此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
1.6. JBoss Data Grid Cache Architecture
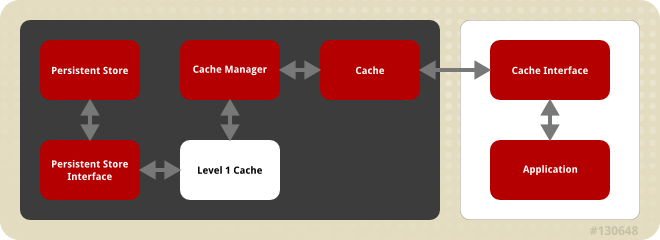
Figure 1.1. JBoss Data Grid Cache Architecture
JBoss Data Grid's cache infrastructure depicts the individual elements and their interaction with each other. For clarity, the cache architecture diagram is separated into two parts:
- Elements that a user cannot directly interact with (depicted within a dark box), which includes the Cache, Cache Manager, Level 1 Cache, Persistent Store Interfaces and the Persistent Store.
- Elements that a user can interact directly with (depicted within a white box), which includes Cache Interfaces and the Application.
Cache Architecture Elements
JBoss Data Grid's cache architecture includes the following elements:
- The Persistent Store permanently houses cache instances and entries.
- JBoss Data Grid offers two Persistent Store Interfaces to access the persistent store. Persistent store interfaces can be either:
- A cache loader is a read only interface that provides a connection to a persistent data store. A cache loader can locate and retrieve data from cache instances and from the persistent store. For details, see Section 10.8, “Cache Loaders”.
- A cache store extends the cache loader functionality to include write capabilities by exposing methods that allow the cache loader to load and store states. For details, see Chapter 10, Cache Stores and Cache Loaders.
- The Level 1 Cache (or L1 Cache) stores remote cache entries after they are initially accessed, preventing unnecessary remote fetch operations for each subsequent use of the same entries. For details, see Chapter 14, The L1 Cache.
- The Cache Manager is the primary mechanism used to retrieve a Cache instance in JBoss Data Grid, and can be used as a starting point for using the Cache. For details, see Chapter 11, Cache Managers.
- The Cache houses cache instances retrieved by a Cache Manager.
- Cache Interfaces use protocols such as Memcached and Hot Rod, or REST to interface with the cache. For details about the remote interfaces, refer to the Developer Guide.
- Memcached is an in-memory caching system used to improve response and operation times for database-driver websites. The Memcached caching system defines a text based, client-server caching protocol called the Memcached protocol.
- Hot Rod is a binary TCP client-server protocol used in JBoss Data Grid. It was created to overcome deficiencies in other client/server protocols, such as Memcached. Hot Rod enables clients to do smart routing of requests in partitioned or distributed JBoss Data Grid server clusters.
- The REST protocol eliminates the need for tightly coupled client libraries and bindings. The REST API introduces an overhead, and requires a REST client or custom code to understand and create REST calls.
- An application allows the user to interact with the cache via a cache interface. Browsers are a common example of such end-user applications.