此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 3. Examples
Below are several examples to illustrate how JBoss EAP works and where it fits into different environments.
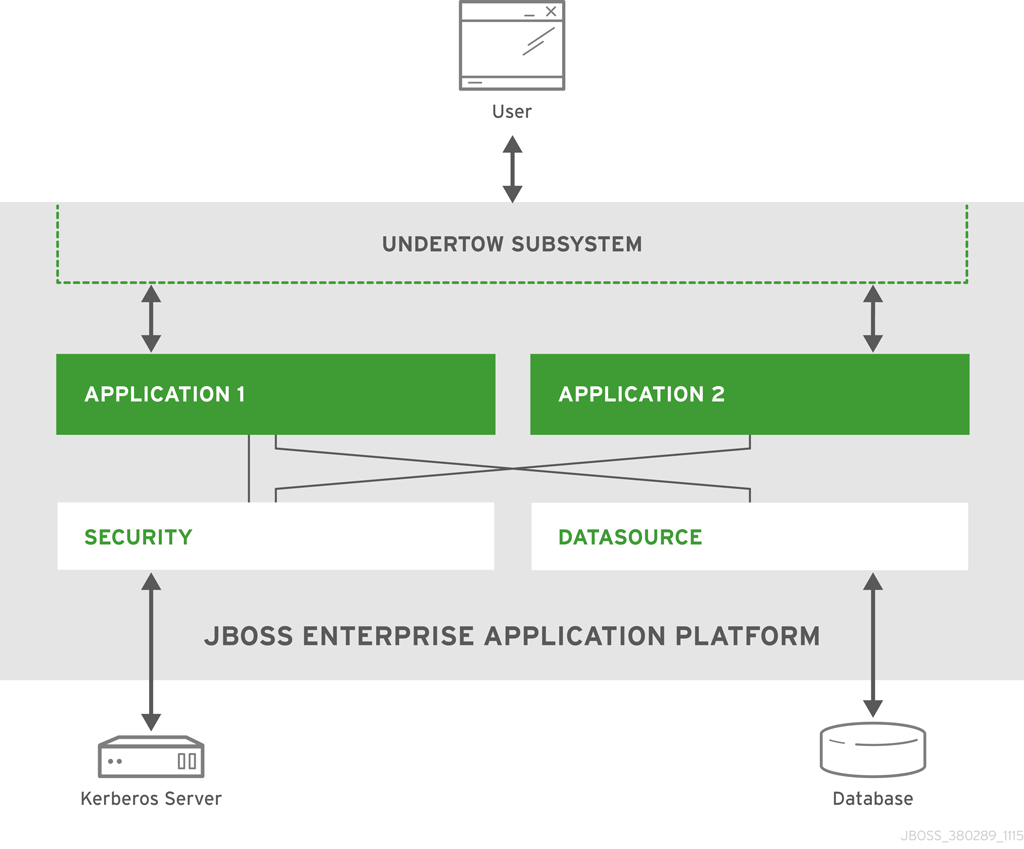
3.1. Simple Example
This example shows a simple JBoss EAP setup. The JBoss EAP instance has two applications deployed to it. It is also configured to connect to a database using the datasources subsystem and a Kerberos server using the security subsystem. These connections are exposed to the deployed applications. The JBoss EAP instance handles requests (through the undertow subsystem) and directs those requests to the appropriate application. The applications use the APIs exposed by JBoss EAP to connect to the database and Kerberos server, and perform their implemented business logic. After completion, the applications send a response back to the requester through the undertow subsystem.
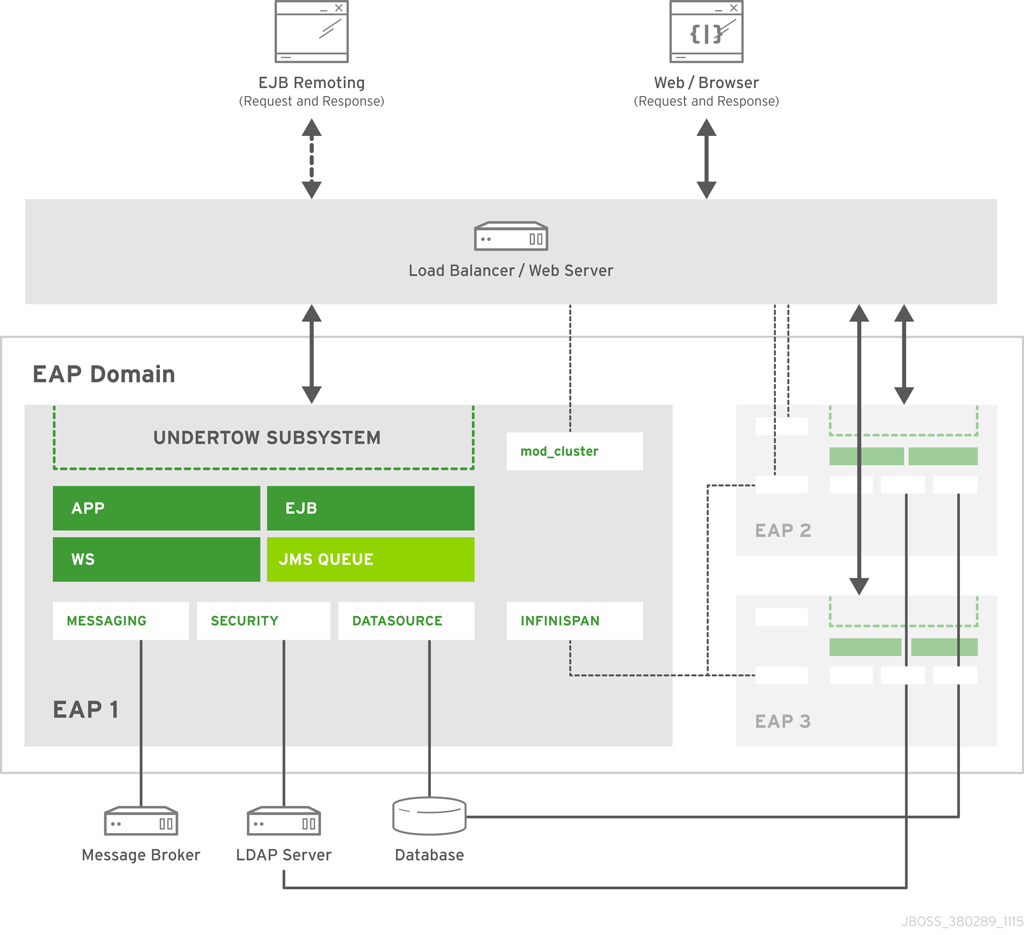
3.2. Expanded Example
This example illustrates a more complex setup involving three JBoss EAP instances arranged in a managed domain with either a load balancer or a web server. The three instances are also configured to support high availability through load balancing (using mod_cluster) and session replication (using Infinispan). All three JBoss EAP instances have a web application, a web service, and EJB deployed. One JBoss EAP instance has a JMS queue configured (through the messaging-activemq subsystem). All three JBoss EAP instances have connections to a database and an LDAP server (through the datasource and security domains, respectively) and one JBoss EAP instance is configured to connect to an external message broker (through the messaging-activemq subsystem). Those configured connections are exposed to the applications, web services, EJBs, and JMS queues deployed to that respective instance.
All inbound requests (intended for the application, web service, or EJB) are first received by the load balancer or web server. Based on the configured load balancing algorithm and the information provided by each JBoss EAP instance, the web server or load balancer directs that request to the appropriate JBoss EAP instance. The JBoss EAP instance handles requests (through the undertow subsystem) and directs those request to the appropriate application. The applications use the APIs exposed by JBoss EAP to connect to the database and Kerberos server, and perform their implemented business logic. After completion, the applications send a response back to the requester through the undertow subsystem. Any non-persisted information (for example, session information) is propagated among the JBoss EAP instances through the infinispan subsystem.
Revised on 2018-02-08 10:17:32 EST