Chapter 3. Container topologies
Ansible Automation Platform provides tested topologies for containerized Ansible Automation Platform. Select the topology that best fits your container-based deployment requirements.
3.1. Container growth topology
The container-based growth topology provides a smaller footprint deployment without redundancy for organizations getting started with Ansible Automation Platform. Included are the tested infrastructure topology, system requirements, network port configurations, and an example inventory file for installation.
3.1.1. Infrastructure topology
The Red Hat tested infrastructure topology for this deployment model:
Figure 3.1. Infrastructure topology diagram
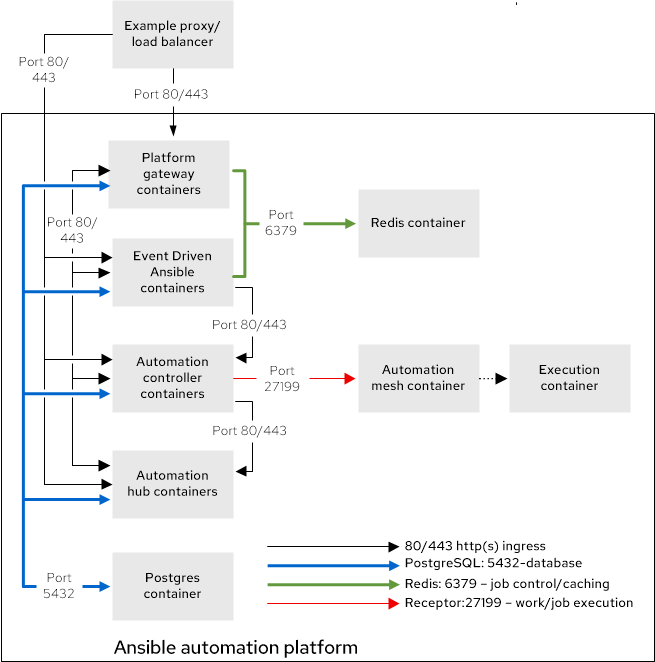
Red Hat tests a single VM with these requirements:
| Requirement | Minimum requirement |
|---|---|
| RAM |
|
| CPUs | 4 |
| Local disk |
|
| Disk IOPS | 3000 |
| Purpose | Example group names |
|---|---|
| All Ansible Automation Platform components |
|
3.1.2. Tested system configurations
Red Hat has tested these configurations to install and run Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform:
| Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription |
| |
| Operating system |
| |
| CPU architecture | x86_64, AArch64, s390x (IBM Z), ppc64le (IBM Power) | |
|
|
|
|
| Browser | A currently supported version of Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome. | |
| Database | PostgreSQL 15 | External (customer supported) databases require International Components for Unicode (ICU) support. |
3.1.3. Network ports
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform uses several ports to communicate with its services. These ports must be open and available for Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform to work. Ensure that these ports are available and are not blocked by a firewall.
| Port number | Protocol | Service | Source | Destination | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Event-Driven Ansible | Automation hub | Pull container decision environments |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Event-Driven Ansible | Automation controller | Launch automation controller jobs |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Automation controller | Automation hub | Pull collections and execution environment images |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation controller | Platform gateway to automation controller communication |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation hub | Platform gateway to automation hub communication |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Event-Driven Ansible | Platform gateway to Event-Driven Ansible communication |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Event-Driven Ansible | Database | Event-Driven Ansible database access |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Platform gateway | Database | Platform gateway database access |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Automation hub | Database | Automation hub database access |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Automation controller | Database | Automation controller database access |
| 6379 | TCP | Redis | Event-Driven Ansible | Redis container | Job launching and data storage for Event-Driven Ansible |
| 6379 | TCP | Redis | Platform gateway | Redis container | Data storage and retrieval for platform gateway services |
| 8443 | TCP | HTTPS | Platform gateway | Platform gateway | Internal gateway NGINX communication |
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Automation controller | Execution container | Mesh nodes connect directly to controllers. Allows two-way communication for job distribution. |
| 8080/8443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation controller |
Automation controller NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
| 8081/8444 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation hub |
Automation hub NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
| 8082/8445 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Event-Driven Ansible |
Event-Driven Ansible NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
| 8083/8446 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Platform gateway |
Platform gateway NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
If you change any port values by using inventory variables, refer to Inventory file variables to review all default port values and ensure there are no port conflicts.
3.1.4. Example inventory file
Use the example inventory file to perform an installation:
SSH keys are only required when installing on remote hosts. If doing a self contained local VM based installation, you can use ansible_connection=local.
3.2. Container enterprise topology
The container-based enterprise topology provides redundancy and higher compute for large volumes of automation. Included are the tested infrastructure topology, system requirements, network port configurations, and an example inventory file for installation.
3.2.1. Infrastructure topology
The Red Hat tested infrastructure topology for this deployment model:
Figure 3.2. Infrastructure topology diagram

Red Hat tests each VM with these requirements:
| Requirement | Minimum requirement |
|---|---|
| RAM | 16 GB |
| CPUs | 4 |
| Local disk |
|
| Disk IOPS | 3000 |
| VM count | Purpose | Example VM group names |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Platform gateway with colocated Redis |
|
| 2 | Automation controller |
|
| 2 | Private automation hub with colocated Redis |
|
| 2 | Event-Driven Ansible with colocated Redis |
|
| 1 | Automation mesh hop node |
|
| 2 | Automation mesh execution node |
|
| 1 | Externally managed database service | N/A |
| 1 | HAProxy load balancer in front of platform gateway (externally managed) | N/A |
- 6 VMs are required for a Redis high availability (HA) compatible deployment. When installing Ansible Automation Platform with the containerized installer, Redis can be colocated on any Ansible Automation Platform component VMs of your choice except for execution nodes or the PostgreSQL database. They might also be assigned VMs specifically for Redis use.
- External Redis is not supported for containerized Ansible Automation Platform.
3.2.2. Tested system configurations
Red Hat has tested these configurations to install and run Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform:
| Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription |
| |
| Operating system |
| |
| CPU architecture | x86_64, AArch64, s390x (IBM Z), ppc64le (IBM Power) | |
|
|
|
|
| Browser | A currently supported version of Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome. | |
| Database | PostgreSQL 15 | External (customer supported) databases require International Components for Unicode (ICU) support. |
3.2.3. Network ports
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform uses several ports to communicate with its services. These ports must be open and available for Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform to work. Ensure that these ports are available and are not blocked by a firewall.
| Port number | Protocol | Service | Source | Destination | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Event-Driven Ansible | Automation hub | Pull container decision environments |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Event-Driven Ansible | Automation controller | Launch automation controller jobs |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Automation controller | Automation hub | Pull collections and execution environment images |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | HAProxy load balancer | Platform gateway | External load balancer access |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation controller | Platform gateway to automation controller communication |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation hub | Platform gateway to automation hub communication |
| 80/443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Event-Driven Ansible | Platform gateway to Event-Driven Ansible communication |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Event-Driven Ansible | External database | Event-Driven Ansible database access |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Platform gateway | External database | Platform gateway database access |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Automation hub | External database | Automation hub database access |
| 5432 | TCP | PostgreSQL | Automation controller | External database | Automation controller database access |
| 6379 | TCP | Redis | Event-Driven Ansible | Redis node | Job launching and data storage for Event-Driven Ansible |
| 6379 | TCP | Redis | Platform gateway | Redis node | Data storage and retrieval for platform gateway services |
| 16379 | TCP | Redis | Redis node | Redis node | Redis cluster bus communication |
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Automation controller | Hop node and execution node | Mesh nodes connect directly to controllers. Allows two-way communication for job distribution. |
| 27199 | TCP | Receptor | Hop node | Execution node | Mesh nodes connect through hop nodes. Allows two-way communication in either direction. |
| 8080/8443 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation controller |
Automation controller NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
| 8081/8444 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Automation hub |
Automation hub NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
| 8082/8445 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Event-Driven Ansible |
Event-Driven Ansible NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
| 8083/8446 | TCP | HTTP/HTTPS | Platform gateway | Platform gateway |
Platform gateway NGINX ports. You can configure these ports with the following inventory variables: |
If you change any port values by using inventory variables, refer to Inventory file variables to review all default port values and ensure there are no port conflicts.
3.2.4. Example inventory file
Use the example inventory file to perform an installation: