此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 56. Implementing the Interceptors Processing Logic
Abstract
Interceptors are straightforward to implement. The bulk of their processing logic is in the
handleMessage() method. This method receives the message data and manipulates it as needed. Developers may also want to add some special logic to handle fault processing cases.
56.1. Interceptor Flow
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Figure 56.1, “Flow through an interceptor” shows the process flow through an interceptor.
Figure 56.1. Flow through an interceptor
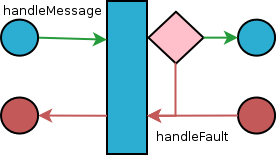
Messages normally pass through an interceptor's handleMessage() method. In the event of a fault occurring at either the current interceptor or a later interceptor, the messages will pass through the interceptor's handleFault() method.
In normal message processing, only the
handleMessage() method is called. The handleMessage() method is where the interceptor's message processing logic is placed.
If an error occurs in the
handleMessage() method of the interceptor, or any subsequent interceptor in the interceptor chain, the handleFault() method is called. The handleFault() method is useful for cleaning up after an interceptor in the event of an error. It can also be used to alter the fault message.