此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 7. BPMN2 gateways in process designer
Gateways are used to create or synchronize branches in the workflow using a set of conditions called the gating mechanism. BPMN2 supports two types of gateways:
- Converging gateways, merging multiple flows into one flow
- Diverging gateways, splitting one flow into multiple flows
One gateway cannot have multiple incoming and multiple outgoing flows.
In the following business process diagram, the XOR gateway evaluates only the incoming flow whose condition evaluates to true:
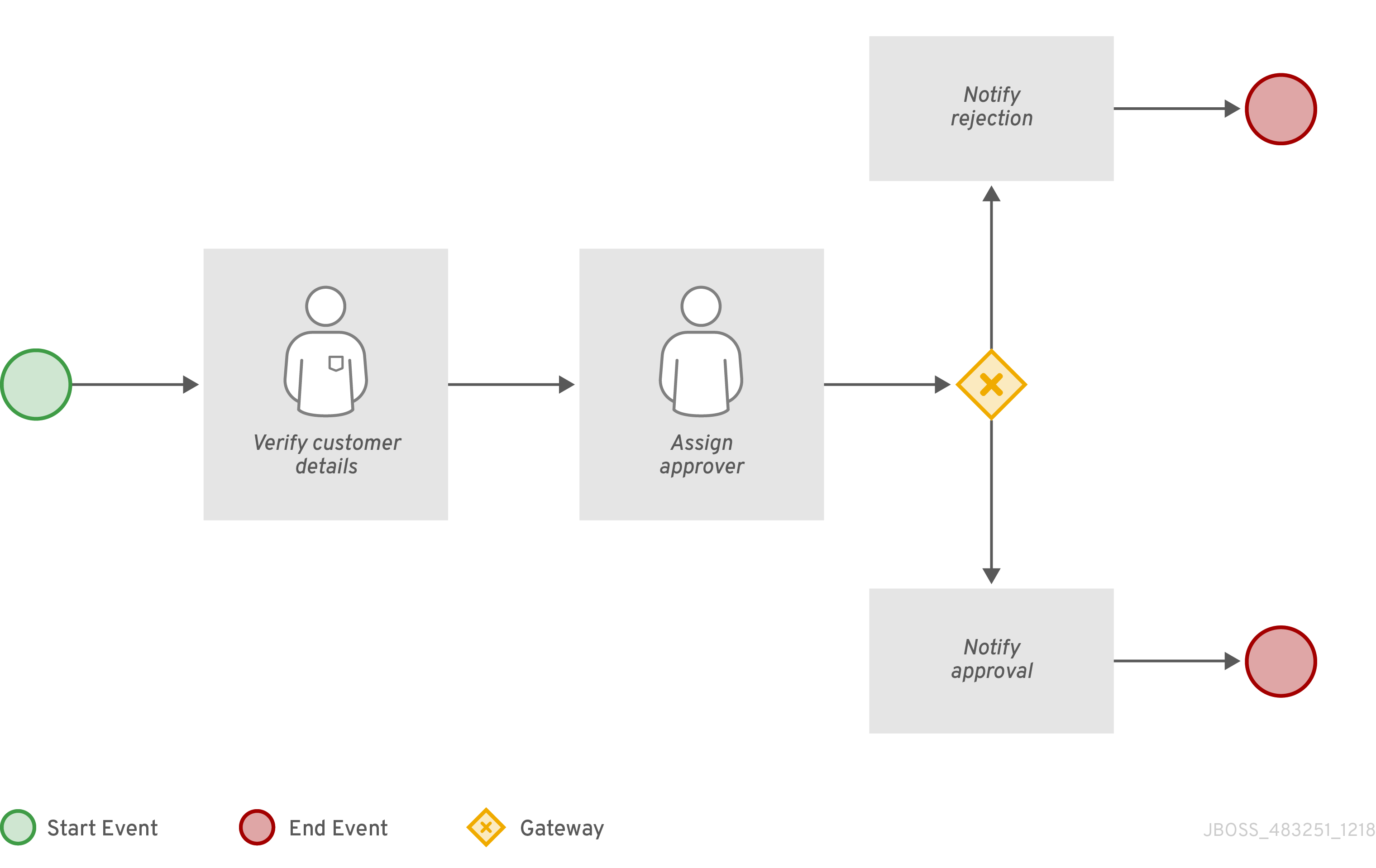
In this example, the customer details are verified by a user and the process is assigned to a user for approval. If approved, an approval notification is sent to the user. If the event of the request is rejected, a rejection notification is sent to the user.
| Element type | Icon |
|---|---|
| exclusive (XOR) |
|
| Inclusive |
|
| Parallel |
|
| Event |
|
Exclusive
In an exclusive diverging gateway, only the first incoming flow whose condition evaluates to true is chosen. In a converging gateway, the next node is triggered for each triggered incoming flow.
The gateway triggers exactly one outgoing flow. The flow with the constraint evaluated to true and the lowest priority number is taken.
Ensure that at least one of the outgoing flows evaluates to true at run time. Otherwise, the process instance terminates with a runtime exception.
The converging gateway enables a workflow branch to continue to its outgoing flow as soon as it reaches the gateway. When one of the incoming flows triggers the gateway, the workflow continues to the outgoing flow of the gateway. If it is triggered from more than one incoming flow, it triggers the next node for each trigger.
Inclusive
With an inclusive diverging gateway, the incoming flow is taken and all outgoing flows that evaluate to true are taken. Connections with lower priority numbers are triggered before triggering higher priority connections. Priorities are evaluated but the BPMN2 specification does not guarantee the priority order. Avoid depending on the priority attribute in your workflow.
Ensure that at least one of the outgoing flows evaluates to true at run time. Otherwise, the process instance terminates with a runtime exception.
A converging inclusive gateway merges all incoming flows previously created by an inclusive diverging gateway. It acts as a synchronizing entry point for the inclusive gateway branches.
Parallel
Use a parallel gateway to synchronize and create parallel flows. With a parallel diverging gateway, the incoming flow is taken, all outgoing flows are taken simultaneously. With a converging parallel gateway, the gateway waits until all incoming flows have entered and only then triggers the outgoing flow.
Event
An event-based gateway is only diverging and enables you to react to possible events as opposed to the data-based exclusive gateway, which reacts to the process data. The outgoing flow is taken based on the event that occurs. Only one outgoing flow is taken at a time. The gateway might act as a start event, where the process is instantiated only if one of the intermediate events connected to the event-based gateway occurs.



