Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 4. Setting up key archival and recovery
This chapter explains how to setup the Key Recovery Authority (KRA), previously known as Data Recovery Manager (DRM), to archive private keys and to recover archived keys for restoring encrypted data.
See 4.4 "Supported Hardware Security Modules" in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition).
When the KRA is installed, it joins a security domain, and is paired up with the CA. At such time, it is configured to archive and recover private encryption keys. However, if the KRA certificates are issued by an external CA rather than one of the CAs within the security domain, then the key archival and recovery process must be set up manually.
For more information, see 12.1 Manually Setting up Key Archival in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition).
4.1. Configuring agent-approved key recovery in the console
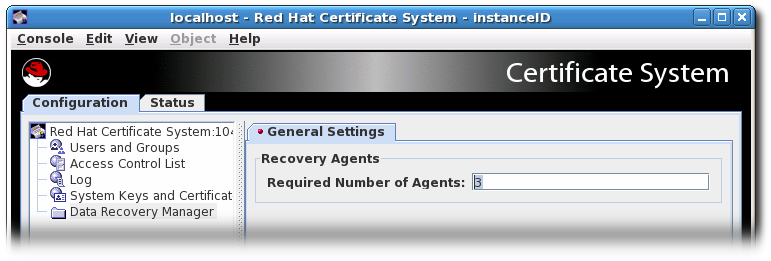
While the number of key recovery agents can be configured in the Console, the group to use can only be set directly in the CS.cfg file. The Console uses the Key Recovery Authority Agents Group by default.
Open the KRA’s console. For example:
pkiconsole -d nssdb -n 'optional client cert nickname' https://server.example.com:8443/kra
# pkiconsole -d nssdb -n 'optional client cert nickname' https://server.example.com:8443/kraCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteTo configure
pkiconsole, please refer to 7.13.6 "Configure pkiconsole login with client authentication" in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition).pkiconsoleis being deprecated and will be replaced by a new browser-based UI in a future major release. Althoughpkiconsolewill continue to be available until the replacement UI is released, we encourage using the command line equivalent ofpkiconsoleat this time, as the pki CLI will continue to be supported and improved upon even when the new browser-based UI becomes available in the future.- Click the Key Recovery Authority link in the left navigation tree.
Enter the number of agents to use to approve key recover in the Required Number of Agents field.
For more information on how to configure agent-approved key recovery in the CS.cfg file, see 12.3.1 Configuring Agent-Approved Key Recovery in the Command Line in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition).
4.2. Testing the key archival and recovery setup
To test whether a key can be successfully archived:
- Create and enroll a CRMF request by following Section 11.3.2.1.1, “Enrolling for a user certificate”.
- Confirm that the key has been archived. In the KRA’s agent services page, select Show completed requests. If the key has been archived successfully, there will be information about that key. If the key is not shown, check the logs, and correct the problem. If the key has been successfully archived, close the browser window.
Test whether an archived key can be recovered successfully:
- Open the KRA’s agent services page, and click the Recover Keys link. Search for the key by the key owner, serial number, or public key. If the key has been archived successfully, the key information will be shown.
- Click .
- In the form that appears, enter the base-64 encoded certificate that corresponds to the private key to recover; use the CA to get this information. If the archived key was searched for by providing the base-64 encoded certificate, then the certificate does not have to be supplied here.
- Only "Async Recovery" is supported. Make sure that the Async Recovery checkbox is selected.
- Depending on the agent scheme, a specified number of agents must authorize this key recovery. Have the agents search for the key to recover and then to approve the initiated recovery.
- Once all the agents have authorized the recovery, the next screen requests a password to encrypt the PKCS #12 file with the certificate.
The next screen returns a link to download a PKCS #12 blob containing the recovered key pair. Follow the link, and save the blob to file.
ImportantOpening the PKCS #12 file directly from the browser in the
gcr-viewerutility can fail in certain situations. To work around the problem, download the file and manually open it ingcr-viewer.- For more information on Key Archival and Recovery, see 2.4.5 Archiving, Recovering, and Rotating Keys in the Planning, Installation and Deployment Guide (Common Criteria Edition).