此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
14.3. How a Maven Proxy Resolves Artifacts
Overview
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
A Maven proxy is essentially a Web server that is configured to behave like a standard Maven repository server. Remember that the purpose of the Maven proxy is to serve artifacts to remote HTTP clients, not to install artifacts locally. So, although Maven proxy configuration properties have similar names to the managed container case, they ultimately serve quite a different purpose.
Fabric8 Maven proxy server
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The Fabric8 Maven proxy server is a HTTP server, implemented as a servlet inside the container's default Jetty container. Hence, the Maven proxy server shares the same port number, 8181, as many of the other Karaf container services. On a given host,
Host, the Maven proxy can be accessed through the following URL:
http://Host:8181/maven/download
http://Host:8181/maven/download
The Fabric8 Maven proxy server is configured by setting properties from the
io.fabric8.maven.proxy PID. By default, some of these properties are set in the default profile and some are set in the fabric profile.
io.fabric8.maven bundle layer
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The
io.fabric8.maven bundle layer offers similar functionality to the Pax URL Aether component (from a standalone Karaf container).
The
io.fabric8.maven bundle is configured by setting properties from the io.fabric8.maven PID and these properties are normally set in the default profile (recommended).
Serving artifacts through the Maven proxy
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Figure 14.3, “Maven Proxy Serving an Artifact” shows how a Maven proxy processes a HTTP download request, by locating the requested Maven artifact and then returning it to the client.
Figure 14.3. Maven Proxy Serving an Artifact
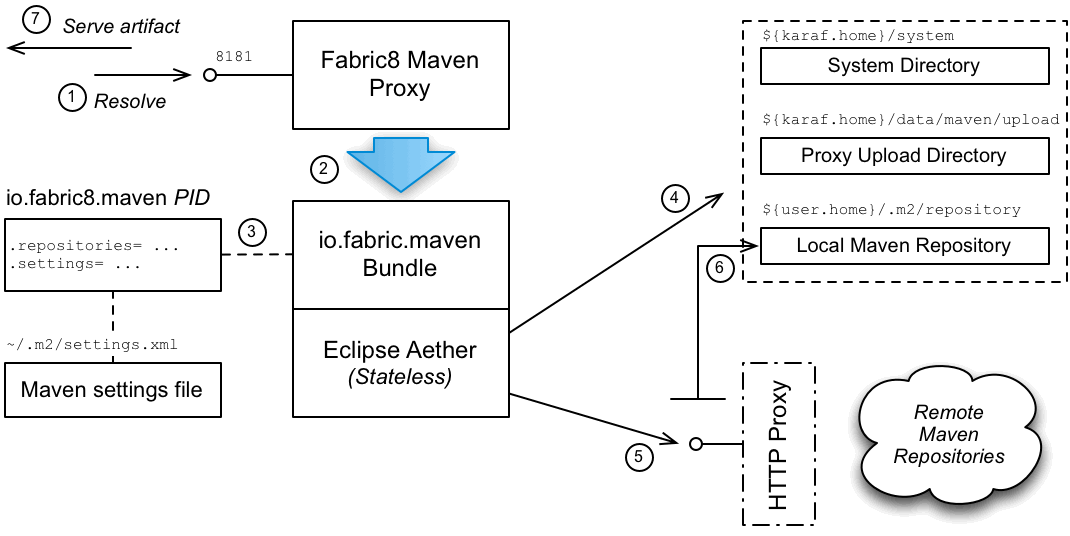
Steps to serve artifacts
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The steps to serve the required Maven artifacts are, as follows:
- Resolution of a Maven artifact is triggered when a managed container sends a request to the Maven proxy server.
- The Maven proxy server parses the incoming HTTP request and then makes a call to the
io.fabric8.mavenlayer, asking it to resolve the requested Maven artifact. - The
io.fabric8.mavenlayer reads its Maven configuration from theio.fabric8.mavenPID in thedefaultprofile (and possibly also from a Mavensettings.xmlfile, if so configured). - When the Aether library is invoked, the first step is to look up any local Maven repositories to try and find the Maven artifact. The following local repositories are configured by default:
InstallDir/system- The JBoss Fuse system directory, which contains all of the Maven artifacts that are bundled with the JBoss Fuse distribution.
InstallDir/data/maven/upload- The Maven proxy's upload directory, which is used to store artifacts that have been directly uploaded to the Maven proxy—see Section 14.6, “Automated Deployment”.
UserHome/.m2/repository- The user's own local Maven repository in the user's home directory,
UserHome.
If the Maven artifact is found locally, skip straight to step 7. - Aether next tries to look up the specified remote repositories. Because the remote repositories are located on the Internet (accessed through the HTTP protocol), it is necessary to have Internet access in order for this step to succeed.NoteIf your local network requires you to use a HTTP proxy to access the Internet, it is possible to configure Fabric8 to use a HTTP proxy. For example, see the section called “Configuring a HTTP proxy” for details.
- If the Maven artifact is found in a remote repository, Aether automatically installs the artifact into the local Maven repository,
UserHome/.m2/repository, so that another remote lookup will not be required. - The Maven proxy server returns the successfully located Maven artifact to the client (or an error message, if the artifact could not be found).