此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
Chapter 19. Threat Model Mitigation
This chapter discusses possible security vulnerabilities any authentication server could have and how Red Hat Single Sign-On mitigates those vulnerabilities. A good list of potential vulnerabilities and what security implementations should do to mitigate them can be found in the OAuth 2.0 Threat Model document put out by the IETF. Many of those vulnerabilities are discussed here.
19.1. Host
Red Hat Single Sign-On uses the public hostname for a number of things. For example, in the token issuer fields and URLs sent in password reset emails.
By default, the hostname is based on the request headers and there is no check to make sure this hostname is valid.
If you are not using a load balancer or proxy in front of Red Hat Single Sign-On that prevents invalid host headers, you must explicitly configure what hostnames should be accepted.
The Hostname SPI provides a way to configure the hostname for a request. The out of the box provider allows setting a fixed URL for frontend requests, while allowing backend requests to be based on the request URI. It is also possible to develop your own provider in the case the built-in provider does not provide the functionality needed.
19.2. Admin Endpoints and Console
The Red Hat Single Sign-On administrative REST API and the web console are exposed by default on the same port as non-admin usage. If access to the admin console is not needed externally, we recommend not exposing the admin endpoints on the Internet.
This can be achieved either directly in Red Hat Single Sign-On or with a proxy such as Apache or nginx.
For the proxy option please follow the documentation for the proxy. You need to control access to any requests to /auth/admin.
To achieve this directly in Red Hat Single Sign-On there are a few options. This document covers two options, IP restriction and separate ports.
Once the admin console is no longer accessible on the frontend URL of Keycloak, you need to configure a fixed admin URL in the default hostname provider.
19.2.1. IP Restriction
It is possible to restrict access to /auth/admin to only specific IP addresses.
The following example restricts access to /auth/admin to IP addresses in the range 10.0.0.1 to 10.0.0.255.
Equivalent configuration using CLI commands:
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=ipAccess:add(,expression="path-prefix[/auth/admin] -> ip-access-control(acl={'10.0.0.0/24 allow'})")
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=ipAccess:add()
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=ipAccess:add(,expression="path-prefix[/auth/admin] -> ip-access-control(acl={'10.0.0.0/24 allow'})")
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=ipAccess:add()For IP restriction if you are using a proxy it is important to configure it correctly to make sure Red Hat Single Sign-On receives the client IP address and not the proxy IP address
19.2.2. Port Restriction
It is possible to expose /auth/admin to a different port that is not exposed on the Internet.
The following example exposes /auth/admin on port 8444 while not permitting access with the default port 8443.
Equivalent configuration using CLI commands:
19.3. Password guess: brute force attacks
A brute force attack happens when an attacker is trying to guess a user’s password. Red Hat Single Sign-On has some limited brute force detection capabilities. If turned on, a user account will be temporarily disabled if a threshold of login failures is reached. To enable this feature go to the Realm Settings left menu item, click on the Security Defenses tab, then additional go to the Brute Force Detection sub-tab.
Brute Force Detection is disabled by default. Enabling this feature is highly recommended to protect against this type of attack.
Brute Force Detection
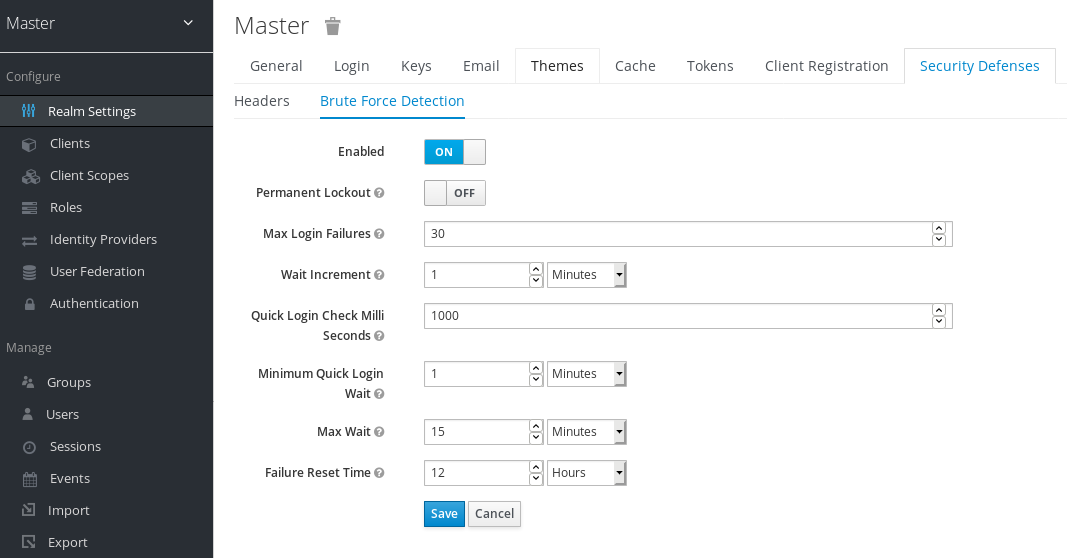
There are 2 different configurations for brute force detection; permanent lockout and temporary lockout. Permanent lockout will disable a user’s account after an attack is detected; the account will be disabled until an administrator renables it. Temporary lockout will disable a user’s account for a time period after an attack is detected; the time period for which the account is disabled increases the longer the attack continues.
