Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 13. Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner on Spring Boot: a school timetable quick start guide
This guide walks you through the process of creating a Spring Boot application with OptaPlanner’s constraint solving artificial intelligence (AI). You will build a REST application that optimizes a school timetable for students and teachers.
Your service will assign Lesson instances to Timeslot and Room instances automatically by using AI to adhere to the following hard and soft scheduling constraints:
- A room can have at most one lesson at the same time.
- A teacher can teach at most one lesson at the same time.
- A student can attend at most one lesson at the same time.
- A teacher prefers to teach in a single room.
- A teacher prefers to teach sequential lessons and dislikes gaps between lessons.
Mathematically speaking, school timetabling is an NP-hard problem. That means it is difficult to scale. Simply iterating through all possible combinations with brute force would take millions of years for a non-trivial data set, even on a supercomputer. Fortunately, AI constraint solvers such as OptaPlanner have advanced algorithms that deliver a near-optimal solution in a reasonable amount of time. What is considered to be a reasonable amount of time is subjective and depends on the goals of your problem.
Prerequisites
- OpenJDK 11 or later is installed. Red Hat build of Open JDK is available from the Software Downloads page in the Red Hat Customer Portal (login required).
- Apache Maven 3.8 or higher is installed. Maven is available from the Apache Maven Project website.
- An IDE, such as IntelliJ IDEA, VSCode, or Eclipse is available.
13.1. Downloading and building the Spring Boot school timetable quick start
If you want to see a completed example of the school timetable project for Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner with Spring Boot product, download the starter application from the Red Hat Customer Portal.
Procedure
Navigate to the Software Downloads page in the Red Hat Customer Portal (login required), and select the product and version from the drop-down options:
- Product: Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner
- Version: 8.33
- Download Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner 8.33 Quick Starts.
Extract the
rhbop-8.33.0-optaplanner-quickstarts-sources.zipfile.The extracted
org.optaplanner.optaplanner-quickstarts-8.33.0.Final-redhat-00004/use-cases/school-timetablingdirectory contains example source code.-
Navigate to the
org.optaplanner.optaplanner-quickstarts-8.33.0.Final-redhat-00004/use-cases/school-timetablingdirectory. -
Download the Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner 8.33.0 Maven Repositroy (
rhbop-8.33.0-optaplanner-maven-repository.zip). -
Extract the
rhbop-8.33.0-optaplanner-maven-repository.zipfile. -
Copy the contents of the
rhbop-8.33.0-optaplanner/maven-repositorysubdirectory into the~/.m2/repositorydirectory. -
Navigate to the
org.optaplanner.optaplanner-quickstarts-8.33.0.Final-redhat-00004/technology/java-spring-bootdirectory. Enter the following command to build the Spring Boot school timetabling project:
mvn clean install -DskipTests
mvn clean install -DskipTestsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To build the Spring Boot school timetabling project, enter the following command:
mvn spring-boot:run -DskipTests
mvn spring-boot:run -DskipTestsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the project, enter the following URL in a web browser:
http://localhost:8080/
http://localhost:8080/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
13.2. Model the domain objects
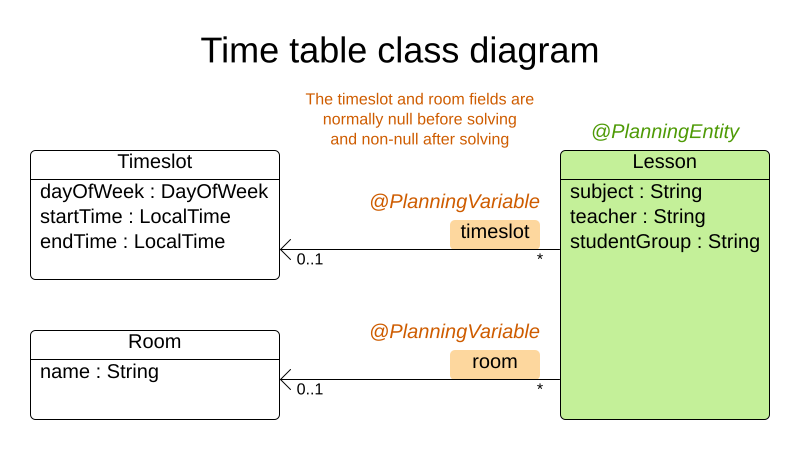
The goal of the Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner timetable project is to assign each lesson to a time slot and a room. To do this, add three classes, Timeslot, Lesson, and Room, as shown in the following diagram:
Timeslot
The Timeslot class represents a time interval when lessons are taught, for example, Monday 10:30 - 11:30 or Tuesday 13:30 - 14:30. In this example, all time slots have the same duration and there are no time slots during lunch or other breaks.
