此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 5. Logical Networks
5.1. Introduction to Logical Networks
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
A logical network is a named set of global network connectivity properties in your system. When a logical network is added to a host, it may be further configured with host-specific network parameters. Logical networks optimize network flow by grouping network traffic by usage, type, and requirements.
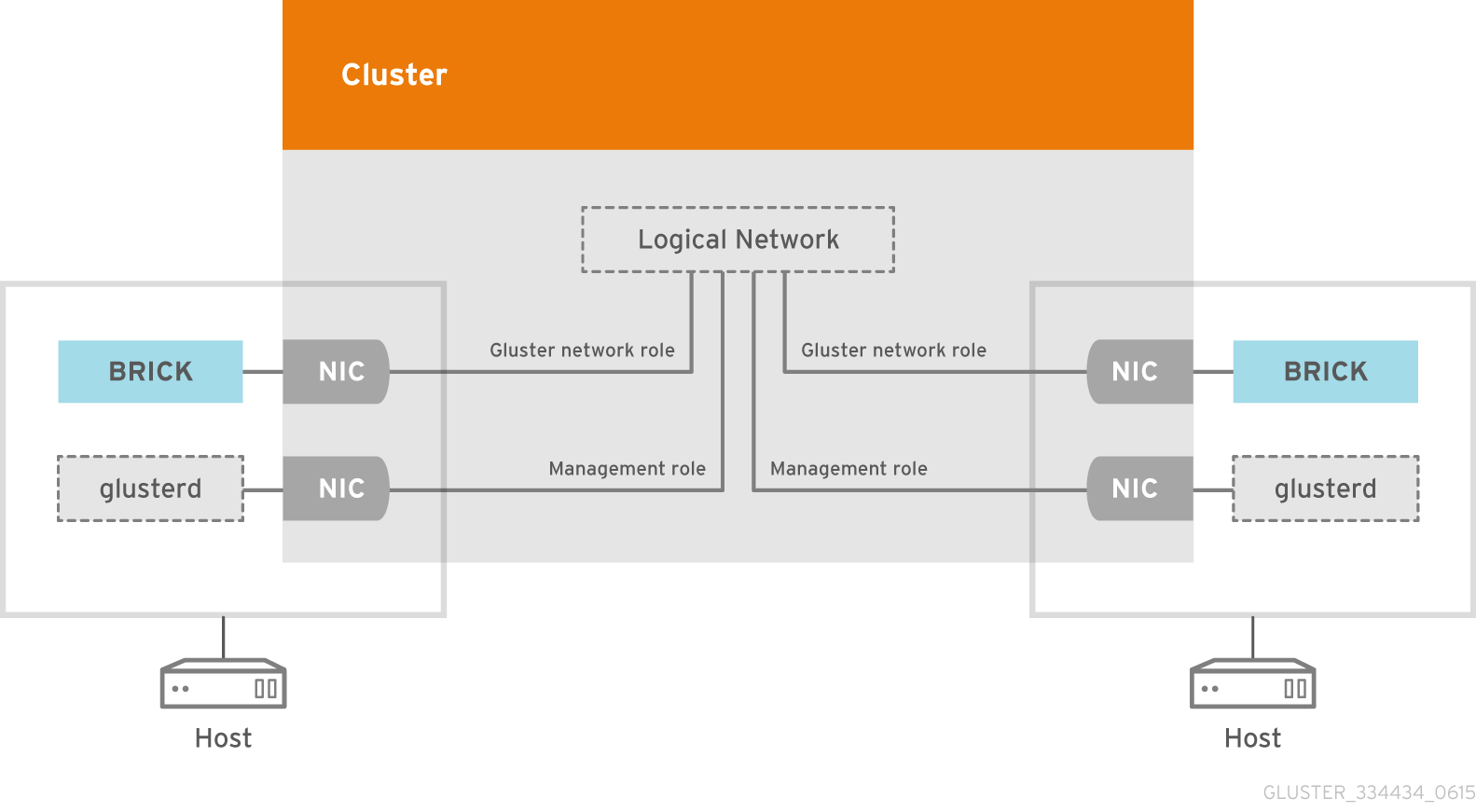
Logical networks allow both connectivity and segregation. You can create a logical network for gluster storage communication to optimize network traffic between hosts and gluster bricks, a logical network specifically for all network traffic, or multiple logical networks to carry the traffic of groups of networks.
The default logical network is the management network called
ovirtmgmt. The ovirtmgmt network carries all traffic, until another logical network is created. It is meant especially for management communication between the Red Hat Gluster Storage Console and hosts.
When a host has multiple interfaces, user can choose the interface to be used while adding the brick, by tagging one of the host's interface with the Gluster Network role. A logical network that has been designated as Required must be configured in all of a cluster's hosts before it is operational. Optional networks can be used by any host they have been added to.
Figure 5.1. Logical Network architecture
Warning
Do not change networking in a cluster if any hosts are running as this risks making the host unreachable.