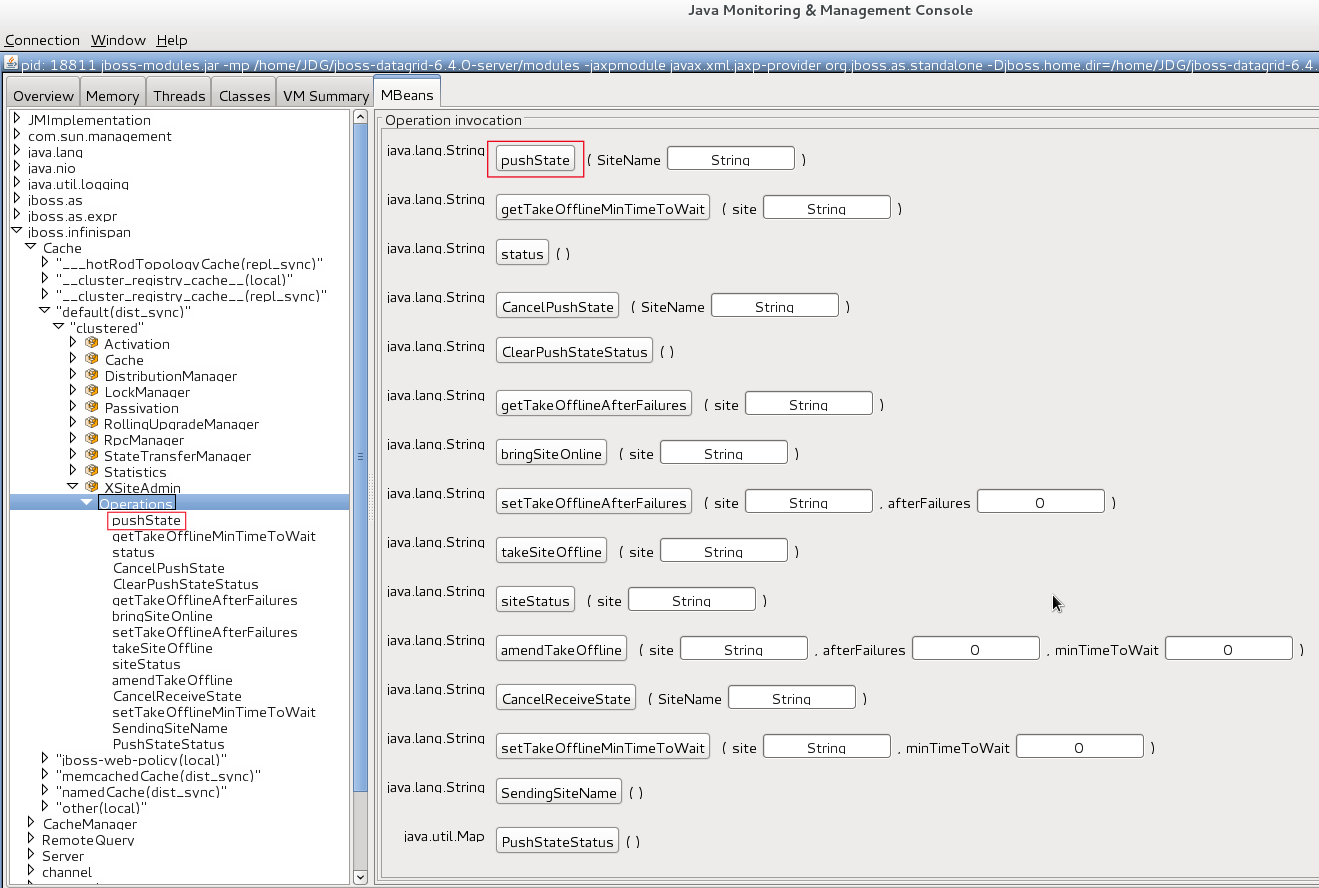
pushState(SiteName String) operation available in the XSiteAdminOperations MBean.
The following interface shows the
pushState(SiteName String) operation in JConsole:
Figure 30.2. PushState Operation
State transfer is also invoked using the Command Line Interface (CLI) by the
site push sitename command. The system administrator invokes the state transfer operation in the backup site, specifying the master site name that is to receive the state.
The master site can be offline at the time of the push operation. On successful state transfer, the state data common to both the sites is overwritten on the master site. For example, if key A exists on the master site but not on the backup site, key A will not be deleted from the master site. Whereas, if key B exists on the backup as well as the master site, key B is overwritten on the master site.
30.4.1. Active-Passive State Transfer
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The active-passive state transfer is used when cross-site replication is used to back up the master site. The master site processes all the requests but if it goes offline, the backup site starts to handle them. When the master site is back online, it receives the state from the backup site and starts to handle the client requests.
In active-passive state transfer mode, the client read-write requests occurs only on the backup site. The master site acts as an invisible backup until the client requests are switched to it when the state transfer is completed. The active-passive state transfer mode is fully supported in cross-datacenter replication.
For example, there is a running backup site and the system administrator wants to bring back the master site online. To use active-passive state transfer, the system administrator will perform the following steps.
- Boot the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cluster in the master site.
- Command the backup site to push state to the master site.
- Wait until the state transfer is complete.
- Make the clients aware that the master site is available to process the requests.
30.4.2. Active-Active State Transfer
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
In active-active state transfer mode, the client requests occur concurrently in both the sites while the state transfer is in progress. The current implementation supports handling requests in the new site while the state transfer is in progress, which may break the data consistency.
Warning
Active-active state transfer mode is not fully supported, as it may lead to data inconsistencies.
Note
In active-active state transfer mode, both the sites, the master and the backup sites share the same role. There is no clear distinction between the master and backup sites in the active-active state transfer mode
For example, there is a running site and the system administrator wants to bring a new site online. To use active-active state transfer, the system administrator must perform the following steps.
- Boot the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cluster in the new site.
- Command the running site to push state to the new site.
- Make the clients aware that the new site is available to process the requests.
30.4.3. State Transfer Configuration
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
State transfer between sites is not enabled or disabled but it allows to tune some parameters. The only configuration is done by the system administrator while configuring the load balancer to switch the request to the master site during or after the state transfer. The implementation handles a case in which a key is updated by a client before it receives the state, ignoring when it is delivered.
The following are default parameter values: