第 1 章 Linux 虚拟服务器总览
Linux 虚拟服务器(LVS)是一组用来在真实服务器间平衡 IP 负载的整合软件组件。LVS 在一对配置相同的计算机中运行:一个是活跃 LVS 路由器,一个是备用 LVS 路由器。活跃 LVS 路由器有两个作用:
- 平衡真实服务器中的负载。
- 检查每个真实服务器中服务的完整性。
备用路由器的任务是监控活跃路由器并在活跃路由器出错的事件中扮演它的角色。
本章提供了 LVS 组件和功能的总览,它们由以下部分组成:
1.1. A Basic LVS Configuration
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
图 1.1 “A Basic LVS Configuration” shows a simple LVS configuration consisting of two layers. On the first layer are two LVS routers — one active and one backup. Each of the LVS routers has two network interfaces, one interface on the Internet and one on the private network, enabling them to regulate traffic between the two networks. For this example the active router is using Network Address Translation or NAT to direct traffic from the Internet to a variable number of real servers on the second layer, which in turn provide the necessary services. Therefore, the real servers in this example are connected to a dedicated private network segment and pass all public traffic back and forth through the active LVS router. To the outside world, the servers appears as one entity.
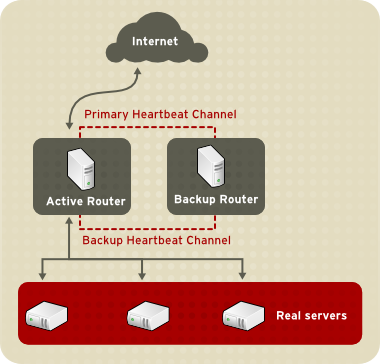
图 1.1. A Basic LVS Configuration
Service requests arriving at the LVS routers are addressed to a virtual IP address, or VIP. This is a publicly-routable address the administrator of the site associates with a fully-qualified domain name, such as www.example.com, and is assigned to one or more virtual servers. A virtual server is a service configured to listen on a specific virtual IP. Refer to 第 4.6 节 “VIRTUAL SERVERS” for more information on configuring a virtual server using the Piranha Configuration Tool. A VIP address migrates from one LVS router to the other during a failover, thus maintaining a presence at that IP address (also known as floating IP addresses).
VIP 地址还可以是同样将 LVS 路由器连接到互联网的设备的别名。例如:如果使用 eth0 连接到互联网,那么多个虚拟服务器就可以别名命名为
eth0:1。另外,每个虚拟服务器还可以根据服务关联到不同的设备。例如:HTTP 流量可由 eth0:1 处理,而 FTP 流量可由 eth0:2 处理。
Only one LVS router is active at a time. The role of the active router is to redirect service requests from virtual IP addresses to the real servers. The redirection is based on one of eight supported load-balancing algorithms described further in 第 1.3 节 “LVS 调度总览”.
活跃路由器还通过 send/expect 脚本动态监控真实服务器中特定服务的总体状态。侦测服务的状态需要动态数据,比如 HTTPS 或者 SSL。管理员还可以调用外部可执行程序。如果真实服务器中的某个服务失效,活跃路由器会停止向该服务器发送任务,直到它能够返回正常操作为止。
备用路由器是一个替补系统。LVS 路由器周期性地通过主要外部公共接口交换 heartbeat 信息,在失效切换的状态下,通过专用接口交换。备用节点应该无法在预期间隔之间接收 heartbeat 信息,它会启动一个失效切换,并假装执行活跃路由器的任务。在失效切换中,备用路由器接替了由出错的路由器提供的 VIP 地址,所用技术就是我们知道的 ARP 嗅探 — 在这里备用 LVS 路由器宣布它自己成为发往出错节点的 IP 数据包的目的地。当出错节点又可以提供服务时,备用节点由将自己设为随时可替换的角色。
The simple, two-layered configuration used in 图 1.1 “A Basic LVS Configuration” is best for serving data which does not change very frequently — such as static webpages — because the individual real servers do not automatically sync data between each node.
因为 LVS 中没有可用来在真实服务器之间共享相同数据的内置组件,所以管理员有两个基本选择:
- 在真实服务器池之间同步数据
- 为共享数据的访问在布局中添加第三层
对于不允许上传大量用户或者在真实服务器中进行数据修改的服务器来说,第一个选择是首选的。如果配置允许大量用户修改数据,比如电子商务网站,最好添加第三层。
管理员可用来同步真实服务器池数据的方法有很多。例如:可采用 shell 脚本,那么如果网页工程师更新了页面,就可同时将该页面发送到所有服务器中。还有,系统管理员可以使用类似
rsync 的程序来在设定的间隔期间重复所有节点中修改的数据。
但是,如果由于用户经常上传文件或者进行数据库传送造成配置超载,这种数据同步就不是最佳的同步方法。对于有高负载的配置,三层布局是最佳解决方案。