A time slot has no date because a high school schedule just repeats every week. There is no need for continuous planning. A timeslot is called a problem fact because no Timeslot instances change during solving. Such classes do not require any OptaPlanner-specific annotations.
Room
The Room class represents a location where lessons are taught, for example, Room A or Room B. In this example, all rooms are without capacity limits and they can accommodate all lessons.
Room instances do not change during solving so Room is also a problem fact.
Lesson
During a lesson, represented by the Lesson class, a teacher teaches a subject to a group of students, for example, Math by A.Turing for 9th grade or Chemistry by M.Curie for 10th grade. If a subject is taught multiple times each week by the same teacher to the same student group, there are multiple Lesson instances that are only distinguishable by id. For example, the 9th grade has six math lessons a week.
During solving, OptaPlanner changes the timeslot and room fields of the Lesson class to assign each lesson to a time slot and a room. Because OptaPlanner changes these fields, Lesson is a planning entity:
Most of the fields in the previous diagram contain input data, except for the orange fields. A lesson’s timeslot and room fields are unassigned (null) in the input data and assigned (not null) in the output data. OptaPlanner changes these fields during solving. Such fields are called planning variables. In order for OptaPlanner to recognize them, both the timeslot and room fields require an @PlanningVariable annotation. Their containing class, Lesson, requires an @PlanningEntity annotation.
Procedure
Create the
src/main/java/com/example/domain/Timeslot.javaclass:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notice the
toString()method keeps the output short so it is easier to read OptaPlanner’sDEBUGorTRACElog, as shown later.Create the
src/main/java/com/example/domain/Room.javaclass:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
src/main/java/com/example/domain/Lesson.javaclass:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
Lessonclass has an@PlanningEntityannotation, so OptaPlanner knows that this class changes during solving because it contains one or more planning variables.The
timeslotfield has an@PlanningVariableannotation, so OptaPlanner knows that it can change its value. In order to find potentialTimeslotinstances to assign to this field, OptaPlanner uses thevalueRangeProviderRefsproperty to connect to a value range provider that provides aList<Timeslot>to pick from. See Section 13.4, “Gather the domain objects in a planning solution” for information about value range providers.The
roomfield also has an@PlanningVariableannotation for the same reasons.
13.3. Define the constraints and calculate the score
When solving a problem, a score represents the quality of a specific solution. The higher the score the better. Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner looks for the best solution, which is the solution with the highest score found in the available time. It might be the optimal solution.
Because the timetable example use case has hard and soft constraints, use the HardSoftScore class to represent the score:
- Hard constraints must not be broken. For example: A room can have at most one lesson at the same time.
- Soft constraints should not be broken. For example: A teacher prefers to teach in a single room.
Hard constraints are weighted against other hard constraints. Soft constraints are weighted against other soft constraints. Hard constraints always outweigh soft constraints, regardless of their respective weights.
To calculate the score, you could implement an EasyScoreCalculator class:
Unfortunately, this solution does not scale well because it is non-incremental: every time a lesson is assigned to a different time slot or room, all lessons are re-evaluated to calculate the new score.
A better solution is to create a src/main/java/com/example/solver/TimeTableConstraintProvider.java class to perform incremental score calculation. This class uses OptaPlanner’s ConstraintStream API which is inspired by Java 8 Streams and SQL. The ConstraintProvider scales an order of magnitude better than the EasyScoreCalculator: O(n) instead of O(n²).
Procedure
Create the following src/main/java/com/example/solver/TimeTableConstraintProvider.java class:
13.4. Gather the domain objects in a planning solution
A TimeTable instance wraps all Timeslot, Room, and Lesson instances of a single dataset. Furthermore, because it contains all lessons, each with a specific planning variable state, it is a planning solution and it has a score:
-
If lessons are still unassigned, then it is an uninitialized solution, for example, a solution with the score
-4init/0hard/0soft. -
If it breaks hard constraints, then it is an infeasible solution, for example, a solution with the score
-2hard/-3soft. -
If it adheres to all hard constraints, then it is a feasible solution, for example, a solution with the score
0hard/-7soft.
The TimeTable class has an @PlanningSolution annotation, so Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner knows that this class contains all of the input and output data.
Specifically, this class is the input of the problem:
A
timeslotListfield with all time slots- This is a list of problem facts, because they do not change during solving.
A
roomListfield with all rooms- This is a list of problem facts, because they do not change during solving.
A
lessonListfield with all lessons- This is a list of planning entities because they change during solving.
Of each
Lesson:-
The values of the
timeslotandroomfields are typically stillnull, so unassigned. They are planning variables. -
The other fields, such as
subject,teacherandstudentGroup, are filled in. These fields are problem properties.
-
The values of the
However, this class is also the output of the solution:
-
A
lessonListfield for which eachLessoninstance has non-nulltimeslotandroomfields after solving -
A
scorefield that represents the quality of the output solution, for example,0hard/-5soft
Procedure
Create the src/main/java/com/example/domain/TimeTable.java class:
The value range providers
The timeslotList field is a value range provider. It holds the Timeslot instances which OptaPlanner can pick from to assign to the timeslot field of Lesson instances. The timeslotList field has an @ValueRangeProvider annotation to connect those two, by matching the id with the valueRangeProviderRefs of the @PlanningVariable in the Lesson.
Following the same logic, the roomList field also has an @ValueRangeProvider annotation.
The problem fact and planning entity properties
Furthermore, OptaPlanner needs to know which Lesson instances it can change as well as how to retrieve the Timeslot and Room instances used for score calculation by your TimeTableConstraintProvider.
The timeslotList and roomList fields have an @ProblemFactCollectionProperty annotation, so your TimeTableConstraintProvider can select from those instances.
The lessonList has an @PlanningEntityCollectionProperty annotation, so OptaPlanner can change them during solving and your TimeTableConstraintProvider can select from those too.
13.5. Create the Timetable service
Now you are ready to put everything together and create a REST service. But solving planning problems on REST threads causes HTTP timeout issues. Therefore, the Spring Boot starter injects a SolverManager, which runs solvers in a separate thread pool and can solve multiple datasets in parallel.
Procedure
Create the src/main/java/com/example/solver/TimeTableController.java class:
In this example, the initial implementation waits for the solver to finish, which can still cause an HTTP timeout. The complete implementation avoids HTTP timeouts much more elegantly.
13.6. Set the solver termination time
If your planning application does not have a termination setting or a termination event, it theoretically runs forever and in reality eventually causes an HTTP timeout error. To prevent this from occurring, use the optaplanner.solver.termination.spent-limit parameter to specify the length of time after which the application terminates. In most applications, set the time to at least five minutes (5m). However, in the Timetable example, limit the solving time to five seconds, which is short enough to avoid the HTTP timeout.
Procedure
Create the src/main/resources/application.properties file with the following content:
quarkus.optaplanner.solver.termination.spent-limit=5s
quarkus.optaplanner.solver.termination.spent-limit=5s13.7. Make the application executable
After you complete the Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner Spring Boot timetable project, package everything into a single executable JAR file driven by a standard Java main() method.
Prerequisites
- You have a completed OptaPlanner Spring Boot timetable project.
Procedure
Create the
TimeTableSpringBootApp.javaclass with the following content:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Replace the
src/main/java/com/example/DemoApplication.javaclass created by Spring Initializr with theTimeTableSpringBootApp.javaclass. -
Run the
TimeTableSpringBootApp.javaclass as the main class of a regular Java application.
13.7.1. Try the timetable application
After you start the Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner Spring Boot timetable application, you can test the REST service with any REST client that you want. This example uses the Linux curl command to send a POST request.
Prerequisites
- The OptaPlanner Spring Boot timetable application is running.
Procedure
Enter the following command:
curl -i -X POST http://localhost:8080/timeTable/solve -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{"timeslotList":[{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"08:30:00","endTime":"09:30:00"},{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"09:30:00","endTime":"10:30:00"}],"roomList":[{"name":"Room A"},{"name":"Room B"}],"lessonList":[{"id":1,"subject":"Math","teacher":"A. Turing","studentGroup":"9th grade"},{"id":2,"subject":"Chemistry","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"9th grade"},{"id":3,"subject":"French","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"10th grade"},{"id":4,"subject":"History","teacher":"I. Jones","studentGroup":"10th grade"}]}'
$ curl -i -X POST http://localhost:8080/timeTable/solve -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{"timeslotList":[{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"08:30:00","endTime":"09:30:00"},{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"09:30:00","endTime":"10:30:00"}],"roomList":[{"name":"Room A"},{"name":"Room B"}],"lessonList":[{"id":1,"subject":"Math","teacher":"A. Turing","studentGroup":"9th grade"},{"id":2,"subject":"Chemistry","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"9th grade"},{"id":3,"subject":"French","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"10th grade"},{"id":4,"subject":"History","teacher":"I. Jones","studentGroup":"10th grade"}]}'
After about five seconds, the termination spent time defined in application.properties, the service returns an output similar to the following example:
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: application/json
...
{"timeslotList":...,"roomList":...,"lessonList":[{"id":1,"subject":"Math","teacher":"A. Turing","studentGroup":"9th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"08:30:00","endTime":"09:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room A"}},{"id":2,"subject":"Chemistry","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"9th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"09:30:00","endTime":"10:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room A"}},{"id":3,"subject":"French","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"10th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"08:30:00","endTime":"09:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room B"}},{"id":4,"subject":"History","teacher":"I. Jones","studentGroup":"10th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"09:30:00","endTime":"10:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room B"}}],"score":"0hard/0soft"}
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: application/json
...
{"timeslotList":...,"roomList":...,"lessonList":[{"id":1,"subject":"Math","teacher":"A. Turing","studentGroup":"9th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"08:30:00","endTime":"09:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room A"}},{"id":2,"subject":"Chemistry","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"9th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"09:30:00","endTime":"10:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room A"}},{"id":3,"subject":"French","teacher":"M. Curie","studentGroup":"10th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"08:30:00","endTime":"09:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room B"}},{"id":4,"subject":"History","teacher":"I. Jones","studentGroup":"10th grade","timeslot":{"dayOfWeek":"MONDAY","startTime":"09:30:00","endTime":"10:30:00"},"room":{"name":"Room B"}}],"score":"0hard/0soft"}Notice that the application assigned all four lessons to one of the two time slots and one of the two rooms. Also notice that it conforms to all hard constraints. For example, M. Curie’s two lessons are in different time slots.
On the server side, the info log shows what OptaPlanner did in those five seconds:
... Solving started: time spent (33), best score (-8init/0hard/0soft), environment mode (REPRODUCIBLE), random (JDK with seed 0). ... Construction Heuristic phase (0) ended: time spent (73), best score (0hard/0soft), score calculation speed (459/sec), step total (4). ... Local Search phase (1) ended: time spent (5000), best score (0hard/0soft), score calculation speed (28949/sec), step total (28398). ... Solving ended: time spent (5000), best score (0hard/0soft), score calculation speed (28524/sec), phase total (2), environment mode (REPRODUCIBLE).
... Solving started: time spent (33), best score (-8init/0hard/0soft), environment mode (REPRODUCIBLE), random (JDK with seed 0).
... Construction Heuristic phase (0) ended: time spent (73), best score (0hard/0soft), score calculation speed (459/sec), step total (4).
... Local Search phase (1) ended: time spent (5000), best score (0hard/0soft), score calculation speed (28949/sec), step total (28398).
... Solving ended: time spent (5000), best score (0hard/0soft), score calculation speed (28524/sec), phase total (2), environment mode (REPRODUCIBLE).13.7.2. Test the application
A good application includes test coverage. This example tests the Timetable Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner Spring Boot application. It uses a JUnit test to generate a test dataset and send it to the TimeTableController to solve.
Procedure
Create the src/test/java/com/example/solver/TimeTableControllerTest.java class with the following content:
This test verifies that after solving, all lessons are assigned to a time slot and a room. It also verifies that it found a feasible solution (no hard constraints broken).
Normally, the solver finds a feasible solution in less than 200 milliseconds. Notice how the @SpringBootTest annotation’s properties overwrites the solver termination to terminate as soon as a feasible solution (0hard/*soft) is found. This avoids hard coding a solver time, because the unit test might run on arbitrary hardware. This approach ensures that the test runs long enough to find a feasible solution, even on slow systems. However, it does not run a millisecond longer than it strictly must, even on fast systems.
13.7.3. Logging
After you complete the Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner Spring Boot timetable application, you can use logging information to help you fine-tune the constraints in the ConstraintProvider. Review the score calculation speed in the info log file to assess the impact of changes to your constraints. Run the application in debug mode to show every step that your application takes or use trace logging to log every step and every move.
Procedure
- Run the timetable application for a fixed amount of time, for example, five minutes.
Review the score calculation speed in the
logfile as shown in the following example:... Solving ended: ..., score calculation speed (29455/sec), ...
... Solving ended: ..., score calculation speed (29455/sec), ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change a constraint, run the planning application again for the same amount of time, and review the score calculation speed recorded in the
logfile. Run the application in debug mode to log every step:
-
To run debug mode from the command line, use the
-Dsystem property. To change logging in the
application.propertiesfile, add the following line to that file:logging.level.org.optaplanner=debug
logging.level.org.optaplanner=debugCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example shows output in the
logfile in debug mode:... Solving started: time spent (67), best score (-20init/0hard/0soft), environment mode (REPRODUCIBLE), random (JDK with seed 0). ... CH step (0), time spent (128), score (-18init/0hard/0soft), selected move count (15), picked move ([Math(101) {null -> Room A}, Math(101) {null -> MONDAY 08:30}]). ... CH step (1), time spent (145), score (-16init/0hard/0soft), selected move count (15), picked move ([Physics(102) {null -> Room A}, Physics(102) {null -> MONDAY 09:30}]). ...... Solving started: time spent (67), best score (-20init/0hard/0soft), environment mode (REPRODUCIBLE), random (JDK with seed 0). ... CH step (0), time spent (128), score (-18init/0hard/0soft), selected move count (15), picked move ([Math(101) {null -> Room A}, Math(101) {null -> MONDAY 08:30}]). ... CH step (1), time spent (145), score (-16init/0hard/0soft), selected move count (15), picked move ([Physics(102) {null -> Room A}, Physics(102) {null -> MONDAY 09:30}]). ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
To run debug mode from the command line, use the
-
Use
tracelogging to show every step and every move for each step.
13.8. Add Database and UI integration
After you create the Red Hat Build of OptaPlanner application example with Spring Boot, add database and UI integration.
Prerequisite
- You have created the OptaPlanner Spring Boot timetable example.
Procedure
-
Create Java Persistence API (JPA) repositories for
Timeslot,Room, andLesson. For information about creating JPA repositories, see Accessing Data with JPA on the Spring website. - Expose the JPA repositories through REST. For information about exposing the repositories, see Accessing JPA Data with REST on the Spring website.
-
Build a
TimeTableRepositoryfacade to read and write aTimeTablein a single transaction. Adjust the
TimeTableControlleras shown in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For simplicity, this code handles only one
TimeTableinstance, but it is straightforward to enable multi-tenancy and handle multipleTimeTableinstances of different high schools in parallel.The
getTimeTable()method returns the latest timetable from the database. It uses theScoreManager(which is automatically injected) to calculate the score of that timetable so the UI can show the score.The
solve()method starts a job to solve the current timetable and store the time slot and room assignments in the database. It uses theSolverManager.solveAndListen()method to listen to intermediate best solutions and update the database accordingly. This enables the UI to show progress while the backend is still solving.Now that the
solve()method returns immediately, adjust theTimeTableControllerTestas shown in the following example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Poll for the latest solution until the solver finishes solving.
- To visualize the timetable, build an attractive web UI on top of these REST methods.
13.9. Using Micrometer and Prometheus to monitor your school timetable OptaPlanner Spring Boot application
OptaPlanner exposes metrics through Micrometer, a metrics instrumentation library for Java applications. You can use Micrometer with Prometheus to monitor the OptaPlanner solver in the school timetable application.
Prerequisites
- You have created the Spring Boot OptaPlanner school timetable application.
- Prometheus is installed. For information about installing Prometheus, see the Prometheus website.
Procedure
-
Navigate to the
technology/java-spring-bootdirectory. Add the Micrometer Prometheus dependencies to the school timetable
pom.xmlfile:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the following property to the application.properties file:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=metrics,prometheus
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=metrics,prometheusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the school timetable application:
mvn spring-boot:run
mvn spring-boot:runCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open
http://localhost:8080/actuator/prometheusin a web browser.