Common Parameters
- Max Login Failures
- Maximum number of login failures permitted. Default value is 30.
- Quick Login Check Milli Seconds
- Minimum time required between login attempts. Default is 1000.
- Minimum Quick Login Wait
- Minimum amount of time the user will be temporarily disabled if logins attempts are quicker than Quick Login Check Milli Seconds. Default is 1 minute.
Temporary Lockout Parameters
- Wait Increment
- Amount of time added to the time a user is temporarily disabled after each time Max Login Failures is reached. Default is 1 minute.
- Max Wait
- The maximum amount of time for which a user will be temporarily disabled. Default is 15 minutes.
- Failure Reset Time
- Time after which the failure count will be reset; timer runs from the last failed login. Default is 12 hours.
Permanent Lockout Algorithm
On successful login
-
Reset
count
-
Reset
On failed login
-
Increment
count If
countgreater than Max Login Failures- Permanently disable user
Else if time between this failure and the last failure is less than Quick Login Check Milli Seconds
- Temporarily disable user for Minimum Quick Login Wait
-
Increment
When a user is disabled they can not login until an administrator enables the user; enabling an account resets count.
Temporary Lockout Algorithm
On successful login
-
Reset
count
-
Reset
On failed login
If time between this failure and the last failure is greater than Failure Reset Time
-
Reset
count
-
Reset
-
Increment
count -
Calculate
waitusing Wait Increment * (count/ Max Login Failures). The division is an integer division so will always be rounded down to a whole number If
waitequals 0 and time between this failure and the last failure is less than Quick Login Check Milli Seconds then setwaitto Minimum Quick Login Wait instead-
Temporarily disable the user for the smaller of
waitand Max Wait seconds
-
Temporarily disable the user for the smaller of
Login failures when a user is temporarily disabled do not increment count.
The downside of Red Hat Single Sign-On brute force detection is that the server becomes vulnerable to denial of service attacks. An attacker can simply try to guess passwords for any accounts it knows and these account will be disabled. Eventually we will expand this functionality to take client IP address into account when deciding whether to block a user.
A better option might be a tool like Fail2Ban. You can point this service at the Red Hat Single Sign-On server’s log file. Red Hat Single Sign-On logs every login failure and client IP address that had the failure. Fail2Ban can be used to modify firewalls after it detects an attack to block connections from specific IP addresses.
19.3.1. Password Policies
Another thing you should do to prevent password guess is to have a complex enough password policy to ensure that users pick hard to guess passwords. See the Password Policies chapter for more details.
The best way to prevent password guessing though is to set up the server to use a one-time-password (OTP).
19.4. Clickjacking
With clickjacking, a malicious site loads the target site in a transparent iFrame overlaid on top of a set of dummy buttons that are carefully constructed to be placed directly under important buttons on the target site. When a user clicks a visible button, they are actually clicking a button (such as a "login" button) on the hidden page. An attacker can steal a user’s authentication credentials and access their resources.
By default, every response by Red Hat Single Sign-On sets some specific browser headers that can prevent this from happening. Specifically, it sets X-FRAME_OPTIONS and Content-Security-Policy. You should take a look at the definition of both of these headers as there is a lot of fine-grain browser access you can control. In the admin console you can specify the values these headers will have. Go to the Realm Settings left menu item and click the Security Defenses tab and make sure you are on the Headers sub-tab.
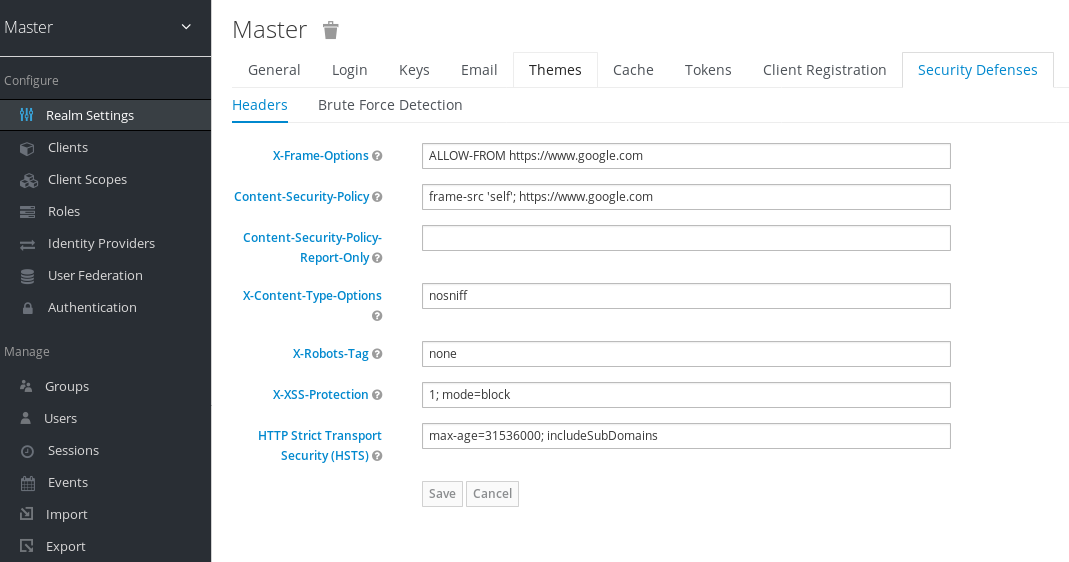
By default, Red Hat Single Sign-On only sets up a same-origin policy for iframes.
19.5. SSL/HTTPS Requirement
If you do not use SSL/HTTPS for all communication between the Red Hat Single Sign-On auth server and the clients it secures, you will be very vulnerable to man in the middle attacks. OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect uses access tokens for security. Without SSL/HTTPS, attackers can sniff your network and obtain an access token. Once they have an access token they can do any operation that the token has been given permission for.
Red Hat Single Sign-On has three modes for SSL/HTTPS. SSL can be hard to set up, so out of the box, Red Hat Single Sign-On allows non-HTTPS communication over private IP addresses like localhost, 192.168.x.x, and other private IP addresses. In production, you should make sure SSL is enabled and required across the board.
On the adapter/client side, Red Hat Single Sign-On allows you to turn off the SSL trust manager. The trust manager ensures identity the client is talking to. It checks the DNS domain name against the server’s certificate. In production you should make sure that each of your client adapters is configured to use a truststore. Otherwise you are vulnerable to DNS man in the middle attacks.
19.6. CSRF Attacks
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a web-based attack whereby HTTP requests are transmitted from a user that the web site trusts or has authenticated with(e.g. via HTTP redirects or HTML forms). Any site that uses cookie based authentication is vulnerable to these types of attacks. These attacks are mitigated by matching a state cookie against a posted form or query parameter.
The OAuth 2.0 login specification requires that a state cookie be used and matched against a transmitted state parameter. Red Hat Single Sign-On fully implements this part of the specification so all logins are protected.
The Red Hat Single Sign-On Admin Console is a pure JavaScript/HTML5 application that makes REST calls to the backend Red Hat Single Sign-On admin REST API. These calls all require bearer token authentication and are made via JavaScript Ajax calls. CSRF does not apply here. The admin REST API can also be configured to validate the CORS origins as well.
The only part of Red Hat Single Sign-On that really falls into CSRF is the user account management pages. To mitigate this Red Hat Single Sign-On sets a state cookie and also embeds the value of this state cookie within hidden form fields or query parameters in action links. This query or form parameter is checked against the state cookie to verify that the call was made by the user.
19.7. Unspecific Redirect URIs
For the Authorization Code Flow, if you register redirect URIs that are too general, then it would be possible for a rogue client to impersonate a different client that has a broader scope of access. This could happen for instance if two clients live under the same domain. So, it’s a good idea to make your registered redirect URIs as specific as feasible.
19.8. Compromised Access and Refresh Tokens
There are a few things you can do to mitigate access tokens and refresh tokens from being stolen. The most important thing is to enforce SSL/HTTPS communication between Red Hat Single Sign-On and its clients and applications. It might seem obvious, but since Red Hat Single Sign-On does not have SSL enabled by default, an administrator might not realize that it is necessary.
Another thing you can do to mitigate leaked access tokens is to shorten their lifespans. You can specify this within the timeouts page. Short lifespans (minutes) for access tokens for clients and applications to refresh their access tokens after a short amount of time. If an admin detects a leak, they can logout all user sessions to invalidate these refresh tokens or set up a revocation policy. Making sure refresh tokens always stay private to the client and are never transmitted ever is very important as well.
You can also mitigate against leaked access tokens and refresh tokens by issuing these tokens as holder-of-key tokens. See OAuth 2.0 Mutual TLS Client Certificate Bound Access Token to learn how.
If an access token or refresh token is compromised, the first thing you should do is go to the admin console and push a not-before revocation policy to all applications. This will enforce that any tokens issued prior to that date are now invalid. Pushing new not-before policy will also ensure that application will be forced to download new public keys from Red Hat Single Sign-On, hence it is also useful for the case, when you think that realm signing key was compromised. More info in the keys chapter.
You can also disable specific applications, clients, and users if you feel that any one of those entities is completely compromised.
19.9. Compromised Authorization Code
For the OIDC Auth Code Flow, it would be very hard for an attacker to compromise Red Hat Single Sign-On authorization codes. Red Hat Single Sign-On generates a cryptographically strong random value for its authorization codes so it would be very hard to guess an access token. An authorization code can only be used once to obtain an access token. In the admin console you can specify how long an authorization code is valid for on the timeouts page. This value should be really short, as short as a few seconds and just long enough for the client to make the request to obtain a token from the code.
You can also mitigate against leaked autorization codes by applying PKCE to clients. See Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) to learn how.
19.10. Open redirectors
An attacker could use the end-user authorization endpoint and the redirect URI parameter to abuse the authorization server as an open redirector. An open redirector is an endpoint using a parameter to automatically redirect a user agent to the location specified by the parameter value without any validation. An attacker could utilize a user’s trust in an authorization server to launch a phishing attack.
Red Hat Single Sign-On requires that all registered applications and clients register at least one redirection URI pattern. Any time a client asks Red Hat Single Sign-On to perform a redirect (on login or logout for example), Red Hat Single Sign-On will check the redirect URI vs. the list of valid registered URI patterns. It is important that clients and applications register as specific a URI pattern as possible to mitigate open redirector attacks.
19.11. Password database compromised
Red Hat Single Sign-On does not store passwords in raw text. It stores a hash of them using the PBKDF2 algorithm. It actually uses a default of 20,000 hashing iterations! This is the security community’s recommended number of iterations. This can be a rather large performance hit on your system as PBKDF2, by design, gobbles up a significant amount of CPU. It is up to you to decide how serious you want to be to protect your password database.
19.12. Limiting Scope
By default, each new client application has an unlimited role scope mappings. This means that every access token that is created for that client will contain all the permissions the user has. If the client gets compromised and the access token is leaked, then each system that the user has permission to access is now also compromised. It is highly suggested that you limit the roles an access token is assigned by using the Scope menu for each client. Or alternatively, you can set role scope mappings at the Client Scope level and assign Client Scopes to your client by using the Client Scope menu.
19.13. Limit Token Audience
In environments where the level of trust among services is low, it is a good practice to limit the audiences on the token. The motivation behind this is described in the OAuth2 Threat Model document and more details are in the Audience Support section.
19.14. SQL Injection Attacks
At this point in time, there is no knowledge of any SQL injection vulnerabilities in Red Hat Single Sign-On.